Motzkin number
Motzkin number
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
In mathematics, a Motzkin number for a given number n is the number of different ways of drawing non-intersecting chords between n points on a circle (not necessarily touching every point by a chord). The Motzkin numbers are named after Theodore Motzkin and have diverse applications in geometry, combinatorics and number theory.
The Motzkin numbers Mn{displaystyle M_{n}}

- 1, 1, 2, 4, 9, 21, 51, 127, 323, 835, 2188, 5798, 15511, 41835, 113634, 310572, 853467, 2356779, 6536382, 18199284, 50852019, 142547559, 400763223, 1129760415, 3192727797, 9043402501, 25669818476, 73007772802, 208023278209, 593742784829, ... (sequence A001006 in the OEIS)
Contents
1 Examples
2 Properties
3 Combinatorial interpretations
4 See also
5 References
6 External links
Examples[edit]
The following figure shows the 9 ways to draw non-intersecting chords between 4 points on a circle (M4 = 9):
The following figure shows the 21 ways to draw non-intersecting chords between 5 points on a circle (M5 = 21):
Properties[edit]
The Motzkin numbers satisfy the recurrence relations
- Mn=Mn−1+∑i=0n−2MiMn−2−i=2n+1n+2Mn−1+3n−3n+2Mn−2.{displaystyle M_{n}=M_{n-1}+sum _{i=0}^{n-2}M_{i}M_{n-2-i}={frac {2n+1}{n+2}}M_{n-1}+{frac {3n-3}{n+2}}M_{n-2}.}
The Motzkin numbers can be expressed in terms of binomial coefficients and Catalan numbers:
- Mn=∑k=0⌊n/2⌋(n2k)Ck.{displaystyle M_{n}=sum _{k=0}^{lfloor n/2rfloor }{binom {n}{2k}}C_{k}.}
A Motzkin prime is a Motzkin number that is prime. As of October 2013[update], four such primes are known:
- 2, 127, 15511, 953467954114363 (sequence A092832 in the OEIS)
Combinatorial interpretations[edit]
The Motzkin number for n is also the number of positive integer sequences of length n − 1 in which the opening and ending elements are either 1 or 2, and the difference between any two consecutive elements is −1, 0 or 1. Equivalently, the Motzkin number for n is the number of positive integer sequences of length n + 1 in which the opening and ending elements are 1, and the difference between any two consecutive elements is −1, 0 or 1.
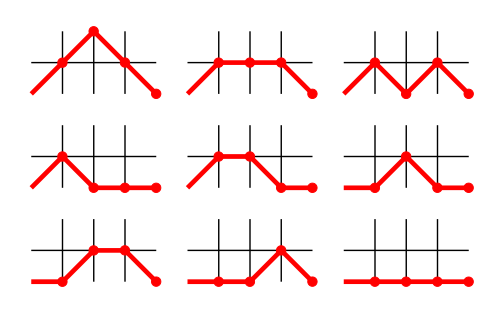
Also, the Motzkin number for n gives the number of routes on the upper right quadrant of a grid from coordinate (0, 0) to coordinate (n, 0) in n steps if one is allowed to move only to the right (up, down or straight) at each step but forbidden from dipping below the y = 0 axis.
For example, the following figure shows the 9 valid Motzkin paths from (0, 0) to (4, 0):
There are at least fourteen different manifestations of Motzkin numbers in different branches of mathematics, as enumerated by Donaghey & Shapiro (1977) in their survey of Motzkin numbers.
Guibert, Pergola & Pinzani (2001) showed that vexillary involutions are enumerated by Motzkin numbers.
See also[edit]
- Delannoy number
- Narayana number
- Schröder number
References[edit]
Bernhart, Frank R. (1999), "Catalan, Motzkin, and Riordan numbers", Discrete Mathematics, 204 (1–3): 73–112, doi:10.1016/S0012-365X(99)00054-0.mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
Donaghey, R.; Shapiro, L. W. (1977), "Motzkin numbers", Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A, 23 (3): 291–301, doi:10.1016/0097-3165(77)90020-6, MR 0505544
Guibert, O.; Pergola, E.; Pinzani, R. (2001), "Vexillary involutions are enumerated by Motzkin numbers", Annals of Combinatorics, 5 (2): 153–174, doi:10.1007/PL00001297, ISSN 0218-0006, MR 1904383
Motzkin, T. S. (1948), "Relations between hypersurface cross ratios, and a combinatorial formula for partitions of a polygon, for permanent preponderance, and for non-associative products", Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society, 54 (4): 352–360, doi:10.1090/S0002-9904-1948-09002-4
External links[edit]
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Motzkin Number". MathWorld.
Categories:
- Integer sequences
- Enumerative combinatorics
(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function(){mw.config.set({"wgPageParseReport":{"limitreport":{"cputime":"0.328","walltime":"0.453","ppvisitednodes":{"value":997,"limit":1000000},"ppgeneratednodes":{"value":0,"limit":1500000},"postexpandincludesize":{"value":93204,"limit":2097152},"templateargumentsize":{"value":655,"limit":2097152},"expansiondepth":{"value":19,"limit":40},"expensivefunctioncount":{"value":4,"limit":500},"unstrip-depth":{"value":0,"limit":20},"unstrip-size":{"value":7889,"limit":5000000},"entityaccesscount":{"value":3,"limit":400},"timingprofile":["100.00% 293.204 1 -total"," 53.55% 156.999 4 Template:Citation"," 20.43% 59.893 7 Template:Navbox"," 16.28% 47.741 1 Template:Asof"," 15.81% 46.367 1 Template:Classes_of_natural_numbers"," 10.27% 30.115 1 Template:DMCA"," 9.42% 27.617 1 Template:Dated_maintenance_category"," 7.45% 21.844 1 Template:FULLROOTPAGENAME"," 6.39% 18.728 1 Template:Ns_has_subpages"," 5.15% 15.095 2 Template:Harvtxt"]},"scribunto":{"limitreport-timeusage":{"value":"0.153","limit":"10.000"},"limitreport-memusage":{"value":3666644,"limit":52428800}},"cachereport":{"origin":"mw1246","timestamp":"20181125223014","ttl":1900800,"transientcontent":false}}});});{"@context":"https://schema.org","@type":"Article","name":"Motzkin number","url":"https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motzkin_number","sameAs":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q2915234","mainEntity":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q2915234","author":{"@type":"Organization","name":"Contributors to Wikimedia projects"},"publisher":{"@type":"Organization","name":"Wikimedia Foundation, Inc.","logo":{"@type":"ImageObject","url":"https://www.wikimedia.org/static/images/wmf-hor-googpub.png"}},"datePublished":"2004-07-23T22:57:13Z","dateModified":"2018-06-26T11:43:29Z","headline":"the number of patterns of non-intersecting chords with a given number of endpoints on a circle"}(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function(){mw.config.set({"wgBackendResponseTime":101,"wgHostname":"mw1323"});});