Golden-crowned kinglet
| Golden-crowned kinglet | |
|---|---|
 | |
| In Canada | |
Conservation status | |
 Least Concern (IUCN 3.1)[1] | |
Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Regulidae |
| Genus: | Regulus |
| Species: | R. satrapa |
Binomial name | |
Regulus satrapa (Lichtenstein, 1823) | |
 | |

In North Carolina
The golden-crowned kinglet (Regulus satrapa) is a very small songbird.
Adults are olive-gray on the upperparts with white underparts, with thin bills and short tails. They have white wing bars, a black stripe through the eyes and a yellow crown surrounded by black. The adult male has an orange patch in the middle of the yellow crown.
Their breeding habitat is coniferous forests across Canada, the northeastern and western United States, Mexico and Central America. They nest in a well-concealed hanging cup suspended from a conifer branch.
These birds migrate to the United States. Some birds are permanent residents in coastal regions and in the southern parts of their range. Northern birds remain further north in winter than the ruby-crowned kinglet.
They forage actively in trees or shrubs, mainly eating insects, insect eggs and spiders.
They give a series of high-pitched calls on a single note, and tend not to fear human approach.
Contents
1 Description
2 Distribution
3 Taxonomy
4 References
5 External links
Description

Adults are olive-gray on the upperparts with white underparts, with thin bills and short tails. They have white wing bars, a black stripe through the eyes and a yellow crown surrounded by black. The adult male has an orange patch in the middle of the yellow crown. The juvenile is similar to the adult, but with a browner back and without the yellow crown.[2] This is one of the smallest passerines in North America. Its length, at 8 to 11 cm (3.1 to 4.3 in), is probably the shortest of any American passerine. However, its weight, which averages around 5.9 g (0.21 oz), with a range of 4 to 7.8 g (0.14 to 0.28 oz),[3] is marginally more on average than the American bushtit[4] and black-tailed gnatcatcher.[5]
Distribution
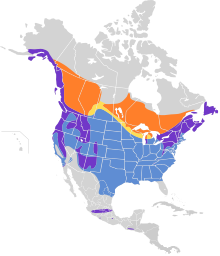
Golden-crowned kinglet is a widespread North American bird, breeding in many US states, and over much of Canada, and wintering across much of the continent south to Florida, Texas and Mexico. It also occurs in isolated mountain ranges in southern Mexico and Guatemala, where it is represented by separate subspecies.
Taxonomy
The kinglets are a small group of birds sometimes included in the Old World warblers, but frequently given family status,[6] especially as recent research showed that, despite superficial similarities, the crests are taxonomically remote from the warblers.[7][8] The names of the family, Regulidae, and its only genus, Regulus, are derived from the Latin regulus, a diminutive of rex, "a king",[9] and refer to the characteristic orange or yellow crests of adult kinglets.
There are three migratory subspecies in the United States and Canada, differing in size, bill length, back and rump colours, wing-bar width and colour, and length of supercilium:[10]
- Subspecies apache, breeding and wintering from southern Alaska and southern Yukon to southwest California and southern New Mexico. This subspecies is medium-small, has a long bill, and has the back and rump bright yellowish olive.
- Subspecies olivaceus, breeding from coastal southeast Alaska to southwest Oregon, wintering to Idaho and southwest California. This subspecies is small, with a medium-long bill, and has the back and rump dark greenish olive.
- Subspecies satrapa, breeding from northern Alberta to Newfoundland and North Carolina. This subspecies is large, with a short bill, has the back and rump olive with a greyish wash. It further differs from apache and olivaceus in two other regards: the white supercilium stops short of the rear of the crown, whereas on the other two species the supercilium extends farther back, and the wingbars are wide, and white (or slightly lemon-tinged) compared with narrow dingy whitish (or lemon- or olive-washed) wingbars of the other two subspecies.
The subspecies "amoenus" has been synonymised with apache as the distinction between these populations are obscured by individual variation.[10]
Two other (non-migratory) subspecies occur south of the bird's core range, although these are weakly differentiated from each other and so are perhaps best synonymised:[11]
- Subspecies aztecus in south-central Mexico, in the mountains from Michoacán south to Oaxaca. This subspecies is dark greenish above, has poorly developed wing markings, and its underparts are washed greyish brown.
- Subspecies clarus in the mountains of Chiapas, southern Mexico, and in Guatemala. This subspecies resembles aztecus but is paler and duller, with a shorter tail.
Hybridization with ruby-crowned kinglet has been reported to have possibly occurred.[10]
References
^ BirdLife International (2012). "Regulus satrapa". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 26 November 2013..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Sibley, David Allen (2000). The Sibley Guide to Birds. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. p. 394. ISBN 0-679-45122-6.
^ Dunning, Jr., J. B. 1993. CRC handbook of avian body masses. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
^ Hertz, P. E., J. V. Remsen, Jr., and S. I. Jones. 1976. Ecological complementarity of three sympatric parids in a California oak woodland. Condor 78:307-316.
^ Atwood, J. L. 1988. Speciation and geographic variation in Black-tailed Gnatcatchers. Ornithol. Monogr. 42
^ Monroe, Burt L. (February 1992). "The new DNA-DNA avian classification: What's it all about?". British Birds. 85 (2): 53–61.
^ Barker, F Keith; Barrowclough, George F; Groth, Jeff G (2002). "A phylogenetic hypothesis for passerine birds: taxonomic and biogeographic implications of an analysis of nuclear DNA sequence data" (PDF). Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B. 269 (1488): 295–308. doi:10.1098/rspb.2001.1883. PMC 1690884. PMID 11839199.
^ Spicer, Greg S; Dunipace, Leslie (2004). "Molecular phylogeny of songbirds (Passerifor-mes) inferred from mitochondrial 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences" (PDF). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 30: 325–335. doi:10.1016/S1055-7903(03)00193-3. PMID 14715224.
^ Brookes, Ian (editor-in-chief) (2006). The Chambers Dictionary, ninth edition. Edinburgh: Chambers. pp. 223, 735, 1277. ISBN 0-550-10185-3.
^ abc pp. 374-75 in Pyle, Peter (1997). Identification Guide to North American Birds Part 1. Bolinas, California: Slate Creek Press. ISBN 0-9618940-2-4.
^ Martens, Jochen; Päckert, Martin "Family Regulidae (Kinglets & Firecrests)" pp. 330–349 in del Hoyo, Josep; Elliott, Andrew; Christie, David A., eds. (2006). Handbook of the Birds of the World: Old World Flycatchers to Old World Warblers v. 11. Barcelona: Lynx Edicions. ISBN 84-96553-06-X.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Golden-crowned Kinglet. |
Wikispecies has information related to Regulus satrapa |
Golden-crowned Kinglet Species Account - Cornell Lab of Ornithology
Golden-crowned Kinglet - Regulus satrapa - USGS Patuxent Bird Identification InfoCenter
"Golden-crowned Kinglet media". Internet Bird Collection.
Golden-crowned Kinglet photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
Interactive range map of Regulus satrapa at IUCN Red List maps