Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European powers formed into various coalitions, financed and usually led by the United Kingdom. The wars stemmed from the unresolved disputes associated with the French Revolution and its resultant conflict. The wars are often categorised into five conflicts, each termed after the coalition that fought Napoleon: the Third Coalition (1805), the Fourth (1806–07), Fifth (1809), Sixth (1813), and the Seventh and final (1815).
Napoleon, upon ascending to First Consul of France in 1799, had inherited a chaotic republic; he subsequently created a state with stable finances, a strong bureaucracy, and a well-trained army. In 1805, Austria and Russia waged war against France. In response, Napoleon defeated the allied Russo-Austrian army at Austerlitz in December 1805, which is considered his greatest victory. At sea, the British severely defeated the joint Franco-Spanish navy in the Battle of Trafalgar on October 1805.
This victory secured British control of the seas and prevented the invasion of Britain itself. Prussian concerns about increasing French power led to a resumption of war in October 1806. Napoleon quickly defeated the Prussians, and defeated Russia in June 1807, bringing an uneasy peace to the continent. The peace failed, though, as war broke out in 1809, and a new coalition was soon defeated.
Hoping to isolate Britain economically, Napoleon invaded Iberia, declaring his brother Joseph king of Spain in 1808. The Spanish and Portuguese revolted with British support, and, after six years of fighting, expelled the French from Iberia in 1814. Concurrently, Russia, unwilling to bear economic consequences of reduced trade, routinely violated the Continental System, enticing Napoleon to launch a massive invasion of Russia in 1812. The resulting campaign ended with the dissolution and withdrawal of the French Grande Armée. Encouraged by the defeat, Prussia, Austria, and Russia began a new campaign against France, decisively defeating Napoleon at Leipzig in October 1813 after several inconclusive engagements. The Allies then invaded France, capturing Paris at the end of March 1814 and forcing Napoleon to abdicate in early April. He was exiled to the island of Elba, and the Bourbons were restored to power. However, Napoleon escaped in February 1815, and reassumed control of France. The Allies responded with the Seventh Coalition, defeating Napoleon permanently at Waterloo in June 1815 and exiling him to St Helena.
The Congress of Vienna redrew the borders of Europe, and brought a lasting peace to the continent. The wars had profound consequences on global history, including the spread of nationalism and liberalism, the rise of the British Empire as the world's foremost power, the appearance of independence movements in Latin America and subsequent collapse of the Spanish Empire, the fundamental reorganisation of German and Italian territories into larger states, and the establishment of radically new methods of conducting warfare.
Contents
1 Overview
2 Background
2.1 Start date and nomenclature
2.2 Napoleon's tactics
3 Prelude
4 War between Britain and France, 1803–1814
4.1 British motivations
4.2 Economic warfare
4.3 Financing the war
5 War of the Third Coalition 1805
6 War of the Fourth Coalition 1806–1807
6.1 Scandinavia and Finland
6.2 Poland
7 War of the Fifth Coalition 1809
8 Subsidiary wars
8.1 War of 1812
8.2 The Latin American Revolutions
9 The Invasion of Russia 1812
10 War of the Sixth Coalition 1812–1814
11 War of the Seventh Coalition 1815
12 Political effects
13 Military legacy
13.1 Enlarged scope
13.2 Innovations
13.3 Total war
14 In fiction
15 See also
16 Notes
17 References
18 Sources
19 Further reading
19.1 General and reference books
19.2 Napoleon and French
19.3 British, Austrian, Prussian & Russian roles
19.4 Historiography and memory
19.5 Primary sources
20 External links
Overview
Napoleon seized power in 1799, creating a de facto military dictatorship.[33] There are a number of opinions on the date to use as the formal beginning of the Napoleonic Wars; 18 May 1803 is often used, when Britain and France ended the only short period of peace between 1792 and 1814.[34] The Napoleonic Wars began with the War of the Third Coalition, which was the first of the Coalition Wars against the First French Republic after Napoleon's accession as leader of France.
Britain ended the Treaty of Amiens and declared war on France in May 1803. Among the reasons were Napoleon's changes to the international system in Western Europe, especially in Switzerland, Germany, Italy and the Netherlands. Kagan argues that Britain was irritated in particular by Napoleon's assertion of control over Switzerland. Furthermore, Britons felt insulted when Napoleon stated that their country deserved no voice in European affairs, even though King George III was an elector of the Holy Roman Empire. For its part, Russia decided that the intervention in Switzerland indicated that Napoleon was not looking toward a peaceful resolution of his differences with the other European powers.[34]
The British quickly enforced a naval blockade of France to starve it of resources. Napoleon responded with economic embargoes against Britain, and sought to eliminate Britain's Continental allies to break the coalitions arrayed against him. The so-called Continental System formed a league of armed neutrality to disrupt the blockade and enforce free trade with France. The British responded by capturing the Danish fleet, breaking up the league, and later secured dominance over the seas, allowing it to freely continue its strategy. Napoleon won the War of the Third Coalition at Austerlitz, forcing the Austrian Empire out of the war and formally dissolving the Holy Roman Empire. Within months, Prussia declared war, triggering a War of the Fourth Coalition. This war ended disastrously for Prussia, defeated and occupied within 19 days of the beginning of the campaign. Napoleon subsequently defeated the Russian Empire at Friedland, creating powerful client states in Eastern Europe and ending the fourth coalition.
Concurrently, the refusal of Portugal to commit to the Continental System, and Spain's failure to maintain it, led to the Peninsular War and the outbreak of the War of the Fifth Coalition. The French occupied Spain and formed a Spanish client kingdom, ending the alliance between the two. Heavy British involvement in the Iberian Peninsula soon followed, while a British effort to capture Antwerp failed. Napoleon oversaw the situation in Iberia, defeating the Spanish, and expelling the British from the Peninsula. Austria, keen to recover territory lost during the War of the Third Coalition, invaded France's client states in Eastern Europe. Napoleon defeated the fifth coalition at Wagram.
Attempts to disrupt the British blockade led to the United States declaring war on Britain, while grievances over control of Poland, and Russia's withdrawal from the Continental System, led to Napoleon invading Russia in June 1812. The invasion was an unmitigated disaster for Napoleon; scorched earth tactics, desertion, French strategic failures and the onset of the Russian winter compelled Napoleon to retreat with massive losses. Napoleon suffered further setbacks; French power in the Iberian Peninsula was broken at Battle of Vitoria the following summer, and a new coalition began the War of the Sixth Coalition.
The coalition defeated Napoleon at Leipzig, precipitating his fall from power and eventual abdication on 6 April 1814. The victors exiled Napoleon to Elba and restored the Bourbon monarchy. Napoleon escaped from Elba in 1815, gathering enough support to overthrow the monarchy of Louis XVIII, triggering a seventh, and final, coalition against him. Napoleon was decisively defeated at Waterloo, and he abdicated again on 22 June. On 15 July, he surrendered to the British at Rochefort, and was exiled to Saint Helena, where he died in 1821. The Treaty of Paris, signed on 20 November 1815, formally ended the war.
The Bourbon monarchy was restored once more, and the victors began the Congress of Vienna, to restore peace to the continent. As a direct result of the war, the Kingdom of Prussia rose to become a great power on the continent,[35] while Great Britain, with its unequalled Royal Navy and growing Empire became the world's dominant superpower, beginning the Pax Britannica.[36] The Holy Roman Empire was dissolved, and the philosophy of nationalism, that emerged early in the war, greatly contributed to the later unification of the German states, and those of the Italian peninsula. The war in Iberia greatly weakened Spanish power, and the Spanish Empire began to unravel; Spain would lose nearly all of its American possessions by 1833. The Portuguese Empire began a rapid decline, with Brazil declaring independence in 1822.[8]
The wars revolutionised European warfare; the application of mass conscription and total war led to campaigns of unprecedented scale, as whole nations committed all their economic and industrial resources to a collective war effort.[37] Tactically, the French Army redefined the role of artillery, while Napoleon emphasised mobility to offset numerical disadvantages,[38] and aerial surveillance was used for the first time in warfare.[39] While not a new tactic, the highly successful Spanish guerrillas demonstrated the capability of a people driven by fervent nationalism, liberalism and religious fundamentalism against an occupying force.[40] Due to the longevity of the wars, and the extent of Napoleon's conquests, the ideals of the French Revolution had a massive impact on European social culture; many subsequent revolutions, such as that of Russia, looked to the French as their source of inspiration,[41][42] while its core founding tenets greatly expanded the arena of Human rights and shaped modern political philosophies in use today.[43]
Background

French victory over the Prussians at the Battle of Valmy in 1792
The outbreak of the French Revolution had been received with great alarm by the rulers of Europe's continental powers, which had been further exacerbated by the execution of Louis XVI of France, and the overthrow of the French monarchy. In 1793, the Austrian Empire, the Kingdom of Sardinia, the Kingdom of Naples, Prussia, the Spanish Empire, and the Kingdom of Great Britain formed the First Coalition to curtail the growing unrest in France. Measures such as mass conscription, military reforms, and total war allowed France to defeat the coalition, despite the concurrent civil war in France. Napoleon, then a general in the French army, forced the Austrians to sign the Treaty of Campo Formio, leaving only Great Britain opposed to the fledgling French Republic.
A Second Coalition formed in 1798 by Great Britain, Austria, Naples, the Ottoman Empire, the Papal States, Portugal, Russia, and Sweden. The French Republic, under the Directory, suffered from heavy levels of corruption and internal strife. The new republic also lacked funds, and no longer enjoyed the services of Lazare Carnot, the minister of war who had guided France to its victories during the early stages of the Revolution. Bonaparte, commander of the Armée d'Italie in the latter stages of the First Coalition, had launched a campaign in Egypt, intending to disrupt the British economic powerhouse of India. Pressed from all sides, the Republic suffered a string of successive defeats against revitalised enemies, supported by Britain's financial help.

Bonaparte defeats the Austrians at the Battle of Rivoli in 1797
Bonaparte returned to France from Egypt on 23 August 1799, his campaign there having failed. He seized control of the French government on 9 November, in a bloodless coup d'état, replacing the Directory with the Consulate and transforming the republic into a de facto dictatorship.[33] He further reorganised the French military forces, establishing a large reserve army positioned to support campaigns on the Rhine or in Italy. Russia had already been knocked out of the war, and, under Napoleon's leadership, the French decisively defeated the Austrians in June 1800, crippling Austrian capabilities in Italy. Austria was definitively defeated that December, by Moreau's forces in Bavaria. The Austrian defeat was sealed by the Treaty of Lunéville early the following year, further compelling the British to sign the Treaty of Amiens with France, establishing a tenuous peace.
Start date and nomenclature
No consensus exists as to when the French Revolutionary Wars ended and the Napoleonic Wars began. Possible dates include 9 November 1799, when Bonaparte seized power on 18 Brumaire, the date according to the Republican Calendar then in use;[44] 18 May 1803, when Britain and France ended the one short period of peace between 1792 and 1814; or 2 December 1804, when Bonaparte crowned himself Emperor.[45]
British historians occasionally refer to the nearly continuous period of warfare from 1792 to 1815 as the Great French War, or as the final phase of the Anglo-French Second Hundred Years' War, spanning the period 1689 to 1815.[46] Historian Mike Rapport (2013) suggested to use the term "French Wars" to unambiguously describe the entire period from 1792 to 1815.[47]
In France, the Napoleonic Wars are generally integrated with the French Revolutionary Wars: Les guerres de la Révolution et de l'Empire.[48]
German historiography may count the War of the Second Coalition (1798/9–1801/2), during which Napoleon seized power, as the Erster Napoleonischer Krieg ("First Napoleonic War").[49]
In Dutch historiography, it is common to refer to the seven major wars between 1792 and 1815 as the Coalition Wars (coalitieoorlogen), referring to the first two as the French Revolution Wars (Franse Revolutieoorlogen).[50]
Napoleon's tactics
Napoleon was, and remains, famous for his battlefield victories, and historians have spent enormous attention in analysing them.[51] In 2008, Donald Sutherland wrote:
The ideal Napoleonic battle was to manipulate the enemy into an unfavourable position through manoeuvre and deception, force him to commit his main forces and reserve to the main battle and then undertake an enveloping attack with uncommitted or reserve troops on the flank or rear. Such a surprise attack would either produce a devastating effect on morale, or force him to weaken his main battle line. Either way, the enemy's own impulsiveness began the process by which even a smaller French army could defeat the enemy's forces one by one.[52]
After 1807, Napoleon's creation of a highly mobile, well-armed artillery force gave artillery usage increased tactical importance. Napoleon, rather than relying on infantry to wear away the enemy's defences, could now use massed artillery as a spearhead to pound a break in the enemy's line. Once that was achieved he sent in infantry and cavalry.[53]
Prelude

French victory over the Austrians and Russians at the Second Battle of Zürich
Britain was irritated by several French actions following the Treaty of Amiens. Bonaparte had annexed Piedmont and Elba, made himself President of the Italian Republic, a state in northern Italy that France had set up, and failed to evacuate Holland. France continued to interfere with British trade despite peace having been made and complained about Britain harbouring certain individuals and not cracking down on the anti-French press.[54]:220–239 In fighting, Napoleon focused on penetration, gaining a central position, and surrounding small groups of enemy forces.[55] To Napoleon, penetration meant "You engage, and then you wait and see." Central Positioning aimed to divide enemy forces into weaker smaller groups.
Malta had been captured by Britain during the war and was subject to a complex arrangement in the 10th article of the Treaty of Amiens where it was to be restored to the Knights of St. John with a Neapolitan garrison and placed under the guarantee of third powers. The weakening of the Knights of St. John by the confiscation of their assets in France and Spain along with delays in obtaining guarantees prevented the British from evacuating it after three months as stipulated in the treaty.[54]:239–247

British victory over the French at the Battle of Alexandria, resulted in the end of Napoleon's military presence in Egypt.
The Helvetic Republic had been set up by France when it invaded Switzerland in 1798. France had withdrawn its troops, but violent strife broke out against the government, which many Swiss saw as overly centralised. Bonaparte reoccupied the country in October 1802 and imposed a compromise settlement. This caused widespread outrage in Britain, which protested that this was a violation of the Treaty of Lunéville. Although continental powers were unprepared to act, the British decided to send an agent to help the Swiss obtain supplies, and also ordered their military not to return Cape Colony to Holland as they had committed to do in the Treaty of Amiens.[54]:248–252
Swiss resistance collapsed before anything could be accomplished, and after a month Britain countermanded the orders not to restore Cape Colony. At the same time Russia finally joined the guarantee with regards to Malta. Concerned that there would be hostilities when Bonaparte found out that Cape Colony had been retained, the British began to procrastinate on the evacuation of Malta.[54]:252–258 In January 1803 a government paper in France published a report from a commercial agent which noted the ease with which Egypt could be conquered. The British seized on this to demand satisfaction and security before evacuating Malta, which was a convenient stepping stone to Egypt. France disclaimed any desire to seize Egypt and asked what sort of satisfaction was required but the British were unable to give a response.[54]:258–264 There was still no thought of going to war; Prime Minister Addington publicly affirmed that Britain was in a state of peace.[54]:265
In early March 1803 the Addington ministry received word that Cape Colony had been re-occupied by the British army in accordance with the orders which had subsequently been countermanded. On 8 March they ordered military preparations to guard against possible French retaliation, and justified them by falsely claiming that it was only in response to French preparations and that they were conducting serious negotiations with France. In a few days it was known that Cape Colony had been surrendered in accordance with the counter-orders, but it was too late. Bonaparte berated the British ambassador in front of 200 spectators over the military preparations.[54]:264–268
The Addington ministry realised they would face an inquiry over their false reasons for the military preparations, and during April unsuccessfully attempted to secure the support of William Pitt the Younger to shield them from damage.[54]:277 In the same month the ministry issued an ultimatum to France demanding the retention of Malta for at least ten years, the permanent acquisition of the island of Lampedusa from the Kingdom of Sicily, and the evacuation of Holland. They also offered to recognise French gains in Italy if they evacuated Switzerland and compensated the King of Sardinia for his territorial losses. France offered to place Malta in the hands of Russia to satisfy British concerns, pull out of Holland when Malta was evacuated, and form a convention to give satisfaction to Britain on other issues. The British falsely denied that Russia had made an offer and their ambassador left Paris.[54]:268–278 Desperate to avoid war, Bonaparte sent a secret offer where he agreed to let Britain retain Malta if France could occupy the Otranto peninsula in Naples.[56] All efforts were futile and Britain declared war on 18 May 1803.
War between Britain and France, 1803–1814
British motivations
Britain ended the uneasy truce created by the Treaty of Amiens when it declared war on France in May 1803. The British were increasingly angered by Napoleon's reordering of the international system in Western Europe, especially in Switzerland, Germany, Italy and the Netherlands. Kagan argues that Britain was especially alarmed by Napoleon's assertion of control over Switzerland. Britons felt insulted when Napoleon said it deserved no voice in European affairs (even though King George was an elector of the Holy Roman Empire), and sought to restrict the London newspapers that were vilifying him.[34]

"Maniac-raving's-or-Little Boney in a strong fit" by James Gillray. His caricatures ridiculing Napoleon greatly annoyed the Frenchman, who wanted them suppressed by the British government.[57]
Britain had a sense of loss of control, as well as loss of markets, and was worried by Napoleon's possible threat to its overseas colonies. McLynn argues that Britain went to war in 1803 out of a "mixture of economic motives and national neuroses – an irrational anxiety about Napoleon's motives and intentions." McLynn concludes that it proved to be the right choice for Britain, because in the long run Napoleon's intentions were hostile to the British national interest. Napoleon was not ready for war and so this was the best time for Britain to stop them. Britain seized upon the Malta issue, refusing to follow the terms of the Treaty of Amiens and evacuate the island.[58]
The deeper British grievance was their perception that Napoleon was taking personal control of Europe, making the international system unstable, and forcing Britain to the sidelines.[59][60][61][62] Numerous scholars have argued that Napoleon's aggressive posture made him enemies and cost him potential allies.[63] As late as 1808, the continental powers affirmed most of his gains and titles, but the continuing conflict with Britain led him to start the Peninsular War and the invasion of Russia, which many scholars see as a dramatic miscalculation.[64][65][66][67][68]

Battle of San Domingo, 6 February 1806

Battle of the Pyrenees, July 1813
There was one serious attempt to negotiate peace with France during the war, made by Charles James Fox in 1806. The British wanted to retain their overseas conquests and have Hanover restored to George III in exchange for accepting French conquests on the continent. The French were willing to cede Malta, Cape Colony, Tobago, and French Indian posts to Britain but wanted to obtain Sicily in exchange for the restoration of Hanover, a condition the British refused.[69]
Unlike its many coalition partners, Britain remained at war throughout the period of the Napoleonic Wars. Protected by naval supremacy (in the words of Admiral Jervis to the House of Lords "I do not say, my Lords, that the French will not come. I say only they will not come by sea"), Britain maintained low-intensity land warfare on a global scale for over a decade. The British government paid out large sums of money to other European states, so that they could pay armies in the field against France. These payments are colloquially known as the Golden Cavalry of St George. The British Army provided long-term support to the Spanish rebellion in the Peninsular War of 1808–1814, assisted by Spanish guerrilla ('little war') tactics. Anglo-Portuguese forces under Arthur Wellesley supported the Spanish, which campaigned successfully against the French armies, eventually driving them from Spain and allowing Britain to invade southern France. By 1815, the British Army played the central role in the final defeat of Napoleon at Waterloo.
Beyond minor naval actions against British imperial interests, the Napoleonic Wars were much less global in scope than preceding conflicts such as the Seven Years' War, which historians term a "world war".
Economic warfare
In response to the naval blockade of the French coasts enacted by the British government on 16 May 1806, Napoleon issued the Berlin Decree on 21 November 1806, which brought into effect the Continental System.[70] This policy aimed to eliminate the threat from Britain by closing French-controlled territory to its trade. Britain maintained a standing army of 220,000 at the height of the Napoleonic Wars, of whom less than half were available for campaigning. The rest were necessary for garrisoning Ireland and the colonies, and providing security for Britain. France's strength peaked at around 2,500,000 full-time and part-time soldiers including several hundred thousand National Guardsmen whom Napoleon could draft into the military if necessary. Both nations enlisted large numbers of sedentary militia who were unsuited for campaigning, and were mostly employed to release regular forces for active duty.[71] The Royal Navy disrupted France's extra-continental trade by seizing and threatening French shipping and colonial possessions, but could do nothing about France's trade with the major continental economies and posed little threat to French territory in Europe. France's population and agricultural capacity far outstripped that of Britain. Britain had the greatest industrial capacity in Europe, and its mastery of the seas allowed it to build up considerable economic strength through trade. This ensured that France could never consolidate its control over Europe in peace. Many in the French government believed that cutting Britain off from the Continent would end its economic influence over Europe and isolate it.
Financing the war
A key element in British success was its ability to mobilise the nation's industrial and financial resources and apply them to defeating France. With a population of 16 million against France's 30 million, the French numerical advantage was offset by British subsidies that paid for many of the Austrian and Russian soldiers, peaking at about 450,000 men in 1813.[71][72] Under the Anglo-Russian agreement of 1803, Britain paid a subsidy of £1.5 million for every 100,000 Russian soldiers in the field.[73]
British national output remained strong, and the well-organised business sector channeled products into what the military needed. Britain used its economic power to expand the Royal Navy, doubling the number of frigates, adding 50% more large ships of the line, and increasing the number of sailors from 15,000 to 133,000 in eight years after the war began in 1793. France saw its navy shrink by more than half.[74] The smuggling of finished products into the continent undermined French efforts to weaken the British economy by cutting off markets. Subsidies to Russia and Austria kept them in the war. The British budget in 1814 reached £66 million, including £10 million for the Royal Navy, £40 million for the army, £10 million for the allies, and £38 million as interest on the national debt, which soared to £679 million, more than double the GDP. This debt was supported by hundreds of thousands of investors and taxpayers, despite the higher taxes on land and a new income tax. The cost of the war came to £831 million.[r] In contrast, the French financial system was inadequate and Napoleon's forces had to rely in part on requisitions from conquered lands.[76][77][78]
War of the Third Coalition 1805

The British HMS Sandwich fires to the French flagship Bucentaure (completely dismasted) in the battle of Trafalgar. Bucentaure also fights HMS Victory (behind her) and HMS Temeraire (left side of the picture). HMS Sandwich never fought at Trafalgar and her depiction is a mistake by the painter.[79]
Britain gathered together allies to form the Third Coalition against France.[80][81] In response, Napoleon seriously considered an invasion of Great Britain,[82][83] and massed 180,000 troops at Boulogne. Before he could invade, he needed to achieve naval superiority—or at least to pull the British fleet away from the English Channel. A complex plan to distract the British by threatening their possessions in the West Indies failed when a Franco-Spanish fleet under Admiral Villeneuve turned back after an indecisive action off Cape Finisterre on 22 July 1805. The Royal Navy blockaded Villeneuve in Cádiz until he left for Naples on 19 October; the British squadron caught and overwhelmingly defeated the combined enemy fleet in the Battle of Trafalgar on 21 October (the British commander, Lord Nelson, died in the battle). Napoleon never again had the opportunity to challenge the British at sea, nor to threaten an invasion. He again turned his attention to enemies on the Continent.

European strategic situation in 1805 before the War of the Third Coalition
In April 1805, Britain and Russia signed a treaty with the aim of removing the French from the Batavian Republic (roughly present-day Netherlands) and the Swiss Confederation. Austria joined the alliance after the annexation of Genoa and the proclamation of Napoleon as King of Italy on 17 March 1805. Sweden, which had already agreed to lease Swedish Pomerania as a military base for British troops against France, entered the coalition on 9 August.
The Austrians began the war by invading Bavaria with an army of about 70,000 under Karl Mack von Leiberich, and the French army marched out from Boulogne in late July 1805 to confront them. At Ulm (25 September – 20 October) Napoleon surrounded Mack's army, forcing its surrender without significant losses. With the main Austrian army north of the Alps defeated (another army under Archduke Charles manoeuvred inconclusively against André Masséna's French army in Italy), Napoleon occupied Vienna. Far from his supply lines, he faced a larger Austro-Russian army under the command of Mikhail Kutuzov, with the Emperor Alexander I of Russia personally present. On 2 December, Napoleon crushed the Austro-Russian force in Moravia at Austerlitz (usually considered his greatest victory). He inflicted 25,000 casualties on a numerically superior enemy army while sustaining fewer than 7,000 in his own force.

Surrender of the town of Ulm, 20 October 1805
Austria signed the Treaty of Pressburg (26 December 1805) and left the coalition. The treaty required the Austrians to give up Venetia to the French-dominated Kingdom of Italy and the Tyrol to Bavaria. With the withdrawal of Austria from the war, stalemate ensued. Napoleon's army had a record of continuous unbroken victories on land, but the full force of the Russian army had not yet come into play. Napoleon had now consolidated his hold on France, had taken control of Belgium, the Netherlands, Switzerland, and most of Western Germany and northern Italy. His admirers say that Napoleon wanted to stop now, but was forced to continue in order to gain greater security from the countries that refused to accept his conquests. Esdaille rejects that explanation and instead says that it was a good time to stop expansion, for the major powers were ready to accept Napoleon as he was:
- in 1806 both Russia and Britain had been positively eager to make peace, and they might well have agreed to terms that would have left the Napoleonic imperium almost completely intact. As for Austria and Prussia, they simply wanted to be left alone. To have secured a compromise peace, then, would have been comparatively easy. But...Napoleon was prepared to make no concessions.[84]
War of the Fourth Coalition 1806–1807

Napoleon in Berlin (Meynier). After defeating Prussian forces at Jena, the French Army entered Berlin on 27 October 1806.
Within months of the collapse of the Third Coalition, the Fourth Coalition (1806–07) against France was formed by Britain, Prussia, Russia, Saxony, and Sweden. In July 1806, Napoleon formed the Confederation of the Rhine out of the many tiny German states which constituted the Rhineland and most other western parts of Germany. He amalgamated many of the smaller states into larger electorates, duchies, and kingdoms to make the governance of non-Prussian Germany smoother. Napoleon elevated the rulers of the two largest Confederation states, Saxony and Bavaria, to the status of kings.
In August 1806, the Prussian king, Frederick William III, decided to go to war independently of any other great power. The army of Russia, a Prussian ally, in particular was too far away to assist. On 8 October 1806, Napoleon unleashed all the French forces east of the Rhine into Prussia. Napoleon defeated a Prussian army at Jena (14 October 1806), and Davout defeated another at Auerstädt on the same day. 160,000 French soldiers (increasing in number as the campaign went on) attacked Prussia, moving with such speed that they destroyed the entire Prussian army as an effective military force. Out of 250,000 troops the Prussians sustained 25,000 casualties, lost a further 150,000 as prisoners, 4,000 artillery pieces, and over 100,000 muskets. At Jena, Napoleon had fought only a detachment of the Prussian force. The battle at Auerstädt involved a single French corps defeating the bulk of the Prussian army. Napoleon entered Berlin on 27 October 1806. He visited the tomb of Frederick the Great and instructed his marshals to remove their hats there, saying, "If he were alive we wouldn't be here today". Napoleon had taken only 19 days from beginning his attack on Prussia to knock it out of the war with the capture of Berlin and the destruction of its principal armies at Jena and Auerstädt. Saxony left Prussia, and together with small states from north Germany, allied with France.

Charge of the Russian Imperial Guard cavalry against French cuirassiers at the Battle of Friedland, 14 June 1807
In the next stage of the war, the French drove Russian forces out of Poland and employed many Polish and German soldiers in several sieges in Silesia and Pomerania, with the assistance of Dutch and Italian soldiers in the latter case. Napoleon then turned north to confront the remainder of the Russian army and to try to capture the temporary Prussian capital at Königsberg. A tactical draw at Eylau (7–8 February 1807), followed by capitulation at Danzig (24 May 1807) and the Battle of Heilsberg (10 June 1807), forced the Russians to withdraw further north. Napoleon decisively beat the Russian army at Friedland (14 June 1807), following which Alexander had to make peace with Napoleon at Tilsit (7 July 1807). In Germany and Poland, new Napoleonic client states, such as the Kingdom of Westphalia, Duchy of Warsaw, and Republic of Danzig, were established.
By September, Marshal Guillaume Brune completed the occupation of Swedish Pomerania, allowing the Swedish army to withdraw with all its munitions of war.
Britain's first response to Napoleon's Continental System was to launch a major naval attack against Denmark. Although ostensibly neutral, Denmark was under heavy French and Russian pressure to pledge its fleet to Napoleon. London could not take the chance of ignoring the Danish threat. In August 1807, the Royal Navy besieged and bombarded Copenhagen, leading to the
capture of the Dano-Norwegian fleet, and assuring use of the sea lanes in the North and Baltic seas for the British merchant fleet. Denmark joined the war on the side of France, but without a fleet it had little to offer,[85][86] beginning an engagement in a naval guerrilla war in which small gunboats attacking larger British ships in Danish and Norwegian waters. Denmark also committed themselves to participate in a war against Sweden together with France and Russia.
At Tilsit, Napoleon and Alexander had agreed that Russia should force Sweden to join the Continental System, which led to a Russian invasion of Finland in February 1808, followed by a Danish declaration of war in March. Napoleon also sent an auxiliary corps, consisting of troops from France, Spain and the Netherlands, led by Marshal Jean-Baptiste Bernadotte, to Denmark to participate in the invasion of Sweden. But British naval superiority prevented the armies from crossing the Øresund strait, and the war came mainly to be fought along the Swedish-Norwegian border. At the Congress of Erfurt (September–October 1808), France and Russia further agreed on the division of Sweden into two parts separated by the Gulf of Bothnia, where the eastern part became the Russian Grand Duchy of Finland. British voluntary attempts to assist Sweden with humanitarian aid remained limited and did not prevent Sweden from adopting a more Napoleon-friendly policy.[87]
The war between Denmark and Britain effectively ended with a British victory at the battle of Lyngør in 1812, involving the destruction of the last large Dano-Norwegian ship—the frigate Najaden.
Poland

Polish cavalry at the Battle of Somosierra in Spain, 1808
In 1807 Napoleon created a powerful outpost of his empire in Central Europe. Poland had recently been partitioned by its three large neighbours, but Napoleon created the Grand Duchy of Warsaw, which depended on France from the very beginning. The duchy consisted of lands seized by Austria and Prussia; its Grand Duke was Napoleon's ally the king of Saxony, but Napoleon appointed the intendants who ran the country. The population of 4.3 million was released from occupation and by 1814 sent about 200,000 men to Napoleon's armies. That included about 90,000 who marched with him to Moscow; few marched back.[88] The Russians strongly opposed any move towards an independent Poland and one reason Napoleon invaded Russia in 1812 was to punish them. The Grand Duchy was dissolved in 1815 and Poland did not become a state until 1918. Napoleon's impact on Poland was huge, including the Napoleonic legal code, the abolition of serfdom, and the introduction of modern middle class bureaucracies.[89][90]
War of the Fifth Coalition 1809

Surrender of Madrid (Gros), 1808. Napoleon enters Spain's capital during the Peninsular War.
The Fifth Coalition (1809) of Britain and Austria against France formed as Britain engaged in the Peninsular War in Spain and Portugal. The sea became a major theatre of war against Napoleon's allies. During the time of the Fifth Coalition, the Royal Navy won a succession of victories in the French colonies. On land the major battles included Battle of Raszyn, Battle of Aspern-Essling, and Battle of Wagram.
On land, the Fifth Coalition attempted few extensive military endeavours. One, the Walcheren Expedition of 1809, involved a dual effort by the British Army and the Royal Navy to relieve Austrian forces under intense French pressure. It ended in disaster after the Army commander, John Pitt, 2nd Earl of Chatham, failed to capture the objective, the naval base of French-controlled Antwerp. For the most part of the years of the Fifth Coalition, British military operations on land (apart from the Iberian Peninsula) remained restricted to hit-and-run operations executed by the Royal Navy, which dominated the sea after having beaten down almost all substantial naval opposition from France and its allies and blockading what remained of France's naval forces in heavily fortified French-controlled ports. These rapid-attack operations were aimed mostly at destroying blockaded French naval and mercantile shipping and the disruption of French supplies, communications, and military units stationed near the coasts. Often, when British allies attempted military actions within several dozen miles or so of the sea, the Royal Navy would arrive, land troops and supplies, and aid the coalition's land forces in a concerted operation. Royal Navy ships even provided artillery support against French units when fighting strayed near enough to the coastline. The ability and quality of the land forces governed these operations. For example, when operating with inexperienced guerrilla forces in Spain, the Royal Navy sometimes failed to achieve its objectives because of the lack of manpower that the Navy's guerrilla allies had promised to supply.

The European strategic situation in February 1809
Economic warfare continued: the French Continental System against the British naval blockade of French-controlled territory. Due to military shortages and lack of organisation in French territory, many breaches of the Continental System occurred as French-dominated states tolerated or even encouraged trade with British smugglers. In terms of economic damage to Great Britain, the blockade was largely ineffective. As Napoleon realised that extensive trade was going through Spain and Russia, he invaded those two countries. He tied down his forces in Spain, and lost very badly in Russia in 1812.[91]
Both sides entered further conflicts in attempts to enforce their blockade; the British fought the United States in the War of 1812 (1812–15), and the French engaged in the Peninsular War (1808–14) to prevent smuggling into Spain. The Iberian conflict began when Portugal continued trade with Britain despite French restrictions. When Spain failed to maintain the Continental System, the uneasy Spanish alliance with France ended in all but name. French troops gradually encroached on Spanish territory until they occupied Madrid, and installed a client monarchy. This provoked an explosion of popular rebellions across Spain. Heavy British involvement soon followed.

The Second of May 1808: The Charge of the Mamelukes, by Francisco de Goya (1814)
Austria, previously an ally of France, took the opportunity to attempt to restore its imperial territories in Germany as held prior to Austerlitz. Austria achieved some initial victories against the thinly spread army of Marshal Berthier. Napoleon had left Berthier with only 170,000 men to defend France's entire eastern frontier (in the 1790s, 800,000 men had carried out the same task, but holding a much shorter front).
After defeats in Spain suffered by France, Napoleon took charge and enjoyed success, retaking Madrid, defeating the Spanish and forcing a withdrawal of the heavily out-numbered British army from the Iberian Peninsula (Battle of Corunna, 16 January 1809). But when he left, the guerrilla war against his forces in the countryside continued to tie down great numbers of troops. Austria's attack prevented Napoleon from successfully wrapping up operations against British forces by necessitating his departure for Austria, and he never returned to the Peninsular theatre. The British then sent in a fresh army under Sir Arthur Wellesley (later the Duke of Wellington) whom the French could not stop.[92]
The Peninsular war proved a major disaster for France. Napoleon did well when he was in direct charge, but severe losses followed his departure, as he severely underestimated how much manpower would be needed. The effort in Spain was a drain on money, manpower and prestige. Historian David Gates called it the "Spanish ulcer."[93] France lost the Peninsular War, and Napoleon realised it had been a disaster for his cause, writing later, "That unfortunate war destroyed me ... All the circumstances of my disasters are bound up in that fatal knot."[94]
The Peninsular campaigns witnessed 60 major battles and 30 major sieges, more than any other of the Napoleonic conflicts, and lasted over six years, far longer than any of the others. France and her allies lost at least 91,000 killed in action and 237,000 wounded in the peninsula.[95]

The French Empire in Europe in 1812, near its peak extent
In the east, the Austrians drove into the Duchy of Warsaw but suffered defeat at the Battle of Raszyn on 19 April 1809. The Polish army captured West Galicia following its earlier success. Napoleon assumed personal command and bolstered the army for a counter-attack on Austria. After a few small battles, the well-run campaign forced the Austrians to withdraw from Bavaria, and Napoleon advanced into Austria. His hurried attempt to cross the Danube resulted in the major Battle of Aspern-Essling (22 May 1809) — Napoleon's first significant tactical defeat. But the Austrian commander, Archduke Charles, failed to follow up on his indecisive victory, allowing Napoleon to prepare and seize Vienna in early July. He defeated the Austrians at Wagram, on 5–6 July. (It was during the middle of that battle that Marshal Bernadotte was stripped of his command after retreating contrary to Napoleon's orders. Shortly thereafter, Bernadotte took up the offer from Sweden to fill the vacant position of Crown Prince there. Later he actively participated in wars against his former Emperor.)
The War of the Fifth Coalition ended with the Treaty of Schönbrunn (14 October 1809). In the east, only the Tyrolese rebels led by Andreas Hofer continued to fight the French-Bavarian army until finally defeated in November 1809. In the west the Peninsular War continued. The British and Portuguese remained restricted to the area around Lisbon (behind their impregnable lines of Torres Vedras) but besieged Cadiz.
In 1810, the French Empire reached its greatest extent. Napoleon married Marie-Louise, an Austrian Archduchess, with the aim of ensuring a more stable alliance with Austria and of providing the Emperor with an heir (something his first wife, Josephine, had failed to do). As well as the French Empire, Napoleon controlled the Swiss Confederation, the Confederation of the Rhine, the Duchy of Warsaw and the Kingdom of Italy. Territories allied with the French included:
- the Kingdom of Denmark
- the Kingdom of Spain (under Joseph Bonaparte, Napoleon's elder brother)
- the Kingdom of Westphalia (Jérôme Bonaparte, Napoleon's younger brother)
- the Kingdom of Naples (under Joachim Murat, husband of Napoleon's sister Caroline)
- the Principality of Lucca and Piombino (under Elisa Bonaparte (Napoleon's sister) and her husband Felice Baciocchi);
and Napoleon's former enemies, Sweden, Prussia and Austria.
Subsidiary wars
The Napoleonic Wars were the direct cause of wars in the Americas and elsewhere.
War of 1812
The War of 1812 coincided with the War of the Sixth Coalition. Historians in the United States and Canada see it as a war in its own right, while Europeans often see it as a minor theatre of the Napoleonic Wars. The United States declared war on Britain because of British interference with American merchant ships and forced enlistment into the British Royal Navy. France had interfered as well, and the US considered declaring war on France. The war ended in a military stalemate, and there were no boundary changes at the Treaty of Ghent, which took effect in early 1815 when Napoleon was on Elba.[96]
The Latin American Revolutions
The abdication of kings Carlos IV and Fernando VII of Spain and the installation of Napoleon's brother as King José provoked civil wars and revolutions leading to the independence of most of Spain's mainland American colonies. In Spanish America many local elites formed juntas and set up mechanisms to rule in the name of Ferdinand VII, whom they considered the legitimate Spanish monarch. The outbreak of the Spanish American wars of independence in most of the empire was a result of Napoleon's destabilizing actions in Spain and led to the rise of strongmen in the wake of these wars.[97]
In contrast, the Portuguese royal family escaped to Brazil and established the court there, resulting in political stability for Portuguese America. With the defeat of Napoleon and the return of the Braganza monarchy to Portugal, the heir remained in Brazil and declared Brazilian independence, achieving it peacefully with the territory intact.
The Haitian Revolution began in 1791, just before the French Revolutionary Wars, and continued until 1804. France's defeat resulted in the independence of Saint-Domingue and led Napoleon to sell the territory making up the Louisiana Purchase to the United States.[citation needed]
The Invasion of Russia 1812

The Battle of Borodino as depicted by Louis Lejeune. The battle was the largest and bloodiest single-day action of the Napoleonic Wars.
The Treaty of Tilsit in 1807 resulted in the Anglo-Russian War (1807–12). Emperor Alexander I declared war on Britain after the British attack on Denmark in September 1807. British men-of-war supported the Swedish fleet during the Finnish War and won victories over the Russians in the Gulf of Finland in July 1808 and August 1809. The success of the Russian army on land, however, forced Sweden to sign peace treaties with Russia in 1809 and with France in 1810, and to join the blockade against Britain. But Franco-Russian relations became progressively worse after 1810, and the Russian war with Britain effectively ended. In April 1812, Britain, Russia and Sweden signed secret agreements directed against Napoleon.[98]
The central issue for both Napoleon and Tsar Alexander I was control over Poland. Each wanted a semi-independent Poland he could control. As Esdaile notes, "Implicit in the idea of a Russian Poland was, of course, a war against Napoleon."[99] Schroeder says Poland was "the root cause" of Napoleon's war with Russia but Russia's refusal to support the Continental System was also a factor.[100]
In 1812, at the height of his power, Napoleon invaded Russia with a pan-European Grande Armée, consisting of 650,000 men (270,000 Frenchmen and many soldiers of allies or subject areas). The French forces crossed the Niemen River on 24 June 1812. Russia proclaimed a Patriotic War, and Napoleon proclaimed a Second Polish war. The Poles supplied almost 100,000 men for the invasion force, but against their expectations, Napoleon avoided any concessions to Poland, having in mind further negotiations with Russia.[101]
The Grande Armée marched through Russia, winning some relatively minor engagements and the major Battle of Smolensk on 16–18 August. In the same days, part of the French Army led by Marshal Nicolas Oudinot was stopped in the Battle of Polotsk by the right wing of the Russian Army, under command of General Peter Wittgenstein. This prevented the French march on the Russian capital, Saint Petersburg; the fate of the invasion was decided in Moscow, where Napoleon led his forces in person.

Napoleon's withdrawal from Russia, a painting by Adolph Northen
Russia used scorched-earth tactics, and harried the Grande Armée with light Cossack cavalry. The Grande Armée did not adjust its operational methods in response.[102] This led to most of the losses of the main column of the Grande Armée, which in one case amounted to 95,000 men, including deserters, in a week.[103]
The main Russian army retreated for almost three months. This constant retreat led to the unpopularity of Field Marshal Michael Andreas Barclay de Tolly and a veteran, Prince Mikhail Kutuzov, was made the new Commander-in-Chief by Tsar Alexander I. Finally, the two armies engaged in the Battle of Borodino on 7 September,[104] in the vicinity of Moscow. The battle was the largest and bloodiest single-day action of the Napoleonic Wars, involving more than 250,000 men and resulting in at least 70,000 casualties. It was indecisive; the French captured the main positions on the battlefield, but failed to destroy the Russian army. Logistical difficulties meant that French casualties could not be replaced, unlike Russian ones.
Napoleon entered Moscow on 14 September, after the Russian Army had retreated yet again.[105] By then, the Russians had largely evacuated the city and released criminals from the prisons to inconvenience the French; the governor, Count Fyodor Rostopchin, ordered the city to be burnt.[106] Alexander I refused to capitulate, and the peace talks attempted by Napoleon failed. In October, with no sign of clear victory in sight, Napoleon began the disastrous Great Retreat from Moscow.

Charles Joseph Minard's graph of the decreasing size of the Grande Armée represented by the width of the line as it marches to Moscow (tan) and back (black)
At the Battle of Maloyaroslavets the French tried to reach Kaluga, where they could find food and forage supplies. The replenished Russian Army blocked the road, and Napoleon was forced to retreat the same way he had come to Moscow, through the heavily ravaged areas along the Smolensk road. In the following weeks, the Grande Armée was dealt a catastrophic blow by the onset of the Russian Winter, the lack of supplies and constant guerrilla warfare by Russian peasants and irregular troops.
When the remnants of the Napoleon's army crossed the Berezina River in November, only 27,000 fit soldiers survived, with 380,000 men dead or missing and 100,000 captured.[107] Napoleon then left his men and returned to Paris to prepare the defence against the advancing Russians. The campaign effectively ended on 14 December 1812, when the last enemy troops left Russia. The Russians had lost around 210,000 men, but with their shorter supply lines, they soon replenished their armies.
War of the Sixth Coalition 1812–1814
Seeing an opportunity in Napoleon's historic defeat, Prussia, Sweden, Austria, and several German states re-entered the war.[108] Napoleon vowed that he would create a new army as large as the one he had sent into Russia, and quickly built up his forces in the east from 30,000 to 130,000 and eventually to 400,000. Napoleon inflicted 40,000 casualties on the Allies at Lützen (2 May 1813) and Bautzen (20–21 May 1813). Both battles involved forces of over 250,000, making them some of the largest conflicts of the wars so far. Metternich in November 1813 offered Napoleon the Frankfurt proposals. They would allow Napoleon to remain Emperor but France would be reduced to its "natural frontiers" and lose control of most of Italy and Germany and the Netherlands. Napoleon still expected to win the wars, and rejected the terms. By 1814, as the Allies were closing in on Paris, Napoleon did agree to the Frankfurt proposals, but it was too late and he rejected the new harsher terms proposed by the Allies.[109]

The Battle of Leipzig involved over 600,000 soldiers, making it the largest battle in Europe prior to World War I.
In the Peninsular War, Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, renewed the Anglo-Portuguese advance into Spain just after New Year in 1812, besieging and capturing the fortified towns of Ciudad Rodrigo, Badajoz, and in the Battle of Salamanca (which was a damaging defeat of the French). As the French regrouped, the Anglo–Portuguese entered Madrid and advanced towards Burgos, before retreating all the way to Portugal when renewed French concentrations threatened to trap them. As a consequence of the Salamanca campaign, the French were forced to end their long siege of Cadiz and to permanently evacuate the provinces of Andalusia and Asturias.[110]
In a strategic move, Wellesley planned to move his supply base from Lisbon to Santander. The Anglo–Portuguese forces swept northwards in late May and seized Burgos. On 21 June, at Vitoria, the combined Anglo-Portuguese and Spanish armies won against Joseph Bonaparte, finally breaking French power in Spain. The French had to retreat out of the Iberian peninsula, over the Pyrenees.[111]
The belligerents declared an armistice from 4 June 1813 (continuing until 13 August) during which time both sides attempted to recover from the loss of approximately a quarter of a million men in the preceding two months. During this time coalition negotiations finally brought Austria out in open opposition to France. Two principal Austrian armies took the field, adding 300,000 men to the coalition armies in Germany. The Allies now had around 800,000 front-line soldiers in the German theatre, with a strategic reserve of 350,000 formed to support the front-line operations.[112]

The Battle of Hanau (30–31 October 1813), took part between Austro-Bavarian and French forces.
Napoleon succeeded in bringing the imperial forces in the region to around 650,000—although only 250,000 came under his direct command, with another 120,000 under Nicolas Charles Oudinot and 30,000 under Davout. The remainder of imperial forces came mostly from the Confederation of the Rhine, especially Saxony and Bavaria. In addition, to the south, Murat's Kingdom of Naples and Eugène de Beauharnais's Kingdom of Italy had 100,000 armed men. In Spain, another 150,000 to 200,000 French troops steadily retreated before Anglo–Portuguese forces numbering around 100,000. Thus around 900,000 Frenchmen in all theatres faced around 1,800,000 coalition soldiers (including the strategic reserve under formation in Germany). The gross figures may mislead slightly, as most of the German troops fighting on the side of the French fought at best unreliably and stood on the verge of defecting to the Allies. One can reasonably say that Napoleon could count on no more than 450,000 men in Germany—which left him outnumbered about four to one.[113]
Following the end of the armistice, Napoleon seemed to have regained the initiative at Dresden (August 1813), where he once again defeated a numerically superior coalition army and inflicted enormous casualties, while sustaining relatively few. The failures of his marshals and a slow resumption of the offensive on his part cost him any advantage that this victory might have secured. At the Battle of Leipzig in Saxony (16–19 October 1813), also called the "Battle of the Nations", 191,000 French fought more than 300,000 Allies, and the defeated French had to retreat into France. After the French withdrawal from Germany, Napoleon's remaining ally, Denmark-Norway, became isolated and fell to the coalition.[114]

The Russian army enters Paris in 1814
Napoleon then fought a series of battles in France, including the Battle of Arcis-sur-Aube, but the overwhelming numbers of the Allies steadily forced him back. The Allies entered Paris on 30 March 1814. During this time Napoleon fought his Six Days' Campaign, in which he won multiple battles against the enemy forces advancing towards Paris. During this entire campaign he never managed to field more than 70,000 men against more than half a million coalition soldiers. At the Treaty of Chaumont (9 March 1814), the Allies agreed to preserve the coalition until Napoleon's total defeat.[115]
Napoleon determined to fight on, even now, incapable of fathoming his fall from power. During the campaign he had issued a decree for 900,000 fresh conscripts, but only a fraction of these materialised, and Napoleon's schemes for victory eventually gave way to the reality of his hopeless situation. Napoleon abdicated on 6 April. Occasional military actions continued in Italy, Spain, and Holland in early 1814.[116]
The victors exiled Napoleon to the island of Elba, and restored the French Bourbon monarchy in the person of Louis XVIII. They signed the Treaty of Fontainebleau (11 April 1814) and initiated the Congress of Vienna to redraw the map of Europe.[117]
War of the Seventh Coalition 1815
- See also: Hundred Days and the Neapolitan War between the Kingdom of Naples and the Austrian Empire

Wellington at Waterloo by Robert Alexander Hillingford
The Seventh Coalition (1815) pitted Britain, Russia, Prussia, Sweden, Switzerland, Austria, the Netherlands and several German states against France. The period known as the Hundred Days began after Napoleon escaped from Elba and landed at Cannes (1 March 1815). Travelling to Paris, picking up support as he went, he eventually overthrew the restored Louis XVIII. The Allies rapidly gathered their armies to meet him again. Napoleon raised 280,000 men, whom he distributed among several armies. To add to the 90,000-strong standing army, he recalled well over a quarter of a million veterans from past campaigns and issued a decree for the eventual draft of around 2.5 million new men into the French army, which was never achieved. This faced an initial coalition force of about 700,000—although coalition campaign plans provided for one million front-line soldiers, supported by around 200,000 garrison, logistics and other auxiliary personnel.
Napoleon took about 124,000 men of the Army of the North on a pre-emptive strike against the Allies in Belgium.[118] He intended to attack the coalition armies before they combined, in hope of driving the British into the sea and the Prussians out of the war. His march to the frontier achieved the surprise he had planned, catching the Anglo-Dutch Army in a dispersed arrangement. The Prussians had been more wary, concentrating 3⁄4 of their army in and around Ligny. The Prussians forced the Armée du Nord to fight all the day of the 15th to reach Ligny in a delaying action by the Prussian 1st Corps. He forced Prussia to fight at Ligny on 16 June 1815, and the defeated Prussians retreated in disorder. On the same day, the left wing of the Armée du Nord, under the command of Marshal Michel Ney, succeeded in stopping any of Wellington's forces going to aid Blücher's Prussians by fighting a blocking action at Quatre Bras. Ney failed to clear the cross-roads and Wellington reinforced the position. But with the Prussian retreat, Wellington too had to retreat. He fell back to a previously reconnoitred position on an escarpment at Mont St Jean, a few miles south of the village of Waterloo.
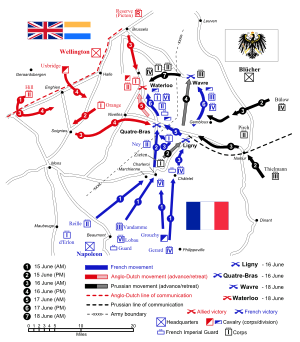
Map of the Waterloo campaign
Napoleon took the reserve of the Army of the North, and reunited his forces with those of Ney to pursue Wellington's army, after he ordered Marshal Grouchy to take the right wing of the Army of the North and stop the Prussians re-grouping. In the first of a series of miscalculations, both Grouchy and Napoleon failed to realise that the Prussian forces were already reorganised and were assembling at the village of Wavre. The French army did nothing to stop a rather leisurely retreat that took place throughout the night and into the early morning by the Prussians. As the 4th, 1st, and 2nd Prussian Corps marched through the town towards Waterloo the 3rd Prussian Corps took up blocking positions across the river, and although Grouchy engaged and defeated the Prussian rearguard under the command of Lt-Gen von Thielmann in the Battle of Wavre (18–19 June) it was 12 hours too late. In the end, 17,000 Prussians had kept 33,000 badly needed French reinforcements off the field.
Napoleon delayed the start of fighting at the Battle of Waterloo on the morning of 18 June for several hours while he waited for the ground to dry after the previous night's rain. By late afternoon, the French army had not succeeded in driving Wellington's forces from the escarpment on which they stood. When the Prussians arrived and attacked the French right flank in ever-increasing numbers, Napoleon's strategy of keeping the coalition armies divided had failed and a combined coalition general advance drove his army from the field in confusion.
Grouchy organised a successful and well-ordered retreat towards Paris, where Marshal Davout had 117,000 men ready to turn back the 116,000 men of Blücher and Wellington. Davout was defeated at the Battle of Issy and negotiations for surrender had begun.

The charge of the French Cuirassiers at the Battle of Waterloo against a square of Scottish Highlanders
On arriving at Paris three days after Waterloo, Napoleon still clung to the hope of a concerted national resistance; but the temper of the legislative chambers, and of the public generally, did not favour his view. Lacking support Napoleon abdicated again on 22 June 1815, and on 15 July he surrendered to the British squadron at Rochefort. The Allies exiled him to the remote South Atlantic island of Saint Helena, where he died on 5 May 1821.
In Italy, Joachim Murat, whom the Allies had allowed to remain King of Naples after Napoleon's initial defeat, once again allied with his brother-in-law, triggering the Neapolitan War (March to May 1815). Hoping to find support among Italian nationalists fearing the increasing influence of the Habsburgs in Italy, Murat issued the Rimini Proclamation inciting them to war. The proclamation failed and the Austrians soon crushed Murat at the Battle of Tolentino (2 May to 3 May 1815), forcing him to flee. The Bourbons returned to the throne of Naples on 20 May 1815. Murat tried to regain his throne, but after that failed, he was executed by firing squad on 13 October 1815.
Political effects
The Napoleonic Wars brought radical changes to Europe, but the reactionary forces returned to power and tried to reverse some of them[119] by restoring the Bourbon house on the French throne. Napoleon had succeeded in bringing most of Western Europe under one rule. In most European countries, subjugation in the French Empire brought with it many liberal features of the French Revolution including democracy, due process in courts, abolition of serfdom, reduction of the power of the Catholic Church, and a demand for constitutional limits on monarchs. The increasing voice of the middle classes with rising commerce and industry meant that restored European monarchs found it difficult to restore pre-revolutionary absolutism and had to retain many of the reforms enacted during Napoleon's rule. Institutional legacies remain to this day in the form of civil law, with clearly defined codes of law—an enduring legacy of the Napoleonic Code.

The national boundaries within Europe are set by the Congress of Vienna, 1815
France's constant warfare with the combined forces of the other major powers of Europe for over two decades finally took its toll. By the end of the Napoleonic Wars, France no longer held the role of the dominant power in Continental Europe, as it had since the times of Louis XIV, as the Congress of Vienna produced a "balance of power" by resizing the main powers so they could balance each other and remain at peace. In this regard, Prussia was restored in its former borders, and also received large chunks of Poland and Saxony. Greatly enlarged, Prussia became a permanent Great Power. In order to drag Prussia's attention towards the west and France, the Congress also gave the Rhineland and Westphalia to Prussia. These industrial regions transformed agrarian Prussia into an industrial leader in the nineteenth century.[120] Britain emerged as the most important economic power, and its Royal Navy held unquestioned naval superiority across the globe well into the 20th century.[121]
After the Napoleonic period, nationalism, a relatively new movement, became increasingly significant. This shaped much of the course of future European history. Its growth spelled the beginning of some states and the end of others, as the map of Europe changed dramatically in the hundred years following the Napoleonic Era. Rule by fiefdoms and aristocracy was widely replaced by national ideologies based on shared origins and culture. Bonaparte's reign over Europe sowed the seeds for the founding of the nation-states of Germany and Italy by starting the process of consolidating city-states, kingdoms and principalities. At the end of the war Denmark was forced to cede Norway to Sweden, but because Norway had signed its own constitution on 17 May 1814, Sweden was forced to fight for the right to own Norway. The resulting union between Sweden and Norway gave Norway more independence than under Denmark and ended with Norway becoming an independent country in 1905. The United Kingdom of the Netherlands created as a buffer state against France dissolved rapidly with the independence of Belgium in 1830.[122]
The Napoleonic wars also played a key role in the independence of the Latin American colonies from Spain and Portugal. The conflict weakened the authority and military power of Spain, especially after the Battle of Trafalgar. There were many uprisings in Spanish America, leading to the wars of independence. In Portuguese America, Brazil experienced greater autonomy as it now served as seat of the Portuguese Empire and ascended politically to the status of Kingdom. These events also contributed to the Portuguese Liberal Revolution in 1820 and the Independence of Brazil in 1822.[8]
The century of relative transatlantic peace, after the Congress of Vienna, enabled the “greatest intercontinental migration in human history”[123] beginning with "a big spurt of immigration after the release of the dam erected by the Napoleonic Wars."[124] Immigration inflows relative to the US population rose to record levels (peaking at 1.6% in 1850-51)[125] as 30 million Europeans relocated to the United States between 1815 and 1914.[126]
Another concept emerged from the Congress of Vienna – that of a unified Europe. After his defeat, Napoleon deplored the fact that his dream of a free and peaceful "European association" remained unaccomplished. Such a European association would share the same principles of government, system of measurement, currency and Civil Code. One-and-a-half centuries later, and after two world wars several of these ideals re-emerged in the form of the European Union.
Military legacy
Enlarged scope

In 1800 Bonaparte took the French Army across the Alps, eventually defeating the Austrians at Marengo.
Until the time of Napoleon, European states employed relatively small armies, made up of both national soldiers and mercenaries. These regulars were highly drilled professional soldiers. Ancien Régime armies could only deploy small field armies due to rudimentary staffs and comprehensive yet cumbersome logistics. Both issues combined to limit field forces to approximately 30,000 men under a single commander.
Military innovators in the mid-18th century began to recognise the potential of an entire nation at war: a "nation in arms".[127]
The scale of warfare dramatically enlarged during the Revolutionary and subsequent Napoleonic Wars. During Europe's major pre-revolutionary war, the Seven Years' War of 1756–1763, few armies ever numbered more than 200,000 with field forces often numbering less than 30,000. The French innovations of separate corps (allowing a single commander to efficiently command more than the traditional command span of 30,000 men) and living off the land (which allowed field armies to deploy more men without requiring an equal increase in supply arrangements such as depots and supply trains) allowed the French republic to field much larger armies than their opponents. Napoleon ensured during the time of the French republic that separate French field armies operated as a single army under his control, often allowing him to substantially outnumber his opponents. This forced his continental opponents to increase the size of their armies as well, moving away from the traditional small, well drilled Ancien Régime armies of the 18th century to mass conscript armies.

Napoleon on the field of Eylau
The Battle of Marengo, which largely ended the War of the Second Coalition, was fought with fewer than 60,000 men on both sides. The Battle of Austerlitz which ended the War of the Third Coalition involved fewer than 160,000 men. The Battle of Friedland which led to peace with Russia in 1807 involved about 150,000 men.
After these defeats, the continental powers developed various forms of mass conscription to allow them to face France on even terms, and the size of field armies increased rapidly. The battle of Wagram of 1809 involved 300,000 men, and 500,000 fought at Leipzig in 1813, of whom 150,000 were killed or wounded.
About a million French soldiers became casualties (wounded, invalided or killed), a higher proportion than in the First World War. The European total may have reached 5,000,000 military deaths, including disease.[128][129]
France had the second-largest population in Europe by the end of the 18th century (27 million, as compared to Britain's 12 million and Russia's 35 to 40 million).[130] It was well poised to take advantage of the levée en masse. Before Napoleon's efforts, Lazare Carnot played a large part in the reorganisation of the French army from 1793 to 1794—a time which saw previous French misfortunes reversed, with Republican armies advancing on all fronts.

Napoleon's retreat from Russia in 1812. His Grande Armée had lost about half a million men.
The French army peaked in size in the 1790s with 1.5 million Frenchmen enlisted although battlefield strength was much less. Haphazard bookkeeping, rudimentary medical support and lax recruitment standards ensured that many soldiers either never existed, fell ill or were unable to withstand the physical demands of soldiering.
About 2.8 million Frenchmen fought on land and about 150,000 at sea, bringing the total for France to almost 3 million combatants during almost 25 years of warfare.[23]

The Battle of Trafalgar
Britain had 750,000 men under arms between 1792 and 1815 as its army expanded from 40,000 men in 1793[131] to a peak of 250,000 men in 1813.[20] Over 250,000 sailors served in the Royal Navy. In September 1812, Russia had 900,000 enlisted men in its land forces, and between 1799 and 1815 2.1 million men served in its army. Another 200,000 served in the Russian Navy. Out of the 900,000 men, the field armies deployed against France numbered less than 250,000.
There are no consistent statistics for other major combatants. Austria's forces peaked at about 576,000 (during the War of the Sixth Coalition) and had little or no naval component yet never fielded more than 250,000 men in field armies. After Britain, Austria proved the most persistent enemy of France; more than a million Austrians served during the long wars. Its large army was overall quite homogeneous and solid and in 1813 operated in Germany (140,000 men), Italy and the Balkans (90,000 men at its peak, about 50,000 men during most of the campaigning on these fronts). Austria's manpower was becoming quite limited towards the end of the wars, leading its generals to favour cautious and conservative strategies, to limit their losses.

French soldiers in skirmish with Bashkirs and Cossacks in 1813
Prussia never had more than 320,000 men under arms at any time. In 1813–1815, the core of its army (about 100,000 men) was characterised by competence and determination, but the bulk of its forces consisted of second- and third-line troops, as well as militiamen of variable strength. Many of these troops performed reasonably well and often displayed considerable bravery but lacked the professionalism of their regular counterparts and were not as well equipped. Others were largely unfit for operations, except sieges. During the 1813 campaign, 130,000 men were used in the military operations, with 100,000 effectively participating in the main German campaign, and about 30,000 being used to besiege isolated French garrisons.[132]
Spain's armies also peaked at around 200,000 men, not including more than 50,000 guerrillas scattered over Spain. In addition the Maratha Confederation, the Ottoman Empire, Italy, Naples and the Duchy of Warsaw each had more than 100,000 men under arms. Even small nations now had armies rivalling the size of the Great Powers' forces of past wars but most of these were poor quality forces only suitable for garrison duties. The size of their combat forces remained modest yet they could still provide a welcome addition to the major powers. The percentage of French troops in the Grande Armee which Napoleon led into Russia was about 50% while the French allies also provided a significant contribution to the French forces in Spain. As these small nations joined the coalition forces in 1813–1814, they provided a useful addition to the coalition while depriving Napoleon of much needed manpower.
Innovations
The initial stages of the Industrial Revolution had much to do with larger military forces—it became easy to mass-produce weapons and thus to equip larger forces. Britain was the largest single manufacturer of armaments in this period. It supplied most of the weapons used by the coalition powers throughout the conflicts. France produced the second-largest total of armaments, equipping its own huge forces as well as those of the Confederation of the Rhine and other allies.[133]
Napoleon showed innovative tendencies in his use of mobility to offset numerical disadvantages, as demonstrated in the rout of the Austro-Russian forces in 1805 in the Battle of Austerlitz. The French Army redefined the role of artillery, forming independent, mobile units, as opposed to the previous tradition of attaching artillery pieces in support of troops.[134]
The semaphore system had allowed the French War-Minister, Carnot, to communicate with French forces on the frontiers throughout the 1790s. The French continued to use this system throughout the Napoleonic wars. Aerial surveillance was used for the first time when the French used a hot-air balloon to survey coalition positions before the Battle of Fleurus, on 26 June 1794.[39]
Total war

Goya's The Disasters of War, showing French atrocities against Spanish civilians
Historians have explored how the Napoleonic wars became total wars. Most historians argue that the escalation in size and scope came from two sources. First was the ideological clash between revolutionary/egalitarian and conservative/hierarchical belief systems. Second was the emerging nationalism in France, Germany, Spain, and elsewhere that made these "people's wars" instead of contests between monarchs.[135] Bell has argued that even more important than ideology and nationalism were the intellectual transformations in the culture of war that came about through the Enlightenment.[136] One factor, he says, is that war was no longer a routine event but a transforming experience for societies—a total experience. Secondly the military emerged in its own right as a separate sphere of society distinct from the ordinary civilian world. The French Revolution made every civilian a part of the war machine, either as a soldier through universal conscription, or as a vital cog in the home front machinery supporting and supplying the army. Out of that, says Bell, came "militarism," the belief that the military role was morally superior to the civilian role in times of great national crisis. The fighting army represented the essence of the nation's soul.[137] As Napoleon proclaimed, "It is the soldier who founds a Republic and it is the soldier who maintains it."[138]
In fiction
See also
- British Army during the Napoleonic Wars
- Coalition forces of the Napoleonic Wars
- Haitian Revolution
- Imperial and Royal Army during the Napoleonic Wars
International relations, 1648–1814, for diplomacy- List of Napoleonic battles
- Royal Prussian Army of the Napoleonic Wars
- Spanish American wars of independence
- Uniforms of La Grande Armée
- War of 1812
- World war
Notes
^ Hanover was in a Personal Union with Great Britain
^ ab The term "Austrian Empire" came into use after Napoleon crowned himself Emperor of the French in 1804, whereby Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor took the title Emperor of Austria (Kaiser von Österreich) in response. The Holy Roman Empire was dissolved in 1806, and consequently "Emperor of Austria" became Francis' primary title. For this reason, "Austrian Empire" is often used instead of "Holy Roman Empire" for brevity's sake when speaking of the Napoleonic Wars, even though the two entities are not synonymous.
^ abc Both Austria and Prussia briefly became allies of France and contributed forces to the French Invasion of Russia in 1812.
^ ab Russia became an ally of France following the Treaty of Tilsit in 1807. The alliance broke down in 1810, which led to the French invasion in 1812. During that time Russia waged war against Sweden (1808–1809) and the Ottoman Empire (1806–1812), and nominally against Britain (1807–1812).
^ ab Nominally, Sweden declared war against Great Britain after its defeat by Russia in the Finnish War (1808–1809).
^ abc Spain was an ally of France until a stealthy French invasion in 1808, then fought France in the Peninsular War.
^ ab The Ottoman Empire fought against Napoleon in the French Campaign in Egypt and Syria as part of the French Revolutionary Wars. During the Napoleonic era of 1803 to 1815, the Empire participated in two wars against the Allies: against Britain in the Anglo-Turkish War (1807–1809) and against Russia in the Russo-Turkish War (1806–1812). Russia was allied with Napoleon 1807–1810.
^ ab Qajar dynasty fought against Russia from 1804 to 1813; the Russians were allied with Napoleon 1807–1812.
^ Sicily remained in personal union with Naples until Naples became a French client-republic following the Battle of Campo Tenese in 1806.
^ The Kingdom of Hungary participated in the war with separate Hungarian regiments[1][2] in the Imperial and Royal Army, and also by a traditional army ("insurrectio").[3] The Hungarian Diet voted to join in war and agreed to pay one third of the war expenses.
^ ab Napoleon established the Duchy of Warsaw, ruled by the Kingdom of Saxony in 1807. Polish Legions had already been serving in the French armies beforehand.
^ The French Empire annexed the Kingdom of Holland in 1810. Dutch troops fought against Napoleon during the Hundred Days in 1815.
^ The French Empire annexed the Kingdom of Etruria in 1807.
^ The Kingdom of Naples, briefly allied with Austria in 1814, allied with France again and fought against Austria during the Neapolitan War in 1815.
^ Sixteen of France's allies among the German states (including Bavaria and Württemberg) established the Confederation of the Rhine in July 1806 following the Battle of Austerlitz (December 1805). Following the Battle of Jena-Auerstedt (October 1806), various other German states that had previously fought alongside the anti-French allies, including Saxony and Westphalia, also allied with France and joined the Confederation. Saxony changed sides again in 1813 during the Battle of Leipzig, causing most other member-states to quickly follow suit and declare war on France.
^ These four states[which?] were the leading nations of the Confederation, but the Confederation was made up of a total of 43 principalities, kingdoms, and duchies.
^ Denmark-Norway remained neutral until the Battle of Copenhagen (1807). Denmark was compelled to cede Norway to Sweden by the Treaty of Kiel in 1814. Following a brief Swedish campaign against Norway, Norway entered a personal union with Sweden.
^ £3 trillion in modern economic cost terms.[75]
References
^ James R. Arnold: Napoleon Conquers Austria: The 1809 Campaign for Vienna, ABC-Clio, 2003 [1]
^ The Austrian Imperial-Royal Army (Kaiserliche-Königliche Heer) 1805 – 1809:
The Hungarian Royal Army [2]
^ Todd Fisher: The Napoleonic Wars: The Empires Fight Back 1808–1812, Oshray Publishing, 2001 [3]
^ John Sainsbury (1842). Sketch of the Napoleon Museum. London. p. 15..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Reich 1905, p. 622
^ "Denmark". World Statesmen. Retrieved 18 January 2015.
^ "Norway". World Statesmen. Retrieved 18 January 2015.
^ abc Benjamin Keen and Keith Haynes, A History of Latin America (2012) ch 8
^ Schäfer, Anton (2002). Zeittafel der Rechtsgeschichte. Von den Anfängen über Rom bis 1919. Mit Schwerpunkt Österreich und zeitgenössischen Bezügen (in German) (3 ed.). Edition Europa Verlag. ISBN 3-9500616-8-1. p. 137
^ Edward et al., pp. 522-524
^ "De Grondwet van 1815". Parlement & Politiek (in Dutch). Retrieved 26 June 2014.
^ "The Royal Navy". Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 15 February 2016.
^ "The Rise of Prussia 1700-1830".
^ Collier, Martin (2003). Italian unification, 1820–71. Heinemann Advanced History (First ed.). Oxford: Heinemann. p. 2. ISBN 0-435-32754-2.The Risorgimento is the name given to the process that ended with the political unification of Italy in 1871
^ Riall, Lucy (1994). The Italian Risorgimento: state, society, and national unification (First ed.). London: Routledge. p. 1. ISBN 0-203-41234-6.The functional importance of the Risorgimento to both Italian politics and Italian historiography has made this short period (1815–60) one of the most contested and controversial in modern Italian history
^ Jakob Walter, and Marc Raeff. The diary of a Napoleonic foot soldier. Princeton, N.J., 1996.
^ Martyn Lyons p. 234–36
^ Payne 1973, pp. 432–433.
^ Esdaile 2008, p. [page needed].
^ ab Chandler & Beckett, p. 132
^ Blücher, scourge of Napoleon, Leggiere
^ Riehn 1991, p. 50.
^ ab John France (2011). Perilous Glory: The Rise of Western Military Power. Yale UP. p. 351.
^ Correspondance générale - Tome 12: La campagne de Russie, 1812 Par Fondation Napoléon - https://books.google.com/books/about/Correspondance_g%C3%A9n%C3%A9rale_Tome_12.html?id=toua1U8uORQC&redir_esc=y
^ ab White 2014, Napoleonic Wars cites Urlanis 1971
^ Canales 2004.
^ White 2014 cites Payne
^ ab White 2014 cites Dumas 1923 citing Hodge
^ abc White 2014 cites Danzer
^ White 2014 cites Clodfelter
^ White 2014 cites Bodart 1916
^ abc Philo 2010.
^ ab Jones, Colin. The Cambridge Illustrated History of France (1st ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 193–194. ISBN 0-521-43294-4.
^ abc Frederick Kagan, The End of the Old Order: Napoleon and Europe, 1801-1805 (2007) pp 42-43
^ "The Rise of Prussia 1700-1830".
^ Ferguson, Niall (2004). Empire, The rise and demise of the British world order and the lessons for global power. Basic Books. ISBN 0-465-02328-2.
^ Bell, David Avrom (2007). The First Total War: Napoleon's Europe and the birth of warfare as we know it. New York: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. p. 51. ISBN 0-618-34965-0.
^ Geoffrey Wawro (2002). Warfare and Society in Europe, 1792–1914. Routledge. p. 9.
^ ab R. R. Palmer (1941). Twelve Who Ruled: The Year of the Terror in the French Revolution. Princeton UP. pp. 81–83.
^ Boot, Max (2013). Invisible Armies: An Epic History of Guerrilla Warfare from Ancient Times to the Present. Liveright. pp. 10–11, 55. ISBN 978-0-87140-424-4.
^ Dmitry Shlapentokh, The French Revolution and the Russian Anti-Democratic Tradition (Edison, NJ: Transaction Publishers, 1997), p. 220-8
^ Palmer, R.R. & Colton, Joel A History of the Modern World p. 361
^ Suzanne Desan et al. eds. The French Revolution in Global Perspective (2013), pp. 3, 8, 10
^ Frank McLynn, Napoleon (1998). p 215.
^ Spencer C. Tucker (2012). The Encyclopedia of the War Of 1812. ABC-CLIO. p. 499.
^ Arthur H. Buffinton, The Second Hundred Years' War, 1689–1815 (1929). See also: Francois Crouzet, "The Second Hundred Years War: Some Reflections". French History 10 (1996), pp. 432–450. and H. M. Scott, "Review: The Second 'Hundred Years War' 1689–1815". The Historical Journal 35 (1992), pp. 443–469.
^ Rapport, Mike (2013). The Napoleonic Wars: A Very Short Introduction. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 4. ISBN 9780191642517. Retrieved 29 May 2016.
^ France - Les guerres de la Révolution et de l'Empire. Herodote.net. Retrieved on 12 July 2013.
^ Rabich, Adalbert (2011). "erster+napoleonischer+krieg"&hl=en Die Regionalgeschichte von Dülmen und Umgebung, Teil 2 (in German). Norderstedt: GRIN Verlag. p. 37. ISBN 9783640805846. Retrieved 29 May 2016.
^ (in Dutch) Encarta-encyclopedie Winkler Prins (1993–2002) s.v. "coalitieoorlogen". Microsoft Corporation/Het Spectrum.
^ Chandler, David (1966). The Campaigns of Napoleon. The Mind and Method of History's Greatest Soldier. New York: Macmillan.
^ Sutherland, Donald M. G. (2008). The French Revolution and Empire: The Quest for a Civic Order. Wiley. p. 356.
^ McConachy, Bruce (2001). "The Roots of Artillery Doctrine: Napoleonic Artillery Tactics Reconsidered". Journal of Military History. 65 (3): 617–640. JSTOR 2677528. McConachy rejects the alternative theory that growing reliance on artillery by the French army beginning in 1807 was an outgrowth of the declining quality of the French infantry and, later, France's inferiority in cavalry numbers.
^ abcdefghi Annual Register... for the Year 1803 (1805)
^ Haine, Scott. The History of France (1st ed.). Greenwood Press. p. 92. ISBN 0-313-30328-2.
^ Mahan, A.T. The influence of sea power on the French Revolution and Empire Vol. II (1892) pp. 106-107
^ Andrew Roberts, Napoleon: A Life (2014) p 316
^ Roberts, Napoleon: A Life (2014) p 309
^ John D. Grainger, Amiens Truce: Britain & Bonaparte, 1801-1803 (2004) has a well-balanced analysis of both sides
^ Arthur Bryant, Years of victory: 1802-1812 (1944), pp 1-52, although older, is a well-regarded interpretation from the British perspective
^ Kagan, The End of the Old Order: Napoleon and Europe, 1801-1805 (2007) pp 1-50 stresses Napoleon's initiatives.
^ Paul Schroeder, The Transformation of European politics 1763-1848 (1994) pp 231-45 is highly analytical and hostile to Napoleon
^ Jean Tulard, Napoleon: The Myth of the Saviour (1984) p 351.
^ Colin S. Gray (2007). War, Peace and International Relations: An Introduction to Strategic History. Routledge. p. 47.
^ Robin Neillands (2003). Wellington & Napoleon: Clash of Arms. Pen and Sword. p. 22.
^ Alistair Horne in Robert Cowley, ed. (2000). What If?: The World's Foremost Historians Imagine What Might Have Been. Penguin. p. 161.CS1 maint: Extra text: authors list (link)
^ Steve Chan (2013). Looking for Balance: China, the United States, and Power Balancing in East Asia. Stanford UP. p. 55.
^ Martin Malia (2008). History's Locomotives: Revolutions and the Making of the Modern World. Yale UP. p. 205.
^ "The Annual Register, Or, A View of the History, Politics, and Literature for ..."
^ Schroeder, The Transformation of European Politics 1763–1848 (1994) pp 307–10
^ ab Paul Kennedy, The Rise and Fall of the Great Powers – economic change and military conflict from 1500 to 2000 (1989), pp. 128–9
^ John M. Sherwig, Guineas and Gunpowder British Foreign Aid in the War with France, 1793–1815 (1969)
^ Alan Palmer, Alexander I (1974) p 86
^ Asa Briggs, The Making of Modern England 1783–1867: The Age of Improvement (1959) p 143
^ "Measuring Worth - Purchase Power of the Pound". Archived from the original on 1 June 2016. Retrieved 15 February 2016.
^ Élie Halévy, A History of the English People in 1815 (1924) vol 2 p 205–28
^ Roger Knight, Britain Against Napoleon: The Organisation of Victory, 1793–1815 (2013)
^ J. Steven Watson, The Reign of George III 1760–1815 (1960), 374-77, 406-7, 463-71,
^ "Auguste Mayer's picture as described by the website of the Musée national de la Marine (in French)". Musee-marine.fr. Archived from the original on 26 May 2010. Retrieved 21 May 2011.
^ Paul W. Schroeder, The Transformation of European Politics 1763–1848 (1994) pp 231–86
^ Frederick Kagan (2007). The End of the Old Order: Napoleon and Europe, 1801–1805. Da Capo Press. pp. 141ff.
^ "Invasion of Britain – National Maritime Museum". Nmm.ac.uk. Retrieved 21 May 2011.
^ "O'Meara's account of Napoleon on the invasion of the England". Napoleon.org. Retrieved 21 May 2011.
^ Esdaille, Napoleon's Wars, pp 252-53
^ A. N. Ryan, "The Causes of the British Attack upon Copenhagen in 1807." English Historical Review (1953): 37-55. in JSTOR
^ Thomas Munch-Petersen, Defying Napoleon: How Britain Bombarded Copenhagen and Seized the Danish Fleet in 1807 (2007)
^ Norbert Götz. “The Good Plumpuddings’ Belief: British Voluntary Aid to Sweden During the Napoleonic Wars.” International History Review 37 (2015) 3: 519–539.
^ Otto Pivka (2012). Napoleon's Polish Troops. Osprey Publishing. pp. 8–10.
^ J. P. Riley, Napoleon and the World War of 1813: Lessons in Coalition Warfighting (2000) pp 27–8.
^ Alexander Grab, Napoleon and the Transformation of Europe (2003) pp 176–87
^ J. M. Thompson, Napoleon Bonaparte: His rise and fall (1951) pp 235-40
^ Gregory Fremont-Barnes, The Napoleonic Wars (3): The Peninsular War 1807-1814 (2014)
^ David Gates, The Spanish Ulcer: A History of the Peninsular War (1986)
^ John Lawrence Tone, "Partisan Warfare in Spain and Total War," in Roger Chickering and Stig Förster, eds. (2010). War in an Age of Revolution, 1775–1815. Cambridge UP. p. 243.CS1 maint: Extra text: authors list (link)
^ Warfare and Armed Conflicts: A Statistical Encyclopedia of Casualty and Other Figures, 1492-2015. p. 157.
^ Jeremy Black, The War of 1812 in the Age of Napoleon (2009)
^ John Lynch, Caudillos in Spanish America 1800-1850. Oxford: Clarendon Press 1992, pp. 402–403.
^ Alan Palmer, Alexander I: Tsar of War and Peace (1974)
^ Charles Esdaile, Napoleon's Wars: An International History, 1803–1815 (2007) p 438
^ Schroeder, The Transformation of European Politics: 1763 – 1848 (1994) p 419
^ Riehn, Richard =K. (1990), 1812: Napoleon's Russian campaign
^ Riehn 1990, pp. 138–140.
^ Reihn 1990, p. 185.
^ Philip Haythornthwaite, Borodino 1812; Napoleon's great gamble (2012).
^ Reihn, 1812, pp. 253–254
^ With Napoleon in Russia, The Memoirs of General Coulaincourt, Chapter VI 'The Fire' pp. 109–107 Pub. William Morrow and Co 1945
^ The Wordsworth Pocket Encyclopedia, page 17, Hertfordshire 1993
^ Philip Dwyer, Citizen Emperor: Napoleon in Power (2013), pp 431-74
^ J. P. Riley (2013). Napoleon and the World War of 1813: Lessons in Coalition Warfighting. Routledge. p. 206.
^ Peter Young and James Philip Lawford, Wellington's masterpiece: the battle and campaign of Salamanca (outledge, 2015).
^ Michael Glover, Wellington's Peninsular Victories: Busaco, Salamanca, Vitoria, Nivelle (1963).
^ J. P. Riley (2013). Napoleon and the World War of 1813: Lessons in Coalition Warfighting. Routledge. p. 206.
^ J. P. Riley (2013). Napoleon and the World War of 1813: Lessons in Coalition Warfighting. Routledge. p. 206.
^ Peter Hofschroer, Leipzig 1813: The Battle of the Nations (1993)
^ Philip Dwyer, Citizen Emperor: Napoleon In Power (2013) pp 464-98
^ Philip Dwyer, Citizen Emperor: Napoleon In Power (2013) pp 464-98
^ Philip Dwyer, Citizen Emperor: Napoleon In Power (2013) pp 464-98
^ Peter Hofschroer, The Waterloo Campaign: Wellington, His German Allies and the Battles of Ligny and Quatre Bras (2006)
^ Jacques Godechot, et al. The Napoleonic era in Europe (1971)
^ "The Rise of Prussia 1700-1830".
^ "The Royal Navy". Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 15 February 2016.
^ "Les Transformations des Universités du Xiiie Au Xxie Siècle".
^ Drew Keeling, “The Transportation Revolution and Transatlantic Migration," Research in Economic History 19 (1999), p. 39.
^ Franklin D. Scott, The Peopling of America: Perspectives of Immigration (1984), p. 24. Marcus Hansen, The Atlantic Migration (1940), pp. 79-106, termed this a "new beginning" for American immigration. For further background context, see "North Atlantic, 1815-19". Migration as a travel business. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
^ Drew Keeling, “Transport Capacity Management and Transatlantic Migration, 1900-1914." Research in Economic History 25 (2008), pp. 267-68.
^ Maldwyn Jones, American Immigration (1992, 2nd ed.)‚ p. 79. Jones referred to this unprecedented migration as “one of the wonders of the age” (p. 78).
^ "Napoleon's Total War". HistoryNet.com. Archived from the original on 1 April 2008. Retrieved 18 November 2008.
^ David A.Bell, The First Total War: Napoleon's Europe and the Birth of Warfare as We Know It (2007) p 7
^ Paul Kennedy, The Rise and Fall of the Great Powers Economic Change and Military Conflict from 1500 to 2000 (1987) pp 99–100
^ Colin McEvedy and Richard M. Jones, Atlas of World Population History (1978) pp 41–222
^ Chappell, p. 8
^ Blücher, scourge of Napoleon, Leggiere
^ Christopher David Hall (1992). British Strategy in the Napoleonic War, 1803–15. Manchester U.P. p. 28.
^ Geoffrey Wawro (2002). Warfare and Society in Europe, 1792–1914. Routledge. p. 9.
^ Donald Stoker; et al. (2008). Conscription in the Napoleonic Era: A Revolution in Military Affairs?. Routledge. pp. 24, 31–32, 38.
^ Bell, The First Total War (2008) pp 7–13
^ Many historians say it was not the "first" total war; for a critique of Bell see Frederick C. Schneid (2012). Napoleonic Wars. Potomac Books. p. 1802.
^ Robert Harvey (2013). The War of Wars. Constable & Robinson. p. 328.
Sources
Canales, Esteban (2004), 1808–1814: demografía y guerra en España (PDF) (in Spanish), Autonomous University of Barcelona, retrieved 3 May 2017
Philo, Tom (2010), Military and Civilian War Related Deaths Through the Ages, archived from the original on 20 April 2010
[unreliable source][better source needed]
Riehn, Richard K. (1991), 1812: Napoleon's Russian Campaign (Paperback ed.), New York: Wiley, ISBN 978-0471543022
White, Matthew (2014), Statistics of Wars, Oppressions and Atrocities of the Nineteenth Century, retrieved 3 May 2017. This source references:
Bodart, Gaston (1916), Losses of Life in Modern Wars
Dumas, Samuel (1923), Losses of Life Caused By War
Urlanis, Boris (1971), Wars and Population
Payne, Stanley G., A History of Spain and Portugal, 2
Danzer, Arme-Zeitun (in German)
Clodfelter, Michael, Warfare and Armed Conflict: A Statistical Reference to Casualty and Other Figures, 1618–1991
Further reading
General and reference books
- Bell, David A. The First Total War: Napoleon's Europe and the Birth of Warfare as We Know It (2008) excerpt and text search
- Bruun, Geoffrey. Europe and the French Imperium, 1799-1814 (1938) online, political and diplomatic context
- Bruce, Robert B. et al. Fighting Techniques of the Napoleonic Age 1792–1815: Equipment, Combat Skills, and Tactics (2008) excerpt and text search
Dupuy, Trevor N. and Dupuy, R. Ernest. The Encyclopedia of Military History (2nd ed. 1970) pp 730–770- Esdaile, Charles. Napoleon's Wars: An International History, 1803–1815 (2008); 645pp excerpt and text search a standard scholarly history
- Gates, David. The Napoleonic Wars 1803-1815 (NY: Random House, 2011)
Godechot, Jacques; Béatrice Fry Hyslop; David Lloyd Dowd; et al. (1971). The Napoleonic era in Europe. Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
Harvey, Robert (2013). The War of Wars. Constable & Robinson. p. 328., well-written popular survey of these wars- Linch, Kevin. Desertion from the British Army during Napoleonic Wars:Journal of Social History, Volume 49 Number 4 (2016) pp 808–828
Pope, Stephen (1999). The Cassel Dictionary of the Napoleonic Wars. Cassel. ISBN 0-304-35229-2.
- Rapport, Mike. The Napoleonic Wars: A Very Short Introduction (Oxford UP, 2013)
- Richardson, Hubert N. B. A Dictionary of Napoleon and His Times (1920) online free 489pp
- Ross, Steven T. European Diplomatic History, 1789–1815: France Against Europe (1969)
- Ross, Steven T. The A to Z of the Wars of the French Revolution (Rowman & Littlefield, 2010); 1st edition was Historical dictionary of the wars of the French Revolution (Scarecrow Press, 1998)
Rothenberg, Gunther E. (1988). "The Origins, Causes, and Extension of the Wars of the French Revolution and Napoleon". Journal of Interdisciplinary History. 18 (4): 771–793. JSTOR 204824.
- Rothenberg, E. Gunther. The Art of Warfare in the Age of Napoleon (1977)
Schneid, Frederick C. (2011). The French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. Mainz: Institute of European History.
- Schneid, Frederick C. Napoleon's Conquest of Europe: The War of the Third Coalition (2005) excerpt and text search
- Schneid, Frederick C. Napoleonic Wars: The Essential Bibliography (2012) excerpt and text search 121 pp. online review in H-FRANCE
- Schroeder, Paul W. The Transformation of European Politics 1763–1848 (1994) 920pp; online; advanced analysis of diplomacy
- Smith, Digby George. The Greenhill Napoleonic Wars Data Book: Actions and Losses in Personnel, Colours, Standards and Artillery (1998)
- Stirk, Peter. "The concept of military occupation in the era of the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars." Comparative Legal History 3#1 (2015): 60-84.
Napoleon and French
- Chandler, David G. The Campaigns of Napoleon (1973) 1172 pp; a detailed guide to all major battles excerpt and text search
- Chandler, David G., ed. Napoleon's Marshals (1987) short scholarly biographies
- Dwyer, Philip. Napoleon: The Path to Power (2008) excerpt vol 1; Citizen Emperor: Napoleon in Power (2013) excerpt and text search v 2; most recent scholarly biography
- Elting, John R. Swords Around a Throne: Napoleon's Grand Armee (1988).
- Forrest, Alan I. Napoleon's Men: The Soldiers of the Empire Revolution and Empire (2002).
- Forrest, Alan. Conscripts and Deserters: The Army and French Society during Revolution and the Empire (1989) excerpt and text search
- Gallaher, John G. Napoleon’s Enfant Terrible: General Dominique Vandamme (2008). excerpt
- Griffith, Paddy. The Art of War of Revolutionary France, 1789–1802 (1998) excerpt and text search
- Haythornthwaite, Philip J. Napoleon's Military Machine (1995) excerpt and text search
- Hazen, Charles Downer. The French Revolution and Napoleon (1917) online free
- Kagan, Frederick W. The End of the Old Order: Napoleon and Europe, 1801-1805 (2007)
- McLynn, Frank. Napoleon: A Biography (1997)
- Nester, William R. Napoleon and the Art of Diplomacy: How War and Hubris Determined the Rise and Fall of the French Empire (2011). excerpt
- Parker, Harold T. "Why Did Napoleon Invade Russia? A Study in Motivation and the Interrelations of Personality and Social Structure," Journal of Military History (1990) 54#2 pp 131–46 in JSTOR.
- Riley, Jonathon P. Napoleon as a General (Hambledon Press, 2007)
- Roberts, Andrew. Napoleon: A Life (2014) Major new biography by a leading British Historian
British, Austrian, Prussian & Russian roles
- Andress, David. The Savage Storm: Britain on the Brink in the Age of Napoleon (2013), emphasises turmoil inside Britain & impact on military
- Bamford, Andrew. Sickness, Suffering, and the Sword: The British Regiment on Campaign, 1808-1815 (2013). excerpt
- Black, Jeremy. "British Strategy and the Struggle with France 1793–1815." Journal of Strategic Studies 31#4 (2008): 553-569.
- Bryant, Arthur. Years of Endurance 1793–1802 (1942); and Years of Victory, 1802–1812 (1944) well-written surveys of the British story
- Christie, Ian R. Wars and Revolutions Britain, 1760–1815 (1982)
- Cookson, J. E. The British Armed Nation 1793–1815 (1997) DOI:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198206583.001.0001 online
- Davey, James. In Nelson's Wake: The Navy and the Napoleonic Wars (2016).
- Ehrman, John. The Younger Pitt: The Consuming Struggle (Volume 3) (1996)
- Esdaile, Charles J. "The British Army in the Napoleonic Wars: Approaches Old and New." English Historical Review 130#542 (2015): 123-137.
- Glover, Richard. Peninsular Preparation: The Reform of the British Army 1795–1809 (1963) excerpt and text search
- Hall, Christopher D. British Strategy in the Napoleonic War, 1803–15 (1992)
- Haythornthwaite, Philip J. Wellington's Military Machine, 1792–1815 (1989)
- Haythornthwaite, Philip J. The Russian Army of the Napoleonic Wars (1987) vol 1: Infantry 1799–1814; vol 2: Cavalry, 1799–1814
- Knight, Roger. Britain Against Napoleon: The Organization Of Victory; 1793-1815 (2013); 710pp
- Lavery, Brian. Nelson's Navy: The Ships, Men, and Organization, 1793–1815 (2nd ed. 2012)
- Leggiere, Michael V. Blücher: Scourge of Napoleon (2014). excerpt
- Lieven, D. C. "Russia and the Defeat of Napoleon (1812–14)," Kritika: Explorations in Russian and Eurasian History (2006) 7#2 pp 283–308.
- Linch, Kevin, and Matthew McCormack. "Wellington's Men: The British Soldier of the Napoleonic Wars" History Compass (2015) 13#6 pp 288–296.
- Muir, Rory. Britain and the Defeat of Napoleon: 1807–1815 (1996)
- Muir, Rory. Wellington: The Path to Victory 1769–1814 (2013) vol 1 of two-volume scholarly biography excerpt and text search
- Nester, William R. Titan: The Art of British Power in the Age of Revolution and Napoleon (2016)
- Robson, Martin. A History of the Royal Navy: The Napoleonic Wars I. B. Tauris, 20140 256pp.
- Rothenberg, Gunther E. Napoleon's Great Adversaries: The Archduke Charles and the Austrian Army 1792–1814 (1982)
- Schneid, Frederick C. ed. European Armies of the French Revolution, 1789–1802 (2015) Nine essays by leading scholars.
- Uglow, Jenny. In These Times: Living in Britain Through Napoleon's Wars, 1793-1815 (2015) 752pp excerpt
- Willis, Sam. In the Hour of Victory: The Royal Navy at War in the Age of Nelson (2013) Excerpt and text search
Historiography and memory
- Esdaile, Charles. "The Napoleonic Period: Some Thoughts on Recent Historiography," European History Quarterly, (1993) 23: 415–32 online
- Forrest, Alan et al. eds. War Memories: The Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars in Modern European Culture (2013)
- Hyatt, Albert M.J. "The Origins of Napoleonic Warfare: A Survey of Interpretations." Military Affairs (1966) 30#4 pp 177–185.
- Lieven, D. C. "Russia and the Defeat of Napoleon (1812–14)." Kritika: Explorations in Russian and Eurasian History (2006) 7#2 pp 283–308.
- Linch, Kevin. "War Memories: The Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars in Modern European Culture." Social History 40#2 (2015): 253-254.
- Martin, Jean-Clément. "War Memories. The Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars in Modern European Culture." Annales Historiques De La Revolution Francaise. (2015) No. 381.
Messenger, Charles, ed. (2001). Reader's Guide to Military History. Routledge. pp. 391–427.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: Extra text: authors list (link) evaluation of the major books on Napoleon and his wars published by 2001.
Mikaberidze, Alexander. "Recent Trends in the Russian Historiography of the Napoleonic Wars," Journal of Military History (2010) 74#1 pp 189–194.
Primary sources
- Dwyer, Philip G. "Public remembering, private reminiscing: French military memoirs and the revolutionary and Napoleonic wars," French Historical Studies (2010) 33#2 pp. 231–258 online
- Kennedy, Catriona. Narratives of the Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars: Military and Civilian Experience in Britain and Ireland (Palgrave Macmillan, 2013)
- Leighton, James. Witnessing the Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars in German Central Europe (2013), diaries, letters and accounts by civilians Online review
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Napoleonic Wars. |
| Wikivoyage has travel information for Napoleonic Wars. |
 Texts on Wikisource:
Texts on Wikisource:
Beck, Archibald Frank (1911). "Waterloo Campaign". Encyclopædia Britannica. 28 (11th ed.). pp. 371–381.
Maude, Frederic Natusch (1911). "Napoleonic Campaigns". Encyclopædia Britannica. 19 (11th ed.). pp. 212–236.
Robinson, Charles Walker (1911). "Peninsular War". Encyclopædia Britannica. 21 (11th ed.). pp. 90–98.
Rose, John Holland (1911). "Napoleon I.". Encyclopædia Britannica. 19 (11th ed.). pp. 190–211.
- The Legend of Bonaparte
- The Napoleonic Wars Exhibition held by The European Library
- 15th Kings Light Dragoons (Hussars) Re-enactment Regiment
2nd Bt. 95th Rifles Reenactment and Living History Society- The Napoleonic Wars Collection Website
- Napoleon, His Army and Enemies
- Napoleonic Guide
War and Peace by Leo Tolstoy
- Napoleonic Wars


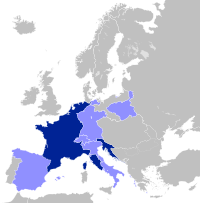 Europe at the height of Napoleon's Empire
Europe at the height of Napoleon's Empire