True toad
| True toads Temporal range: 57–0 Ma PreЄ Є O S D C P T J K Pg N | |
|---|---|
 | |
Common toad or European toad, Bufo bufo | |
| Territorial call of an Atelopus franciscus male | |
Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Suborder: | Neobatrachia |
| Family: | Bufonidae Gray, 1825 |
| Genera | |
Over 35 see text | |
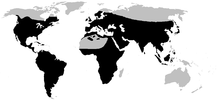 | |
| Native distribution of Bufonidae (in black) | |
Song of Common toad or European toad, Bufo bufo.
A true toad is any member of the family Bufonidae, in the order Anura (frogs and toads). This is the only family of anurans in which all members are known as toads, although some may be called frogs (such as harlequin frogs). The bufonids now comprise more than 35 genera, Bufo being the most widespread and well known.
Contents
1 Characteristics
2 Taxonomy
3 References
4 External links
Characteristics
True toads are widespread and are native to every continent except Australia and Antarctica, inhabiting a variety of environments, from arid areas to rainforest. Most lay eggs in paired strings that hatch into tadpoles, although, in the genus Nectophrynoides, the eggs hatch directly into miniature toads.[1]
True toads are toothless and generally warty in appearance. They have a pair of parotoid glands on the back of their heads. These glands contain an alkaloid poison which the toads excrete when stressed. The poison in the glands contains a number of toxins causing different effects. Bufotoxin is a general term. Different animals contain significantly different substances and proportions of substances. Some, like the cane toad Rhinella marina, are more toxic than others. Some "psychoactive toads", such as the Colorado River toad Bufo alvaris, have been used recreationally for the effects of their bufotoxin.
Male toads possess a Bidder's organ. Under the right conditions, the organ becomes an active ovary and the toad, in effect, becomes female.[2]
Taxonomy
The family Bufonidae contains about 500 species among 38 genera.
| Genus Latin name and author | Common name | Species |
|---|---|---|
Adenomus Cope, 1861 | Dwarf toads | 3 |
Altiphrynoides Dubois, 1987 | Ethiopian toads | 2 |
Amazophrynella Fouquet et al., 2012 | 7 | |
Amietophrynus Frost et al., 2006 | 38 | |
Anaxyrus Tschudi, 1845 | 22 | |
Ansonia Stoliczka, 1870 | Stream toads | 29 |
Atelopus Duméril & Bibron, 1841 | Stubfoot toads | 96 |
Blythophryne Chandramouli et al., 2016[3] | Andaman bush toads | 1 |
Bufo Laurenti, 1768 | Toads | 37 |
Bufoides Pillai & Yazdani, 1973 | Mawblang toad | 1 |
Capensibufo Grandison, 1980 | Cape toads | 2 |
Churamiti Channing & Stanley, 2002 | 1 | |
Crepidophryne Cope, 1889 | Cerro Utyum toads | 3 |
Dendrophryniscus Jiménez de la Espada, 1871 | Tree toads | 10 |
Didynamipus Andersson, 1903 | Four-digit toad | 1 |
Duttaphrynus Frost et al., 2006 | 6 | |
Epidalea Cope, 1864 | Natterjack toad | 1 |
Frostius Cannatella, 1986 | Frost's toads | 2 |
Ingerophrynus Frost et al., 2006 | 11 | |
Laurentophryne Tihen, 1960 | Parker's tree toad | 1 |
Leptophryne Fitzinger, 1843 | Indonesia tree toads | 2 |
Melanophryniscus Gallardo, 1961 | South American redbelly toads | 20 |
Mertensophryne Tihen, 1960 | Snouted frogs | 20 |
Metaphryniscus Señaris, Ayarzagüena & Gorzula, 1994 | 1 | |
Nectophryne Buchholz & Peters, 1875 | African tree toads | 2 |
Nectophrynoides Buchholz & Peters, 1875 | African live-bearing toads | 13 |
Nimbaphrynoides Dubois, 1987 | Nimba toads | 2 |
Oreophrynella Boulenger, 1895 | Bush toads | 8 |
Osornophryne Ruiz-Carranza & Hernández-Camacho, 1976 | Plump toads | 6 |
Parapelophryne Fei, Ye & Jiang, 2003 | 1 | |
Pedostibes Günther, 1876 | Asian tree toads | 6 |
Pelophryne Barbour, 1938 | Flathead toads | 9 |
Pseudepidalea Frost, et al. 2006 | 16 | |
Pseudobufo Tschudi, 1838 | False toad | 1 |
Rhinella Fitzinger, 1826 | Beaked toads | 72 |
Sabahphrynus Matsui, Yambun, and Sudin, 2007 | Sabah earless toad | 1 |
Schismaderma Smith, 1849 | African split-skin toad | 1 |
Truebella Graybeal & Cannatella, 1995 | 2 | |
Werneria Poche, 1903 | Smalltongue toads | 6 |
Wolterstorffina Mertens, 1939 | Wolterstorff toads | 3 |
Xanthophryne Biju, Van Bocxlaer, Giri, Loader & Bossuyt, 2009 | 2 |
References
^ ab Zweifel, Richard G. (1998). Cogger, H.G.; Zweifel, R.G., eds. Encyclopedia of Reptiles and Amphibians. San Diego: Academic Press. pp. 91–92. ISBN 0-12-178560-2..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Brown, Federico D.; Del Pino, Eugenia M.; Krohne, Georg (December 2002). "Bidder's organ in the toad Bufo marinus: Effects of orchidectomy on the morphology and expression of lamina-associated polypeptide 2". Development, Growth & Differentiation. 44 (6): 527–535. doi:10.1046/j.1440-169X.2002.00665.x. ISSN 1440-169X.
^ S. R. Chandramouli, Karthikeyan, Vasudevan, S Harikrishnan, Sushil Kumar Dutta, S Jegath Janani, Richa Sharma, Indraneil Das, Ramesh Aggarwal. “A new genus and species of arboreal toad with phytotelmonous larvae, from the Andaman Islands, India (Lissamphibia, Anura, Bufonidae)” ZooKeys (2016) 555: 57-90, https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.555.6522
"Amphibian Species of the World 5.1 - Bufonidae". Archived from the original on 2012-07-15. Retrieved 2008-04-10.
Stebbins, Robert. Western Reptiles & Amphibians (3rd ed.). Houghton Mifflin Co., 2003.- Halliday, Tim R., and Kraig Adler (editors). The New Encyclopedia of Reptiles & Amphibians. Facts on File, New York, 2002.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bufonidae. |
Wikispecies has information related to Bufonidae |
| Look up toad in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- Tolweb.org: Bufonidae
- Bufonidae.com
- Amphibian and Reptiles of Peninsular Malaysia - Family Bufonidae
- FED.us
Bufonidae recordings from the British Library Sound Archive