Adrianople Vilayet
Adrianople Vilayet
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
ولايت ادرنه Vilâyet-i Edirne | |||||
Vilayet of the Ottoman Empire | |||||
| |||||
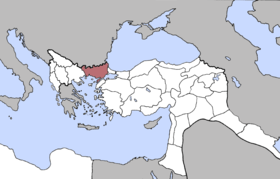 | |||||
Capital | Edirne[1] | ||||
History | |||||
| • | Established | 1867 | |||
| • | Disestablished | 1922 | |||
Population | |||||
| • | Muslim, 1914[2] | 360,411 | |||
| • | Greek, 1914[2] | 224,680 | |||
| • | Armenian, 1914[2] | 19,773 | |||
| • | Jewish, 1914[2] | 22,515 | |||
Today part of | |||||
The Vilayet of Adrianople or Vilayet of Edirne (Ottoman Turkish: ولايت ادرنه, Vilâyet-i Edirne)[3] was a first-level administrative division (vilayet) of the Ottoman Empire.
This vilayet was split between Turkey and Greece in 1923, culminating in the formation of Western and Eastern Thrace after World War I as part of the Treaty of Lausanne. A small portion of the Vilayet was given to Bulgaria in the Treaty of Bucharest (1913) after the Balkan wars. In the late 19th century it reportedly had an area of 26,160 square miles (67,800 km2).[4] In the east it bordered with the Istanbul Vilayet, the Black Sea and the Sea of Marmara, in the west with the Salonica Vilayet, in the north with Eastern Rumelia (Bulgaria since 1885) and in the south with the Aegean Sea. Sometimes the area is described also as Southern Thrace,[5] or Adrianopolitan Thrace.[6]
After the city of Edirne (pop. in 1905 about 80,000), the principal towns were Tekirdağ (35,000), Gelibolu (25,000), Kırklareli (16,000), İskeçe (14,000), Çorlu (11,500), Dimetoka (10,000), Enez (8000), Gümülcine (8000) and Dedeağaç (3000).[1]
Contents
1 Administrative divisions
2 Demographics
2.1 Sanjak of Filibe
2.2 Sanjak of İslimiye
2.3 Sanjak of Gümülcine
3 Gallery
4 References
5 External links
Administrative divisions[edit]
Sanjaks of the Vilayet:[7]
- Sanjak of Edirne (Edirne, Cisr-i Mustafapaşa, Kırcaali, Dimetoka, Ortaköy, Cisr-i Ergene, Havsa. It had also kazas of Kırkkilise, Baba-yı Atik, Beykar Hisar, Maa Hatunili-Kızılağaç (Its centre was Kızılağaç) and Ferecik. Kızılağaç went to Yanbolu sanjak of Şarki Rumeli Vilayeti, Ferecik went initially to Gelibolu in 1876, later to Dedeağaç and was demoted to nahiya in 1878, Kırkkilise, Baba-yı Atik and Beykar Hisar went to recreated Kırkkilise sanjak in 1878. Beykar Hisar was demoted to nahiya in 1879)
- Sanjak of Kirklareli (Since 1879) (Kirkkilise) (Kırkkilise, Tırnovacık, Lüleburgaz, Vize, Ahtabolu, Midye, Baba-yı Atik. Most of Tırnovacık and Ahtopol were ceded to Bulgaria in 1913. Saray separated from Vize and became kaza in 1916)
- Sanjak of Tekirdag (Tekfurdagi) (Tekfurdağı, Çorlu, Malkara, Hayrabolu. It had also kazas Vize, Lüleburgaz and Midye till 1879, it was gone to recreated Kırkkilise sanjak)
Sanjak of Gelibolu (Gelibolu, Maydos, Şarköy, Mürefte, Keşan. It had also Enez and Gümülcine kazas till 1878. Gümülcine promoted to sanjak in 1878. Enez went to Dedeağaç sanjak. Finally İpsala (promoted to kaza) and Enez returned to Gelibolu in 1913)
Sanjak of Dedeağaç (1878-1912) (Dedeağaç, Sofulu, Enez)
Sanjak of Gümülcine (1878-1912) (Gümülcine, İskeçe, Koşukavak, Ahiçelebi, Eğridere, Darıdere). The whole Sanjak was ceded to Bulgaria, with a small part to Greece in 1913.- Sanjak of Filibe (Filibe, Pazarcık, Hasköy, Zağra-i Atik, Kızanlık, Çırpan, Sultanyeri, Ahiçelebi) (until 1878, then it became part of Eastern Rumelia)
- Sanjak of Slimia (İslimye, Yanbolu, Misivri, Karinabat, Aydos, Zağra-i Cedid, Ahyolu, Burgaz) (until 1878, then became part of Eastern Rumelia)
Demographics[edit]
Ethno-religious groups in Adrianople Vilayet, 1906-07
Muslim (57%)
Orthodox (36%)
Armenian (3%)
Jewish (4%)
Total population of the Adrianople Vilayet (including Eastern Rumelia) in 1878 according to the Turkish author Kemal Karpat:[8]
| Group | POPULATION |
|---|---|
| Bulgarians | 40% (526,691) |
| Other Christians | 22% (283,603) |
| Muslims | 39% (503,058) |
TOTAL Adrianople Vilayet | 100% (1,304,352) |
Population of the groups of the Vilayet and Sanjaks according to the Ottoman census in 1906/7, in thousands, adjusted to round numbers.[9]
The groups are counted according to the Millet System of the Ottoman Empire not according to the mother tongue, some Bulgarian-speakers were part of the Greek Rum millet and counted as Greeks, while the Muslim millet included Turks and Pomaks (Bulgarian speaking Muslims).
| Groups | Edirne | Gümülcine | Kırklareli | Dedeağac | Tekirdağ | Gelibolu | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muslims | 154 | 240 | 78 | 44 | 77 | 26 | 619 |
| Greeks | 103 | 22 | 71 | 28 | 53 | 65 | 341 |
| Bulgarians | 37 | 29 | 30 | 17 | 6 | 1 | 120 |
| Jews | 16 | 1 | 2 | – | 3 | 2 | 24 |
| Armenians | 5 | – | - | – | 19 | 1 | 26 |
| Others | 2 | - | – | - | 1 | - | 2 |
| Total | 317 | 292 | 181 | 89 | 159 | 96 | 1,134 |
A publication from December 21, 1912, in the Belgian magazine Ons Volk Ontwaakt (Our Nation Awakes) estimated 1,006,500 inhabitants:[10]
- Muslim Turks – 250,000
Muslim Bulgarians – 115,000- Muslim Roma people – 15,000
- Orthodox Armenians – 30,000
- Orthodox Greeks – 220,000
- Orthodox Bulgarians – 370,000
- Orthodox Albanians – 3,500
- Orthodox Turks – 3,000
Sanjak of Filibe[edit]
Male population of the Filibe Sanjak of the Adrianople Vilayet in 1876 according to the British R. J. Moore:
[11][12]
| Turks | Muslim Gypsies | Christian Gypsies | Bulgarians | Greeks | Armenians | Jews | KAZA TOTAL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Filibe kaza | 28% (35,400) | 4% (5,474) | 0% (495) | 63% (80,107) | 3% (3,700) | 0% (380) | 1% (691) | 100% (126,247) |
| Tatar Pazardzhik kaza | 23% (10,805) | 4% (2,120) | 1% (579) | 70% (33,395) | 1% (300) | 0% (94) | 1% (344) | 100% (47,637) |
Hasköy kaza | 55% (33,323) | 3% (1,548) | 0% (145) | 42% (25,503) | 0% (0) | 0% (3) | 0% (65) | 100% (60,587) |
Zagora kaza | 20% (6,677) | 3% (989) | 0% (70) | 75% (24,857) | 0% (0) | 0% (0) | 2% (740) | 100% (33,333) |
Kazanlak kaza | 46% (14,365) | 4% (1,384) | 0% (24) | 48% (14,906) | 0% (0) | 0% (0) | 1% (219) | 100% (30,898) |
Chirpan kaza | 24% (5,157) | 2% (420) | 0% (88) | 74% (15,959) | 0% (0) | 0% (0) | 0% (0) | 100% (21,624) |
Sultan-Jeri kaza | 97% (13,336) | 1% (159) | 0% (0) | 2% (262) | 0% (0) | 0% (0) | 0% (0) | 100% (13,757) |
Akcselebi kaza | 59% (8,197) | 3% (377) | 0% (0) | 38% (5,346) | 0% (0) | 0% (0) | 0% (0) | 100% (13,920) |
TOTAL Filibe Sanjak | 37% (127,260) | 4% (12,471) | 0% (1,401) | 58% (200,335) | 1% (4,000) | 0% (477) | 1% (2,059) | 100% (348,000) |
Sanjak of İslimiye[edit]
Male population of İslimiye sanjak of Adrianople Vilayet in 1873 according to Ottoman almanacs:
[13]
| Community | Population |
|---|---|
| Muslims | 37,200 (47%) |
| Non-Muslims | 46,961 (53%) |
TOTAL Islimiye sanjak | 100% (84,161) |
Male population of İslimiye sanjak of Adrianople Vilayet in 1875 according to British R.J. Moore:
[14]
| Community | Population |
|---|---|
| Muslims | 42% (44,747) |
| Non-Muslims | 58% (60,854) |
TOTAL Islimiye sanjak | 100% (105,601) |
Sanjak of Gümülcine[edit]
Total population of the Sanjak of Gümülcine of the Adrianople Vilayet In the 19th century:[15]
Sanjak | Muslims | Christian Bulgarians | Christian Greeks |
|---|---|---|---|
Gümülcine | 206.914 | 20.671 | 15.241 |
Gallery[edit]
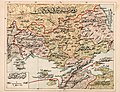
1907 Ottoman Turkish map of the vilayet

Ethnic map of 1912 according to Bulgarian ethnographers
References[edit]
^ ab Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. 1 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 217..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. 1 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 217..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ abcd "1914 Census Statistics" (PDF). Turkish General Staff. pp. 605–606. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 October 2011. Retrieved 29 January 2011.
^ Salname-yi Vilâyet-i Edirne ("Yearbook of the Vilayet of Edirne"), Edirne vilâyet matbaası, Edirne, 1300 [1882]; on the website of Hathi Trust Digital Libray.
^ Europe by Éliseé Reclus, page 152
^ Migration, Memory, Heritage: Socio-cultural Approaches to the Bulgarian-turkish Border, Magdalena Elchinova, Valentina Ganeva-Raycheva, Lina Gergova, Stoyka Penkova, Natalia Rashkova, Nikolai Vukov, Meglena Zlatkova, Lina Gergova,
ISBN 954845842X, p. 30.
^ Europe and the Historical Legacies in the Balkans, Raymond Detrez, Barbara Segaert, Peter Lang, 2008,
ISBN 9052013748, p. 58.
^ Edirne Vilayeti | Tarih ve Medeniyet
^ Karpat, K.H. (1985). Ottoman population, 1830-1914: demographic and social characteristics. Madison, Wis: University of Wisconsin Press
^ Ottoman Population, 1830-1914: Demographic and Social Characteristics, Kemal H. Karpat, page 91, 1985
^ Published on December 21, 1912, in the Belgian magazine Ons Volk Ontwaakt (Our Nation Awakes) – view the table of Vilajet Manastir: Skynet GodsdBalkan Archived 2012-08-31 at the Wayback Machine
^ Demeter, Gabor. "Ethnic maps as political advertisements and instruments of symbolic nation-building and their role in influencing decision-making from Berlin (1877-1881), to Bucharest (1913)".
^ More, R.J., Under the Balkans. Notes of a visit to the district of Philippopolis in 1876. London, 1877.
^ [1]
^ Димитър Аркадиев. ИЗМЕНЕНИЯ В БРОЯ НА НАСЕЛЕНИЕТО ПО БЪЛГАРСКИТЕ ЗЕМИ В СЪСТАВА НА ОСМАНСКАТА ИМПЕРИЯ http://spisaniestatistika.nsi.bg/page/bg/details.php?article_id=84&tab=en] National Statistical Institute
^ [2]
External links[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Adrianople Vilayet. |
Categories:
- States and territories established in 1867
- States and territories disestablished in 1922
- Vilayets of the Ottoman Empire in Europe
- History of Western Thrace
- History of Çanakkale Province
- History of Edirne Province
- History of Kırklareli Province
- History of Tekirdağ Province
- 1867 establishments in the Ottoman Empire
- Adrianople Vilayet
- Ottoman period in the history of Bulgaria
- Ottoman Thrace
- 1922 disestablishments in the Ottoman Empire
(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function(){mw.config.set({"wgPageParseReport":{"limitreport":{"cputime":"0.756","walltime":"0.969","ppvisitednodes":{"value":8243,"limit":1000000},"ppgeneratednodes":{"value":0,"limit":1500000},"postexpandincludesize":{"value":105851,"limit":2097152},"templateargumentsize":{"value":8261,"limit":2097152},"expansiondepth":{"value":13,"limit":40},"expensivefunctioncount":{"value":7,"limit":500},"unstrip-depth":{"value":1,"limit":20},"unstrip-size":{"value":22920,"limit":5000000},"entityaccesscount":{"value":1,"limit":400},"timingprofile":["100.00% 834.412 1 -total"," 34.92% 291.341 1 Template:Infobox_Former_Subdivision"," 21.97% 183.280 80 Template:Percent_and_number"," 21.86% 182.375 2 Template:Rtl-lang"," 21.02% 175.405 1 Template:Reflist"," 16.79% 140.056 80 Template:Percentage"," 15.45% 128.937 80 Template:Number_table_sorting"," 11.03% 92.007 1 Template:Cite_EB1911"," 9.48% 79.127 1 Template:Cite_encyclopedia"," 7.10% 59.225 1 Template:Commons_category"]},"scribunto":{"limitreport-timeusage":{"value":"0.330","limit":"10.000"},"limitreport-memusage":{"value":19137914,"limit":52428800}},"cachereport":{"origin":"mw1270","timestamp":"20190411134624","ttl":2592000,"transientcontent":false}}});});{"@context":"https://schema.org","@type":"Article","name":"Adrianople Vilayet","url":"https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrianople_Vilayet","sameAs":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q1311980","mainEntity":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q1311980","author":{"@type":"Organization","name":"Contributors to Wikimedia projects"},"publisher":{"@type":"Organization","name":"Wikimedia Foundation, Inc.","logo":{"@type":"ImageObject","url":"https://www.wikimedia.org/static/images/wmf-hor-googpub.png"}},"datePublished":"2006-01-18T04:04:16Z","dateModified":"2019-03-20T04:55:20Z","image":"https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/b8/Adrianople_Vilayet%2C_Ottoman_Empire_%281900%29.png","headline":"Ottoman province"}(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function(){mw.config.set({"wgBackendResponseTime":117,"wgHostname":"mw1268"});});

