Fick's laws of diffusion
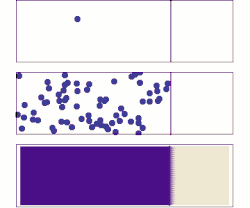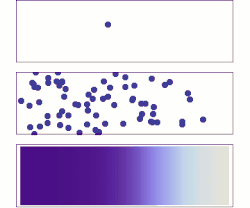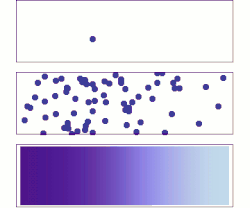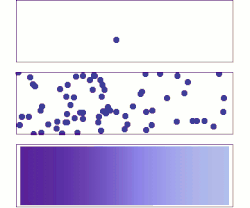
Molecular diffusion from a microscopic and macroscopic point of view. Initially, there are solute molecules on the left side of a barrier (purple line) and none on the right. The barrier is removed, and the solute diffuses to fill the whole container. Top: A single molecule moves around randomly. Middle: With more molecules, there is a clear trend where the solute fills the container more and more uniformly. Bottom: With an enormous number of solute molecules, randomness becomes undetectable: The solute appears to move smoothly and systematically from high-concentration areas to low-concentration areas. This smooth flow is described by Fick's laws.
Fick's laws of diffusion describe diffusion and were derived by Adolf Fick in 1855. They can be used to solve for the diffusion coefficient, D. Fick's first law can be used to derive his second law which in turn is identical to the diffusion equation.
Contents
1 Fick's first law
2 Fick's second law
3 Derivation of Fick's laws
3.1 Fick's first law
3.2 Fick's second law
4 Derivation
4.1 Example solution in one dimension: diffusion length
4.2 Generalizations
5 Applications
5.1 Biological perspective
5.2 Fick's flow in liquids
5.3 Semiconductor fabrication applications
6 History
7 See also
8 Notes
9 References
10 External links
Fick's first law
Fick's first law relates the diffusive flux to the concentration under the assumption of steady state. It postulates that the flux goes from regions of high concentration to regions of low concentration, with a magnitude that is proportional to the concentration gradient (spatial derivative), or in simplistic terms the concept that a solute will move from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration across a concentration gradient. In one (spatial) dimension, the law is:
- J=−Ddφdx{displaystyle J=-D{frac {dvarphi }{dx}}}
where
J is the diffusion flux, of which the dimension is amount of substance per unit area per unit time, so it is expressed in such units as mol m−2 s−1. J measures the amount of substance that will flow through a unit area during a unit time interval.
D is the diffusion coefficient or diffusivity. Its dimension is area per unit time, so typical units for expressing it would be m2/s.
φ (for ideal mixtures) is the concentration, of which the dimension is amount of substance per unit volume. It might be expressed in units of mol/m3.
x is position, the dimension of which is length. It might thus be expressed in the unit m.
D is proportional to the squared velocity of the diffusing particles, which depends on the temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles according to the Stokes–Einstein relation. In dilute aqueous solutions the diffusion coefficients of most ions are similar and have values that at room temperature are in the range of 6990600000000000000♠(0.6–2)×10−9 m2/s. For biological molecules the diffusion coefficients normally range from 10−11 to 10−10 m2/s.
In two or more dimensions we must use ∇, the del or gradient operator, which generalises the first derivative, obtaining
- J=−D∇φ{displaystyle mathbf {J} =-Dnabla varphi }
where J denotes the diffusion flux vector.
The driving force for the one-dimensional diffusion is the quantity −∂φ/∂x, which for ideal mixtures is the concentration gradient. In chemical systems other than ideal solutions or mixtures, the driving force for diffusion of each species is the gradient of chemical potential of this species. Then Fick's first law (one-dimensional case) can be written as:
- Ji=−DciRT∂μi∂x{displaystyle J_{i}=-{frac {Dc_{i}}{RT}}{frac {partial mu _{i}}{partial x}}}
where the index i denotes the ith species, c is the concentration (mol/m3), R is the universal gas constant (J/K/mol), T is the absolute temperature (K), and μ is the chemical potential (J/mol).
If the primary variable is mass fraction (yi, given, for example, in kg/kg), then the equation changes to:
- Ji=−ρD∇yi{displaystyle J_{i}=-rho Dnabla y_{i}}
where ρ is the fluid density (for example, in kg/m3). Note that the density is outside the gradient operator.
Fick's second law
Fick's second law predicts how diffusion causes the concentration to change with time. It is a partial differential equation which in one dimension reads:
- ∂φ∂t=D∂2φ∂x2{displaystyle {frac {partial varphi }{partial t}}=D,{frac {partial ^{2}varphi }{partial x^{2}}}}
where
φ{displaystyle varphi }is the concentration in dimensions of [(amount of substance) length−3], example mol/m3; φ{displaystyle varphi }
= φ{displaystyle varphi }
(x,t) is a function that depends on location x and time t
t is time, example s
D is the diffusion coefficient in dimensions of [length2 time−1], example m2/s
x is the position [length], example m
In two or more dimensions we must use the Laplacian Δ = ∇2, which generalises the second derivative, obtaining the equation
- ∂φ∂t=DΔφ{displaystyle {frac {partial varphi }{partial t}}=DDelta varphi }
Derivation of Fick's laws
Fick's first law
In one dimension, the following derivation is based on a similar argument made in Berg 1977 (see references).
Consider a collection of particles performing a random walk in one dimension with length scale Δx and time scale Δt. Let N(x,t) be the number of particles at position x at time t.
At a given time step, half of the particles would move left and half would move right. Since half of the particles at point x move right and half of the particles at point x + Δx move left, the net movement to the right is:
- −12[N(x+Δx,t)−N(x,t)]{displaystyle -{tfrac {1}{2}}{bigl [}N(x+Delta x,t)-N(x,t){bigr ]}}
The flux, J, is this net movement of particles across some area element of area a, normal to the random walk during a time interval Δt. Hence we may write:
- J=−12[N(x+Δx,t)aΔt−N(x,t)aΔt]{displaystyle J=-{frac {1}{2}}left[{frac {N(x+Delta x,t)}{aDelta t}}-{frac {N(x,t)}{aDelta t}}right]}
Multiplying the top and bottom of the right hand side by (Δx)2 and rewriting, one obtains:
- J=−(Δx)22Δt[N(x+Δx,t)a(Δx)2−N(x,t)a(Δx)2]{displaystyle J=-{frac {left(Delta xright)^{2}}{2Delta t}}left[{frac {N(x+Delta x,t)}{aleft(Delta xright)^{2}}}-{frac {N(x,t)}{aleft(Delta xright)^{2}}}right]}
Concentration is defined as particles per unit volume, and hence
- φ(x,t)=N(x,t)aΔx.{displaystyle varphi (x,t)={frac {N(x,t)}{aDelta x}}.}
In addition, (Δx)2/2Δt is the definition of the one-dimensional diffusion constant, D. Thus our expression simplifies to:
- J=−D[φ(x+Δx,t)Δx−φ(x,t)Δx]{displaystyle J=-Dleft[{frac {varphi (x+Delta x,t)}{Delta x}}-{frac {varphi (x,t)}{Delta x}}right]}
In the limit where Δx is infinitesimal, the right-hand side becomes a space derivative:
- J=−D∂φ∂x{displaystyle J=-D{frac {partial varphi }{partial x}}}
Fick's second law
Fick's second law can be derived from Fick's first law and the mass conservation in absence of any chemical reactions:
- ∂φ∂t+∂∂xJ=0⇒∂φ∂t−∂∂x(D∂∂xφ)=0{displaystyle {frac {partial varphi }{partial t}}+{frac {partial }{partial x}}J=0Rightarrow {frac {partial varphi }{partial t}}-{frac {partial }{partial x}}left(D{frac {partial }{partial x}}varphi right),=0}
Assuming the diffusion coefficient D to be a constant, one can exchange the orders of the differentiation and multiply by the constant:
- ∂∂x(D∂∂xφ)=D∂∂x∂∂xφ=D∂2φ∂x2{displaystyle {frac {partial }{partial x}}left(D{frac {partial }{partial x}}varphi right)=D{frac {partial }{partial x}}{frac {partial }{partial x}}varphi =D{frac {partial ^{2}varphi }{partial x^{2}}}}
and, thus, receive the form of the Fick's equations as was stated above.
For the case of diffusion in two or more dimensions Fick's second law becomes
- ∂φ∂t=D∇2φ,{displaystyle {frac {partial varphi }{partial t}}=Dnabla ^{2}varphi ,}
which is analogous to the heat equation.
If the diffusion coefficient is not a constant, but depends upon the coordinate or concentration, Fick's second law yields
- ∂φ∂t=∇⋅(D∇φ).{displaystyle {frac {partial varphi }{partial t}}=nabla cdot (Dnabla varphi ).}
An important example is the case where φ is at a steady state, i.e. the concentration does not change by time, so that the left part of the above equation is identically zero. In one dimension with constant D, the solution for the concentration will be a linear change of concentrations along x. In two or more dimensions we obtain
- ∇2φ=0{displaystyle nabla ^{2}varphi =0}
which is Laplace's equation, the solutions to which are referred to by mathematicians as harmonic functions.
Derivation
Fick's second law is a special case of the convection–diffusion equation in which there is no advective flux and no net volumetric source. It can be derived from the continuity equation:
- ∂φ∂t+∇⋅j=R,{displaystyle {frac {partial varphi }{partial t}}+nabla cdot mathbf {j} =R,}
where j is the total flux and R is a net volumetric source for φ. The only source of flux in this situation is assumed to be diffusive flux:
- jdiffusion=−D∇φ{displaystyle mathbf {j} _{text{diffusion}}=-Dnabla varphi }
Plugging the definition of diffusive flux to the continuity equation and assuming there is no source (R = 0), we arrive at Fick's second law:
- ∂φ∂t=D∂2φ∂x2{displaystyle {frac {partial varphi }{partial t}}=D{frac {partial ^{2}varphi }{partial x^{2}}}}
If flux were the result of both diffusive flux and advective flux, the convection–diffusion equation is the result.
Example solution in one dimension: diffusion length
A simple case of diffusion with time t in one dimension (taken as the x-axis) from a boundary located at position x = 0, where the concentration is maintained at a value n0 is
n(x,t)=n0erfc(x2Dt){displaystyle nleft(x,tright)=n_{0}mathrm {erfc} left({frac {x}{2{sqrt {Dt}}}}right)}.
where erfc is the complementary error function. This is the case when corrosive gases diffuse through the oxidative layer towards the metal surface (if we assume that concentration of gases in the environment is constant and the diffusion space – that is, the corrosion product layer – is semi-infinite, starting at 0 at the surface and spreading infinitely deep in the material). If, in its turn, the diffusion space is infinite (lasting both through the layer with n(x,0) = 0, x > 0 and that with n(x,0) = n0, x ≤ 0), then the solution is amended only with coefficient 1/2 in front of n0 (as the diffusion now occurs in both directions). This case is valid when some solution with concentration n0 is put in contact with a layer of pure solvent. (Bokstein, 2005) The length 2√Dt is called the diffusion length and provides a measure of how far the concentration has propagated in the x-direction by diffusion in time t (Bird, 1976).
As a quick approximation of the error function, the first 2 terms of the Taylor series can be used:
- n(x,t)=n0[1−2(x2Dtπ)]{displaystyle nleft(x,tright)=n_{0}left[1-2left({frac {x}{2{sqrt {Dtpi }}}}right)right]}
If D is time-dependent, the diffusion length becomes
2∫0tDτdτ.{displaystyle 2{sqrt {int _{0}^{t}Dtau ,dtau }}.}.
This idea is useful for estimating a diffusion length over a heating and cooling cycle, where D varies with temperature.
Generalizations
- In non-homogeneous media, the diffusion coefficient varies in space, D = D(x). This dependence does not affect Fick's first law but the second law changes:
- ∂φ(x,t)∂t=∇⋅(D(x)∇φ(x,t))=D(x)Δφ(x,t)+∑i=13∂D(x)∂xi∂φ(x,t)∂xi{displaystyle {frac {partial varphi (x,t)}{partial t}}=nabla cdot {bigl (}D(x)nabla varphi (x,t){bigr )}=D(x)Delta varphi (x,t)+sum _{i=1}^{3}{frac {partial D(x)}{partial x_{i}}}{frac {partial varphi (x,t)}{partial x_{i}}}}
- ∂φ(x,t)∂t=∇⋅(D(x)∇φ(x,t))=D(x)Δφ(x,t)+∑i=13∂D(x)∂xi∂φ(x,t)∂xi{displaystyle {frac {partial varphi (x,t)}{partial t}}=nabla cdot {bigl (}D(x)nabla varphi (x,t){bigr )}=D(x)Delta varphi (x,t)+sum _{i=1}^{3}{frac {partial D(x)}{partial x_{i}}}{frac {partial varphi (x,t)}{partial x_{i}}}}
- In anisotropic media, the diffusion coefficient depends on the direction. It is a symmetric tensor D = Dij. Fick's first law changes to
J=−D∇φ{displaystyle J=-Dnabla varphi },
- it is the product of a tensor and a vector:
- Ji=−∑j=13Dij∂φ∂xj.{displaystyle J_{i}=-sum _{j=1}^{3}D_{ij}{frac {partial varphi }{partial x_{j}}}.}
- Ji=−∑j=13Dij∂φ∂xj.{displaystyle J_{i}=-sum _{j=1}^{3}D_{ij}{frac {partial varphi }{partial x_{j}}}.}
- For the diffusion equation this formula gives
- ∂φ(x,t)∂t=∇⋅(D∇φ(x,t))=∑i=13∑j=13Dij∂2φ(x,t)∂xi∂xj.{displaystyle {frac {partial varphi (x,t)}{partial t}}=nabla cdot {bigl (}Dnabla varphi (x,t){bigr )}=sum _{i=1}^{3}sum _{j=1}^{3}D_{ij}{frac {partial ^{2}varphi (x,t)}{partial x_{i}partial x_{j}}}.}
- ∂φ(x,t)∂t=∇⋅(D∇φ(x,t))=∑i=13∑j=13Dij∂2φ(x,t)∂xi∂xj.{displaystyle {frac {partial varphi (x,t)}{partial t}}=nabla cdot {bigl (}Dnabla varphi (x,t){bigr )}=sum _{i=1}^{3}sum _{j=1}^{3}D_{ij}{frac {partial ^{2}varphi (x,t)}{partial x_{i}partial x_{j}}}.}
- The symmetric matrix of diffusion coefficients Dij should be positive definite. It is needed to make the right hand side operator elliptic.
- For inhomogeneous anisotropic media these two forms of the diffusion equation should be combined in
- ∂φ(x,t)∂t=∇⋅(D(x)∇φ(x,t))=∑i,j=13(Dij(x)∂2φ(x,t)∂xi∂xj+∂Dij(x)∂xi∂φ(x,t)∂xj).{displaystyle {frac {partial varphi (x,t)}{partial t}}=nabla cdot {bigl (}D(x)nabla varphi (x,t){bigr )}=sum _{i,j=1}^{3}left(D_{ij}(x){frac {partial ^{2}varphi (x,t)}{partial x_{i}partial x_{j}}}+{frac {partial D_{ij}(x)}{partial x_{i}}}{frac {partial varphi (x,t)}{partial x_{j}}}right).}
- ∂φ(x,t)∂t=∇⋅(D(x)∇φ(x,t))=∑i,j=13(Dij(x)∂2φ(x,t)∂xi∂xj+∂Dij(x)∂xi∂φ(x,t)∂xj).{displaystyle {frac {partial varphi (x,t)}{partial t}}=nabla cdot {bigl (}D(x)nabla varphi (x,t){bigr )}=sum _{i,j=1}^{3}left(D_{ij}(x){frac {partial ^{2}varphi (x,t)}{partial x_{i}partial x_{j}}}+{frac {partial D_{ij}(x)}{partial x_{i}}}{frac {partial varphi (x,t)}{partial x_{j}}}right).}
- The approach based on Einstein's mobility and Teorell formula gives the following generalization of Fick's equation for the multicomponent diffusion of the perfect components:
- ∂φi∂t=∑j∇⋅(Dijφiφj∇φj).{displaystyle {frac {partial varphi _{i}}{partial t}}=sum _{j}nabla cdot left(D_{ij}{frac {varphi _{i}}{varphi _{j}}}nabla ,varphi _{j}right).}
- ∂φi∂t=∑j∇⋅(Dijφiφj∇φj).{displaystyle {frac {partial varphi _{i}}{partial t}}=sum _{j}nabla cdot left(D_{ij}{frac {varphi _{i}}{varphi _{j}}}nabla ,varphi _{j}right).}
- where φi are concentrations of the components and Dij is the matrix of coefficients. Here, indices i and j are related to the various components and not to the space coordinates.
The Chapman–Enskog formulae for diffusion in gases include exactly the same terms. These physical models of diffusion are different from the test models ∂tφi = ∑jDij Δφj which are valid for very small deviations from the uniform equilibrium. Earlier, such terms were introduced in the Maxwell–Stefan diffusion equation.
For anisotropic multicomponent diffusion coefficients one needs a rank-four tensor, for example Dij,αβ, where i, j refer to the components and α, β = 1, 2, 3 correspond to the space coordinates.
Applications
Equations based on Fick's law have been commonly used to model transport processes in foods, neurons, biopolymers, pharmaceuticals, porous soils, population dynamics, nuclear materials, plasma physics, and semiconductor doping processes. Theory of all voltammetric methods is based on solutions of Fick's equation. Much experimental research in polymer science and food science has shown that a more general approach is required to describe transport of components in materials undergoing glass transition. In the vicinity of glass transition the flow behavior becomes "non-Fickian". It can be shown that the Fick's law can be obtained from the Maxwell–Stefan equations[1]
of multi-component mass transfer. The Fick's law is limiting case of the Maxwell–Stefan equations, when the mixture is extremely dilute and every chemical species is interacting only with the bulk mixture and not with other species. To account for the presence of multiple species in a non-dilute mixture, several variations of the Maxwell–Stefan equations are used. See also non-diagonal coupled transport processes (Onsager relationship).
Biological perspective
The first law gives rise to the following formula:[2]
- flux=−P(c2−c1){displaystyle {text{flux}}={-Pleft(c_{2}-c_{1}right)}}
in which,
P is the permeability, an experimentally determined membrane "conductance" for a given gas at a given temperature.
c2 − c1 is the difference in concentration of the gas across the membrane for the direction of flow (from c1 to c2).
Fick's first law is also important in radiation transfer equations. However, in this context it becomes inaccurate when the diffusion constant is low and the radiation becomes limited by the speed of light rather than by the resistance of the material the radiation is flowing through. In this situation, one can use a flux limiter.
The exchange rate of a gas across a fluid membrane can be determined by using this law together with Graham's law.
Fick's flow in liquids
When two miscible liquids are brought into contact, and diffusion takes place, the macroscopic (or average) concentration evolves following Fick's law. On a mesoscopic scale, that is, between the macroscopic scale described by Fick's law and molecular scale, where molecular random walks take place, fluctuations cannot be neglected. Such situations can be successfully modeled with Landau-Lifshitz fluctuating hydrodynamics. In this theoretical framework, diffusion is due to fluctuations whose dimensions range from the molecular scale to the macroscopic scale.[3]
In particular, fluctuating hydrodynamic equations include a Fick's flow term, with a given diffusion coefficient, along with hydrodynamics equations and stochastic terms describing fluctuations. When calculating the fluctuations with a perturbative approach, the zero order approximation is Fick's law. The first order gives the fluctuations, and it comes out that fluctuations contribute to diffusion. This represents somehow a tautology, since the phenomena described by a lower order approximation is the result of a higher approximation: this problem is solved only by renormalizing the fluctuating hydrodynamics equations.
Semiconductor fabrication applications
Integrated circuit fabrication technologies, model processes like CVD, thermal oxidation, wet oxidation, doping, etc. use diffusion equations obtained from Fick's law.
In certain cases, the solutions are obtained for boundary conditions such as constant source concentration diffusion, limited source concentration, or moving boundary diffusion (where junction depth keeps moving into the substrate).
History
In 1855, physiologist Adolf Fick first reported[4] his now well-known laws governing the transport of mass through diffusive means. Fick's work was inspired by the earlier experiments of Thomas Graham, which fell short of proposing the fundamental laws for which Fick would become famous. The Fick's law is analogous to the relationships discovered at the same epoch by other eminent scientists: Darcy's law (hydraulic flow), Ohm's law (charge transport), and Fourier's Law (heat transport).
Fick's experiments (modeled on Graham's) dealt with measuring the concentrations and fluxes of salt, diffusing between two reservoirs through tubes of water. It is notable that Fick's work primarily concerned diffusion in fluids, because at the time, diffusion in solids was not considered generally possible.[5] Today, Fick's Laws form the core of our understanding of diffusion in solids, liquids, and gases (in the absence of bulk fluid motion in the latter two cases). When a diffusion process does not follow Fick's laws (which happens in cases of diffusion through porous media and diffusion of swelling penetrants, among others),[6][7] it is referred to as non-Fickian.
See also
- Diffusion
- Osmosis
- Mass flux
- Maxwell–Stefan diffusion
- Churchill–Bernstein equation
- Nernst–Planck equation
- Gas exchange
- False diffusion
- Advection
Notes
^ Taylor, Ross; Krishna, R. (1993). "Multicomponent mass transfer". Wiley..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Essentials of Human Physiology by Thomas M. Nosek. Section 3/3ch9/s3ch9_2.
^ Brogioli, D.; Vailati, A. (2001). "Diffusive mass transfer by nonequilibrium fluctuations: Fick's law revisited". Phys. Rev. E. 63 (1–4): 012105. arXiv:cond-mat/0006163. Bibcode:2001PhRvE..63a2105B. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.63.012105.
^
Fick, A. (1855). "Ueber Diffusion". Annalen der Physik (in German). 94: 59–86. doi:10.1002/andp.18551700105.
Fick, A. (1855). Phil. Mag. 10: 30. Missing or empty|title=(help)
^ Philibert, Jean (2005). "One and a Half Centuries of Diffusion: Fick, Einstein, before and beyond" (PDF). Diffusion Fundamentals. 2: 1.1–1.10. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2009.
^ Vázquez, J. L. (2006). "The Porous Medium Equation". Mathematical Theory. Oxford Univ. Press.
^ Gorban,, A. N.; Sargsyan, H. P.; Wahab, H. A. (2011). "Quasichemical Models of Multicomponent Nonlinear Diffusion". Mathematical Modelling of Natural Phenomena. 6 (05): 184–262. arXiv:1012.2908. doi:10.1051/mmnp/20116509.
References
Smith, W. F. (2004). Foundations of Materials Science and Engineering (3rd ed.). McGraw-Hill.
Berg, H. C. (1977). Random Walks in Biology. Princeton.
Bird, R. B.; Stewart, W. E.; Lightfoot, E. N. (1976). Transport Phenomena. John Wiley & Sons.
Crank, J. (1980). The Mathematics of Diffusion. Oxford University Press.
Bokshtein, B. S.; Mendelev, M. I.; Srolovitz, D. J., eds. (2005). Thermodynamics and Kinetics in Materials Science: A Short Course. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 167–171.
Fick, A. (1855). "On liquid diffusion". Poggendorffs Annalen. 94: 59. – reprinted in "On liquid diffusion". Journal of Membrane Science. 100: 33–38. 1995. doi:10.1016/0376-7388(94)00230-v.
External links
Fick's equations, Boltzmann's transformation, etc. (with figures and animations)
Fick's Second Law on OpenStax






![{displaystyle -{tfrac {1}{2}}{bigl [}N(x+Delta x,t)-N(x,t){bigr ]}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d5c4b85ec1e33f9722c72d3ba1227dafbe4b191a)
![J = - frac{1}{2} left[frac{ N(x + Delta x, t)}{a Delta t} - frac{ N(x, t)}{a Delta t}right]](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/0189eaf823ce9c7d5a5737f4ef42a9dec2e4d45d)
![{displaystyle J=-{frac {left(Delta xright)^{2}}{2Delta t}}left[{frac {N(x+Delta x,t)}{aleft(Delta xright)^{2}}}-{frac {N(x,t)}{aleft(Delta xright)^{2}}}right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8ac4fa578b6a883284274d63620e58b2804fa5f9)

![{displaystyle J=-Dleft[{frac {varphi (x+Delta x,t)}{Delta x}}-{frac {varphi (x,t)}{Delta x}}right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/70f74bdc01996709857aab88c38cd978aa763f91)









![n left(x,t right)=n_0 left[ 1 - 2 left(frac{x}{2sqrt{Dtpi}}right) right]](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9de7f0847f6b083c5bc3c4063fb343e78cf9c0c7)





