Nonvenereal endemic syphilis
Nonvenereal endemic syphilis
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Nonvenereal endemic syphilis | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | nonvenereal syphilis, endemic syphilis, bejel |
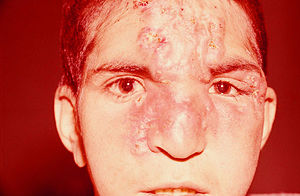 | |
| Disfiguring infiltration of the nose, glabella, and forehead with clustered nodules in left interciliary region of boy with endemic syphilis, Iran, 2010. | |
| Pronunciation |
|
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
Bejel, or endemic syphilis, is a chronic skin and tissue disease caused by infection by the endemicum subspecies of the spirochete Treponema pallidum. Bejel is one of the "endemic trepanematoses" (endemic infections caused by spiral-shaped bacteria called treponemes), a group that also includes yaws and pinta. Typically, endemic trepanematoses begin with localized lesions on the skin or mucous membranes. Pinta is limited to affecting the skin, whereas bejel and yaws are considered to be invasive because they can also cause disease in bone and other internal tissues.[1]
Contents
1 Signs and symptoms
2 Causes
3 Diagnosis
4 Treatment
5 Epidemiology
6 See also
7 References
8 External links
Signs and symptoms[edit]
Bejel usually begins in childhood as a small mucous patch, often on the interior of the mouth, followed by the appearance of raised, eroding lesions on the limbs and trunk. Periostitis (inflammation) of the leg bones is commonly seen, and gummas of the nose and soft palate develop in later stages.
Causes[edit]
Although the organism that causes bejel, Treponema pallidum endemicum,[2] is morphologically and serologically indistinguishable from Treponema pallidum pallidum, which causes venereal syphilis, transmission of bejel is not venereal in nature,[3] generally resulting from mouth-to-mouth contact or sharing of domestic utensils, and the courses of the two diseases are somewhat different.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of bejel is based on the geographic history of the patient as well as laboratory testing of material from the lesions. (dark-field microscopy). The responsible spirochaete is readily identifiable on sight in a microscope as a treponema.[4]
Treatment[edit]
It is treatable with penicillin or other antibiotics, resulting in a complete recovery.
Epidemiology[edit]
Bejel is mainly found in arid countries of the eastern Mediterranean region and in West Africa, where it is known as sahel. (Sahel disease should be distinguished from "Sahel", the geographical band between the Northern Sahara and Southern Sudan.)
See also[edit]
- Pinta (disease)
- Syphilis
- Yaws
References[edit]
^ Mitjà O, Šmajs D, Bassat Q (2013). "Advances in the diagnosis of endemic treponematoses: yaws, bejel, and pinta". PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 7 (10): e2283. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0002283. PMC 3812090. PMID 24205410..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Antal GM, Lukehart SA, Meheus AZ (January 2002). "The endemic treponematoses". Microbes and Infection. 4 (1): 83–94. doi:10.1016/S1286-4579(01)01513-1. PMID 11825779.
^ Pace JL, Csonka GW (October 1984). "Endemic non-venereal syphilis (bejel) in Saudi Arabia". The British Journal of Venereal Diseases. 60 (5): 293–7. doi:10.1136/sti.60.5.293. PMC 1046341. PMID 6487985.
^ Marks M, Solomon AW, Mabey DC (October 2014). "Endemic treponemal diseases". Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 108 (10): 601–7. doi:10.1093/trstmh/tru128. PMC 4162659. PMID 25157125.
External links[edit]
| Classification | D
|
|---|
Categories:
- Bacterium-related cutaneous conditions
- Syphilis
- Infectious diseases
- Neglected diseases
- Tropical diseases
(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function(){mw.config.set({"wgPageParseReport":{"limitreport":{"cputime":"0.348","walltime":"0.466","ppvisitednodes":{"value":982,"limit":1000000},"ppgeneratednodes":{"value":0,"limit":1500000},"postexpandincludesize":{"value":50249,"limit":2097152},"templateargumentsize":{"value":1950,"limit":2097152},"expansiondepth":{"value":10,"limit":40},"expensivefunctioncount":{"value":2,"limit":500},"unstrip-depth":{"value":1,"limit":20},"unstrip-size":{"value":14346,"limit":5000000},"entityaccesscount":{"value":3,"limit":400},"timingprofile":["100.00% 389.669 1 -total"," 38.48% 149.950 1 Template:Reflist"," 36.67% 142.896 2 Template:Infobox"," 35.59% 138.681 4 Template:Cite_journal"," 29.97% 116.790 1 Template:Infobox_medical_condition_(new)"," 13.28% 51.747 1 Template:Medical_resources"," 10.78% 42.023 1 Template:IPAc-en"," 9.63% 37.513 5 Template:Navbox"," 8.93% 34.800 1 Template:Distinguish"," 8.39% 32.692 1 Template:Gram-negative_non-proteobacterial_bacterial_diseases"]},"scribunto":{"limitreport-timeusage":{"value":"0.191","limit":"10.000"},"limitreport-memusage":{"value":5150555,"limit":52428800}},"cachereport":{"origin":"mw1246","timestamp":"20190319222449","ttl":2592000,"transientcontent":false}}});});{"@context":"https://schema.org","@type":"Article","name":"Nonvenereal endemic syphilis","url":"https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nonvenereal_endemic_syphilis","sameAs":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q682798","mainEntity":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q682798","author":{"@type":"Organization","name":"Contributors to Wikimedia projects"},"publisher":{"@type":"Organization","name":"Wikimedia Foundation, Inc.","logo":{"@type":"ImageObject","url":"https://www.wikimedia.org/static/images/wmf-hor-googpub.png"}},"datePublished":"2005-07-17T15:00:50Z","dateModified":"2019-03-11T06:53:57Z","image":"https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/0/04/Infiltration_of_skin_due_to_endemic_syphilis.jpg","headline":"Human disease"}(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function(){mw.config.set({"wgBackendResponseTime":107,"wgHostname":"mw1272"});});