1984 Summer Olympics
 | |||
| Host city | Los Angeles, California, United States | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nations | 140 | ||
| Athletes | 6,829 (5,263 men, 1,566 women) | ||
| Events | 221 in 21 sports (29 disciplines) | ||
| Opening | July 28 | ||
| Closing | August 12 | ||
| Opened by | President Ronald Reagan | ||
| Cauldron | Rafer Johnson | ||
| Stadium | Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum | ||
| Summer | |||
| |||
| Winter | |||
| |||
| Part of a series on |
1984 Summer Olympics
|
The 1984 Summer Olympics, officially known as the Games of the XXIII Olympiad, was an international multi-sport event that was held from July 28 to August 12, 1984, in Los Angeles, California, United States. This was the second time that Los Angeles had hosted the Games, the first being in 1932.
California was the home state of the incumbent U.S. President Ronald Reagan, who officially opened the Games. The logo for the 1984 Games, branded "Stars in Motion", featured red, white and blue stars arranged horizontally and struck through with alternating streaks.
The official mascot of the Games was Sam the Olympic Eagle. These were the first Summer Olympic Games under the IOC presidency of Juan Antonio Samaranch.
The 1984 Games were boycotted by a total of fourteen Eastern Bloc countries, including the Soviet Union and East Germany, in response to the American-led boycott of the previous 1980 Summer Olympics in Moscow in protest of the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan; Romania was the only Eastern Bloc nation that opted to attend the Games. Iran and Libya also chose to boycott the Games for unrelated reasons. Despite the field being depleted in certain sports due to the boycott, 140 National Olympic Committees took part, which was a record at the time.[1][2]
The 1984 Summer Olympics are widely considered to be the most financially successful modern Olympics[3] and serve as an example of how to run the model Olympic Games. As a result of low construction costs, coupled with a heavy reliance on private corporate funding, the 1984 Olympic Games generated a profit of more than $200 million.
On July 18, 2009, a 25th anniversary celebration was held in the main Olympic Stadium. The celebration included a speech by the former president of the Los Angeles Olympic Organizing Committee, Peter Ueberroth, and a re-creation of the lighting of the cauldron. Los Angeles will host the Summer Olympics for the third time in 2028.
Contents
1 Host selection
2 Torch relay
3 Music
4 Highlights
4.1 Arts Festival
4.2 General
4.3 Track and field
4.4 Other sports
5 Venues
5.1 Los Angeles venues
5.2 Southern California venues
5.3 Other venues
6 Cost
7 Medals awarded
7.1 Demonstration sports
8 Calendar
9 Medal count
10 Participating National Olympic Committees
11 Boycotting countries
11.1 Soviet doping plan
12 Success of Los Angeles as host city
13 In popular culture
14 Broadcast rights
15 See also
16 References
17 External links
18 Further reading
Host selection
After the murder of Israeli athletes by Palestinian terrorists in Munich (1972) and the significant financial debts of Montreal (1976), few cities by the late 1970s were willing to bid for the Summer Olympics. Only two cities (Tehran and Los Angeles) made serious bids for the 1984 Summer Games, but before the final selection of a "winning" city in 1978, the bid from Tehran was withdrawn as a result of Iran's policy changes following the Iranian Revolution and a change in the country's ruling system. Hence, the selection process for the 1984 Summer Olympics consisted of a single finalized bid from Los Angeles, which the International Olympic Committee (IOC) accepted. The selection was officially made at the 80th IOC Session in Athens on 18 May 1978.[4]
Los Angeles had unsuccessfully bid for the two previous Summer Olympics, for 1976 and 1980. The United States Olympic Committee (USOC) had submitted at least one bid for every Olympics since 1944, but had not succeeded since the Los Angeles Olympics in 1932, the previous time only a single bid had been issued for the Summer Olympics.
Torch relay
The 1984 Olympic Torch Relay began in New York City and ended in Los Angeles, traversing 33 states and the District of Columbia. Unlike later torch relays, the torch was continuously carried by runners on foot. The route covered more than 9,320 mi (15,000 km) and involved 3,636 runners, including 200 from the sponsoring company AT&T. Noted athlete O.J. Simpson was among the runners, carrying the torch up the California Incline in Santa Monica. Gina Hemphill, granddaughter of Jesse Owens, carried the torch into the Coliseum, completed a lap around the track, then handed it off to the final runner, Rafer Johnson, winner of the decathlon at the 1960 Summer Olympics. With the torch, he touched off the flame which passed through a specially designed flammable Olympic logo, igniting all five rings. The flame then passed up to cauldron atop the peristyle and remained aflame for the duration of the Games.

The Opening Ceremony at the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum
Music
 | "Olympic Fanfare and Theme" composed by John Williams for the 1984 Summer Olympics in Los Angeles and performed by the Boston Pops Orchestra |
Problems playing this file? See media help. | |
John Williams composed the theme for the Olympiad, "Olympic Fanfare and Theme". This piece won a Grammy for Williams and became one of the most well-known musical themes of the Olympic Games, along with Leo Arnaud's "Bugler's Dream"; the latter is sometimes attached to the beginning of Olympic Fanfare and Theme. Composer Bill Conti also wrote a song to inspire the weightlifters called "Power". An album, The Official Music of the XXIII Olympiad—Los Angeles 1984, featured three of those tracks along with sports themes written for the occasion by popular musical artists including Foreigner, Toto, Loverboy, Herbie Hancock, Quincy Jones, Christopher Cross, Philip Glass and Giorgio Moroder.[5]
The Brazilian composer Sérgio Mendes also produced a special song for the 1984 Olympic Games, "Olympia," from his 1984 album Confetti. A choir of approximately one thousand voices was assembled of singers in the region. All were volunteers from nearby churches, schools and universities.
Etta James performed "When the Saints Go Marching In" at the Opening Ceremony.[6]
Vicki McClure along with the International Children's Choir of Long Beach sang "Reach Out and Touch".
Lionel Richie performed a 9-minute version of his hit single "All Night Long" at the closing ceremonies.[7]
Highlights
Arts Festival
The 1984 Summer Olympics was preceded by the 10-week-long adjunct Los Angeles Olympic Arts Festival, which opened on June 2 and ended on August 12. It provided more than 400 performances by 146 theater, dance and music companies, representing every continent and 18 countries. It was organized by then-CalArts President Robert Fitzpatrick.
General
- The opening ceremony featured the arrival of Bill Suitor by means of the Bell Aerosystems rocket pack (also known as a Jet Pack).
- The United States Army Band formed the Olympic rings to start the opening ceremony.
- The United States topped the medal count for the first time since 1968, winning a record 83 gold medals and surpassing the Soviet Union’s total of 80 golds at the 1980 Summer Olympics.
- As a result of an IOC agreement designating the Republic of China (Taiwan) in the name of Chinese Taipei, the People's Republic of China returned to the summer Olympics for the first time since Helsinki 1952. The Military anthem of China was played for both teams during the opening ceremony.
- Local Los Angeles artist Rodolfo Escalera was commissioned to create nine paintings depicting the Summer Games that would later be turned into collectible plates and presented as "The Official Gift of the 1984 Olympics".
The Los Angeles Olympic Organizing Committee named Ernie Barnes "Sports Artist of the 1984 Olympic Games". LAOOC President Peter V. Ueberroth said Barnes and his art "captured the essence of the Olympics" and "portray the city's ethnic diversity, the power and emotion of sports competition, the singleness of purpose and hopes that go into the making of athletes the world over." Barnes was commissioned to create five Olympic-themed paintings and serve as an official Olympic spokesman to encourage inner city youth.[
Track and field
Carl Lewis of the United States, making his first of four appearances at the Olympics, equaled the 1936 performance of Jesse Owens by winning four gold medals, in the 100 m, 200 m, 4 × 100 m relay and long jump.
Edwin Moses of the United States won the gold medal in the 400m hurdles 8 years after winning in 1976.
Joaquim Cruz of Brazil won the 800 meter run with a time of 1:43.00 to set an Olympic record.
Nawal El Moutawakel of Morocco became the first female Olympic champion of a Muslim nation—and the first of her country—in the 400 m hurdles.
Carlos Lopes, from Portugal, won the Marathon at the age of 37, with a time of 2:09:21, an Olympic record that stood for 24 years. It was the first gold medal ever for Portugal. Gold medal favorite, World Record holder and the then World Champion, Robert de Castella from Australia, finished in 5th place, 1:48 behind Lopes.- A marathon for women was held for the first time at the Olympics (won by Joan Benoit of the U.S.). The event was considered notable because of Swiss runner Gabi Andersen-Schiess, who – suffering from heat exhaustion – stumbled through the last lap, providing dramatic images.
Daley Thompson of Great Britain apparently missed a new world record in winning his second consecutive gold medal in the decathlon; the next year his score was retroactively raised to 8847, giving him the record.
Sebastian Coe of Great Britain became the first man to win consecutive gold medals in the 1500m.
Maricica Puică of Romania won the 3000 meters, known for the Mary Decker vs Zola Budd rivalry. As Decker fell, Budd was initially blamed and large parts of the crowd began to boo her, then the very young Budd deliberately slowed down finishing seventh. However Puică had the best annual time at the distance, easily run away from Silver medalist Wendy Sly of Great Britain and appeared to have more to give if it had been necessary. Puică was injured during the very first Track and Field World Championships in Helsinki the year before, in which Decker had won both the 1500 meters and the 3000 meters.[8]
Other sports
- The first gold medal to be awarded at the Los Angeles Olympics was also the first-ever medal to be won by an athlete from China when Xu Haifeng won the 50 m Pistol event.
Archer Neroli Fairhall from New Zealand was the first paraplegic Olympian at any Olympic Games, coming 35th in the Women's individual event.
Synchronized swimming and rhythmic gymnastics debuted in Los Angeles as Olympic events, as did wind surfing.
Li Ning from the People's Republic of China won 6 medals in gymnastics, 3 gold, 2 silver, and 1 bronze, earning him the nickname "Prince of Gymnasts" in China. Li would later light the Olympic Cauldron at the 2008 Olympics.[9]
Steve Redgrave of Great Britain won his first title in rowing of the record five he would go on to win in five Olympic competitions.
Victor Davis of Canada set a new world record in winning the gold medal in the 200-meter breaststroke in swimming.
Mary Lou Retton of the United States became the first gymnast outside Eastern Europe to win the gymnastics all-around competition.- In men's gymnastics, the American team won the Gold Medal.
France won the Olympic association football (soccer) tournament, defeating Brazil 2–0 in the final. Olympic football was unexpectedly played before massive crowds throughout America, with several sell-outs at the 100,000+ seat Rose Bowl. This interest eventually led to the US hosting the 1994 FIFA World Cup.- The Soviet-led boycott affected weightlifting more than any other sport: 94 of the world's top 100 ranked lifters were absent, as were 29 of the 30 medalists from the recent world championships. All 10 of the defending world champions in the 10 weight categories were absent. Success of the Eastern Bloc countries might be explained by state-run doping programs that had been developed there.[10]
- Future Dream Team members Michael Jordan, Patrick Ewing, and Chris Mullin were on the team that won the gold medal in basketball. The 1984 US men's Olympic basketball team was coached by Indiana Hoosiers head coach Bobby Knight.
Connie Carpenter-Phinney of the United States became the first woman to win an Olympic cycling event when she won the women's individual road race.
Venues

The Forum hosted the basketball events
Los Angeles venues
Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum – opening/closing ceremonies, athletics
Los Angeles Memorial Sports Arena – boxing
Dodger Stadium – baseball
Pauley Pavilion, University of California, Los Angeles – gymnastics
Eagle's Nest Arena, California State University, Los Angeles – judo
Olympic Swim Stadium, University of Southern California – swimming, diving, synchronized swimming- Olympic Village (athlete housing), University of Southern California
Los Angeles Tennis Center, University of California, Los Angeles – tennis- Athletes Village, University of California, Los Angeles
Albert Gersten Pavilion, Loyola Marymount University, Westchester, California – weightlifting- Streets of Los Angeles – athletics (marathon)
Southern California venues
El Dorado Park, Long Beach, California – archery
The Forum, Inglewood, California – basketball
Lake Casitas, Ventura County, California – canoeing, rowing
Olympic Velodrome, California State University, Dominguez Hills, Carson, California – cycling (track)
Mission Viejo, Orange County, California – cycling (individual road race)
Santa Anita Park, Arcadia, California – equestrian
Fairbanks Ranch Country Club, Rancho Santa Fe, California, California – equestrian sports (eventing endurance)
Long Beach Convention Center, Long Beach, California – fencing
Rose Bowl, Pasadena, California – football (final)
Titan Gymnasium, California State University, Fullerton, Fullerton, California – handball
Weingart Stadium, East Los Angeles College, Monterey Park, California – field hockey
Coto de Caza, Orange County, California – modern pentathlon (fencing, riding, running, shooting)- Olympic Shooting Range, Prado Recreational Area, Chino, California – shooting
Long Beach Arena, Long Beach, California – volleyball
Raleigh Runnels Memorial Pool, Pepperdine University, Malibu, California – water polo
Anaheim Convention Center, Anaheim, California – wrestling
Long Beach Shoreline Marina, Long Beach, California – sailing
Artesia Freeway – cycling (road team time trial)
Heritage Park Aquatic Center – modern pentathlon (swimming)
Santa Monica College – athletics (marathon start)
Santa Monica, California – athletics (marathon)
Other venues
Harvard Stadium, Harvard University, Boston, Massachusetts – football preliminaries
Navy–Marine Corps Memorial Stadium, United States Naval Academy, Annapolis, Maryland – football preliminaries
Stanford Stadium, Stanford University, Stanford, California – football preliminaries
Cost
The Oxford Olympics Study established the outturn cost of the Los Angeles 1984 Summer Olympics at USD 719 million in 2015-dollars.[11] This includes sports-related costs only, that is, (i) operational costs incurred by the organizing committee for the purpose of staging the Games, e.g., expenditures for technology, transportation, workforce, administration, security, catering, ceremonies, and medical services, and (ii) direct capital costs incurred by the host city and country or private investors to build, e.g., the competition venues, the Olympic village, international broadcast center, and media and press center, which are required to host the Games. Indirect capital costs are not included, such as for road, rail, or airport infrastructure, or for hotel upgrades or other business investment incurred in preparation for the Games but not directly related to staging the Games. The cost for Los Angeles 1984 compares with costs of USD 4.6 billion for Rio 2016, USD 40-44 billion for Beijing 2008 and USD 51 billion for Sochi 2014, the most expensive Olympics in history. Average cost for the Summer Games since 1960 is USD 5.2 billion.
Medals awarded
The 1984 Summer Olympic program featured 221 events in the following 21 sports:
|
|
|
|
Demonstration sports
- Baseball
- Tennis
Calendar
- All times are in Pacific Daylight Time (UTC-7); the other two cities, Boston and Annapolis uses Eastern Daylight Time (UTC-4)
| ● | Opening ceremony | Event competitions | ● | Event finals | ● | Closing ceremony |
| Date | July | August | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28th Sat | 29th Sun | 30th Mon | 31st Tue | 1st Wed | 2nd Thu | 3rd Fri | 4th Sat | 5th Sun | 6th Mon | 7th Tue | 8th Wed | 9th Thu | 10th Fri | 11th Sat | 12th Sun | |
Archery | ● ● | |||||||||||||||
Athletics | ● ● | ● ● ● | ● ● ● ● | ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● | ● ● ● ● | ● ● ● | ● ● ● ● ● | ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● | ● | |||||||
Basketball | ● | ● | ||||||||||||||
Boxing | ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● | |||||||||||||||
Canoeing | ● ● ● ● ● ● | ● ● ● ● ● ● | ||||||||||||||
Cycling | ● ● | ● | ● | ● ● ● | ● | |||||||||||
Diving | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||||||
Equestrian | ● ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||||
Fencing | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
Field hockey | ● | ● | ||||||||||||||
Football | ● | |||||||||||||||
Gymnastics | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● ● ● ● ● ● | ● ● ● ● | ● | |||||||||
Handball | ● | ● | ||||||||||||||
Judo | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
Modern pentathlon | ● ● | |||||||||||||||
Rowing | ● ● ● ● ● ● | ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● | ||||||||||||||
Sailing | ● ● ● ● ● ● | |||||||||||||||
Shooting | ● ● | ● | ● ● ● | ● | ● | ● ● | ● | |||||||||
Swimming | ● ● ● ● | ● ● ● ● ● | ● ● ● ● ● | ● ● ● ● ● | ● ● ● ● ● | ● ● ● ● ● | ||||||||||
Synchronized swimming | ● | ● | ||||||||||||||
Volleyball | ● | ● | ||||||||||||||
Water polo | ● | |||||||||||||||
Weightlifting | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
Wrestling | ● ● ● | ● ● ● | ● ● ● ● | ● ● ● | ● ● ● | ● ● ● ● | ||||||||||
| Total gold medals | 9 | 8 | 13 | 10 | 12 | 16 | 25 | 21 | 10 | 5 | 14 | 11 | 20 | 43 | 3 | |
| Ceremonies | ● | ● | ||||||||||||||
| Date | 28th Sat | 29th Sun | 30th Mon | 31st Tue | 1st Wed | 2nd Thu | 3rd Fri | 4th Sat | 5th Sun | 6th Mon | 7th Tue | 8th Wed | 9th Thu | 10th Fri | 11th Sat | 12th Sun |
| July | August | |||||||||||||||
Medal count
These are the top ten nations that won medals at the 1984 Games.
| Rank | Nation | Gold | Silver | Bronze | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 83 | 61 | 30 | 174 | |
| 2 | 20 | 16 | 17 | 53 | |
| 3 | 17 | 19 | 23 | 59 | |
| 4 | 15 | 8 | 9 | 32 | |
| 5 | 14 | 6 | 12 | 32 | |
| 6 | 10 | 18 | 16 | 44 | |
| 7 | 10 | 8 | 14 | 32 | |
| 8 | 8 | 1 | 2 | 11 | |
| 9 | 7 | 4 | 7 | 18 | |
| 10 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 19 | |
| Totals (10 nations) | 190 | 147 | 137 | 474 | |
Participating National Olympic Committees

Participating nations
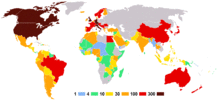
Number of athletes
Athletes from 140 nations competed at the 1984 Summer Olympics. Eighteen nations made their Olympic debut: Bahrain, Bangladesh, Bhutan, British Virgin Islands, Djibouti, Equatorial Guinea, Gambia, Grenada, Mauritania, Mauritius, North Yemen, Oman, Qatar, Rwanda, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, and the United Arab Emirates. Zaire had previously competed at the 1968 Summer Olympics as Congo-Kinshasa. The People's Republic of China made its first appearance in a Summer Olympics since 1952, while for the first time the Republic of China team participated under the politically contrived name of Chinese Taipei.
The Soviet Union led the Warsaw Pact members and other Communist and Socialist countries in a boycott of the Los Angeles Olympics, in retaliation for the U.S.-led boycott of the Moscow Olympics four years earlier (over the Soviet Union's invasion of Afghanistan in 1979). The pretexts for the 1984 Soviet-led boycott were concerns over security, "chauvinistic sentiments" and "an anti-Soviet hysteria ... being whipped up" in the United States.[12] However, a handful of Socialist countries disregarded the boycott and attended the Games anyway, among them Yugoslavia (host of the 1984 Winter Olympics), the People's Republic of China, and Romania (the only Warsaw Pact country that had opted to ignore the Soviet demands). The Romanian team received a particularly warm reception from the United States; when the Romanian athletes entered during the opening ceremonies, they were greeted by a standing ovation from the spectators, who were mostly U.S. citizens. This would turn out to be Romania's most successful Olympic Games – they won 53 medals, including 20 golds.
In the table below, the number of athletes representing each nation is shown in parentheses.
| Participating National Olympic Committees |
|---|
|
Boycotting countries

Countries that boycotted the 1984 Summer Olympics are shaded blue
Fourteen countries took part in the Soviet-led boycott of the 1984 Summer Olympics:[13]
 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Angola
Angola
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Cuba
Cuba
 Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia
 East Germany
East Germany
 Ethiopia
Ethiopia
 Hungary
Hungary
 Laos
Laos
 Mongolia
Mongolia
 North Korea
North Korea
 Poland
Poland
 Soviet Union
Soviet Union
 Vietnam
Vietnam
Albania, Iran and Libya also boycotted the Los Angeles Olympics, citing political reasons, but these countries were not a part of the Soviet-led boycott. Albania and Iran were the only two countries to boycott both the 1980 and 1984 Summer Games.
 Albania
Albania
 Iran
Iran
 Libya
Libya
Soviet doping plan
Documents obtained in 2016 revealed the Soviet Union's plans for a statewide doping system in track and field in preparation for the 1984 Summer Olympics in Los Angeles. Dated prior to the country's decision to boycott the Games, the document detailed the existing steroids operations of the program, along with suggestions for further enhancements. The communication, directed to the Soviet Union's head of track and field, was prepared by Dr. Sergei Portugalov of the Institute for Physical Culture. Portugalov was also one of the main figures involved in the implementation of the Russian doping program prior to the 2016 Summer Olympics.[10] Filmmaker and director of 2017 movie Icarus Bryan Fogel has said that stricter doping controls might have been the main reason of the Soviet boycott.[14]
Success of Los Angeles as host city

Newspaper vending machine announcing the 1984 Olympics.
Following the news of the massive financial losses of the 1976 Summer Olympics in Montreal, the only two cities to express a serious interest in hosting the 1984 Games were Los Angeles and New York. Given that only one city per country is allowed to bid for any one Games, the USOC vote for the American bid city was effectively the deciding vote for the 1984 Olympics host city. In this case, the Los Angeles bid received 55 votes compared with New York's 39 votes – this is the closest that the city of New York has ever come to being selected to host the Olympic Games, coming closer in 1984 than they did in their 2012 bid (when they lost to London).[15]
The low level of interest among potential host cities for the 1984 Games had been viewed as a major threat to the future of the Olympic Games. However, after the financial success of the Los Angeles Games, cities began to line up to be hosts again. The Los Angeles and Montreal Games are seen as examples of what to do and what not to do when organizing the Olympics, and serve as abject lessons to prospective host cities.
Ambitious construction projects for the two previous Summer Olympics, Montreal 1976 and Moscow 1980, had burdened organizers with substantial debts as expenses greatly exceeded revenues. Consequently, Los Angeles enforced strict controls on their expenditure and rather than constructing new venues with overly ambitious designs, they chose instead to utilise existing venues and facilities wherever possible. The main example of this was the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum, which was also the Olympic Stadium for the 1932 Summer Olympics.[16] The only two new venues constructed specifically for the 1984 Summer Olympics were secured with the backing of corporate sponsors: the Olympic Velodrome was largely funded by the 7-Eleven corporation and the Olympic Swim Stadium by McDonald's.
As the only bidding city, the Los Angeles OCOG was able to extract a number of concessions from the IOC. Not only was it agreed that the city could make use of existing venues, but also that it would not be held responsible for any cost overruns. The latter concession was necessitated by a charter amendment resoundingly passed by Los Angeles voters barring the use of taxpayers' money for the Games without reimbursement, largely the work of City Councilman and Games critic Bob Ronka.[17]
In addition to corporate support, the Olympic committee also made use of the burgeoning prices being paid for exclusive television rights. Starting with the Los Angeles Games, these contracts would be a significant source of revenue. Adjusted for inflation, the Los Angeles Games received twice the amount received by the 1980 Moscow Summer Olympics and four times that of the 1976 Montreal Summer Olympics.[18] Due to these contracts being signed well in advance of the Games, Los Angeles found itself in an easier planning position because most of its revenue was already assured before the Games.[15]
Following the success of the 1984 Games, the Los Angeles OCOG, led by Peter Ueberroth, used some of the profits to create the LA84 Foundation to promote youth sports in Southern California, educate coaches and maintain a sports library.
In popular culture
McDonald's ran a promotion titled, "When the U.S. Wins, You Win" where customers scratched off a ticket with the name of an Olympic event on it, and if the U.S. won a medal in that event then they would be given a free menu item: a Big Mac for a gold medal, an order of french fries for a silver medal, and a Coca-Cola for a bronze medal. The promotion became more popular than expected due to the Soviet boycott which led to the U.S. winning far more Olympic medals than expected.[19]
This promotion was parodied in The Simpsons episode "Lisa's First Word", where Krusty Burger runs a similar offer. The promotion was intended to be rigged so that prizes would only be offered in events dominated by the Eastern Bloc, but the Soviet-led boycott causes Krusty to personally lose $44 million. He vehemently promises "to spit in every fiftieth burger," to which Homer retorts "I like those odds!" Chief Wiggum also exclaims that he could kiss Carl Lewis, who won four gold medals at the Games.
On NCIS, Tim McGee has an obsession with jet packs, stemming from having attended the 1984 Olympic ceremony as a child and having Bill Suitor fly over his head in his jet pack.[20] This storyline is based on the real experience of executive producer and writer Jesse Stern.[21]
Pop punk band Bowling for Soup references the games in the song "I Can't Stand LA". During a section showing appreciation for the city, the song states, "thank you for hair metal and the '84 Olympics."
Jilly Cooper's novel Riders has a storyline set at the show jumping event at the 1984 Summer Olympics.
Broadcast rights
The 1984 Games were covered by the following broadcasters:
 Australia: Network Ten
Australia: Network Ten
 Brazil: Rede Globo, Rede Manchete, SBT, Rede Record and Rede Bandeirantes
Brazil: Rede Globo, Rede Manchete, SBT, Rede Record and Rede Bandeirantes
 Ireland: RTÉ
Ireland: RTÉ
 United Kingdom: BBC
United Kingdom: BBC
 China: CCTV
China: CCTV
 United States: KABC-7 (ABC)
United States: KABC-7 (ABC)
 Sri Lanka: Rupavahini (SLRC)
Sri Lanka: Rupavahini (SLRC)
 Netherlands: NPO
Netherlands: NPO
 Sweden: SVT
Sweden: SVT
 Norway: NRK
Norway: NRK
 Canada: CBC
Canada: CBC
 Japan: NHK
Japan: NHK
 Hong Kong: ATV and TVB
Hong Kong: ATV and TVB
 Macau: TDM
Macau: TDM
 Portugal: RTP
Portugal: RTP
 Spain: TVE
Spain: TVE
 Taiwan: TTV, CTV and CTS
Taiwan: TTV, CTV and CTS
 South Korea: KBS and MBC
South Korea: KBS and MBC
 Mexico: Televisa
Mexico: Televisa
 West Germany: ARD and ZDF
West Germany: ARD and ZDF
 France: TF1
France: TF1
 Thailand: National Television Thailand
Thailand: National Television Thailand
 India: Doordarshan
India: Doordarshan
 Turkey: TRT
Turkey: TRT
 New Zealand: TVNZ
New Zealand: TVNZ
 Indonesia: TVRI Jakarta
Indonesia: TVRI Jakarta
 Malaysia: Sistem Televisyen Malaysia Berhad TV3, a member of New Straits Times Press (live direct television broadcast transmission)
Malaysia: Sistem Televisyen Malaysia Berhad TV3, a member of New Straits Times Press (live direct television broadcast transmission)
 Singapore: Sistem Televisyen Malaysia Berhad TV3, a member of New Straits Times Press (live direct television broadcast transmission)
Singapore: Sistem Televisyen Malaysia Berhad TV3, a member of New Straits Times Press (live direct television broadcast transmission)
 Philippines: GMA Radio-Television Arts and Radio Philippines Network
Philippines: GMA Radio-Television Arts and Radio Philippines Network
 Venezuela: Venevision
Venezuela: Venevision
 Brunei: Sistem Televisyen Malaysia Berhad TV3, a member of New Straits Times Press (live direct television broadcast transmission)
Brunei: Sistem Televisyen Malaysia Berhad TV3, a member of New Straits Times Press (live direct television broadcast transmission)
 Italy: RAI
Italy: RAI
 Chile: TVN, UC-TV
Chile: TVN, UC-TV
 Argentina: Argentina Televisora Color, Canal 13, Canal 11
Argentina: Argentina Televisora Color, Canal 13, Canal 11
 Paraguay: Paraguay Televisora Color, Canal 4, Canal 9 Cerro Corá
Paraguay: Paraguay Televisora Color, Canal 4, Canal 9 Cerro Corá
 Uruguay: SODRE Canal 14, Monte Carlo TV, Channel 10, Teledoce.
Uruguay: SODRE Canal 14, Monte Carlo TV, Channel 10, Teledoce.
 Romania: TVR
Romania: TVR
 Ecuador:Teleamazonas
Ecuador:Teleamazonas
See also
- 1984 Summer Paralympics
- 1984 Winter Paralympics
- 1984 Winter Olympics
- Olympic Games celebrated in the United States
1904 Summer Olympics – St. Louis
1932 Summer Olympics – Los Angeles
1932 Winter Olympics – Lake Placid
1960 Winter Olympics – Squaw Valley
1980 Winter Olympics – Lake Placid
1984 Summer Olympics – Los Angeles
1996 Summer Olympics – Atlanta
2002 Winter Olympics – Salt Lake City
- Olympic Games with significant boycotts
1976 Summer Olympics – Montreal – African boycott
1980 Summer Olympics – Moscow – United States-led boycott
1984 Summer Olympics – Los Angeles – Soviet-led boycott
- Summer Olympic Games
- Olympic Games
- International Olympic Committee
- List of IOC country codes
- Use of performance-enhancing drugs in the Olympic Games — 1984 Los Angeles
People
Bob Ronka, Los Angeles City Council member, 1977–81, skeptical of hosting the Olympics.
References
^ "NO BOYCOTT BLUES". olympic.org. Retrieved January 6, 2017..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "Games of the XXIII Olympiad". International Olympic Committee. Archived from the original on August 30, 2008. Retrieved August 31, 2008.
^ Abrahamson, Alan (July 25, 2004). "LA the Best Site, Bid Group Insists; Olympics: Despite USOC rejection". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved August 17, 2008.
^ "Past Olympic host city election results". GamesBids. Archived from the original on 17 March 2011. Retrieved 13 November 2018.
^ "Various – The Official Music Of The XXIIIrd Olympiad – Los Angeles 1984 (LP) at Discogs". Archived from the original on September 12, 2009. Retrieved September 10, 2009.
^ Los Angeles 1984 Olympic Opening Ceremony Complete [Go to time stamp 29:40 for Etta James' performance. A previously cited Associated Press story (in which James was credited for singing the national anthem) was an AP reporting error. The national anthem was performed by a choir, and James appeared to perform 'When The Saints Go Marching In' later in the ceremony.]. YouTube. September 6, 2014.
^ Malone, MacKenzie (July 19, 2012). "Tuning into the Games, Watching the Olympics is the next best thing to playing". Times Union. Retrieved April 4, 2014.
^ Sky Documentary "Mary Decker vs Zola Budd", aired on Danish DR2, 2.August 2018, 23:30 CEST
^ Nick Mulvenney (August 8, 2008). "Li Ning, "Prince of Gymnasts" and businessman". Reuters.
^ ab "The Soviet Doping Plan: Document Reveals Illicit Approach to '84 Olympics". The New York Times. August 13, 2016. Retrieved November 13, 2017.
^ Flyvbjerg, Bent; Stewart, Allison; Budzier, Alexander (2016). The Oxford Olympics Study 2016: Cost and Cost Overrun at the Games. Oxford: Saïd Business School Working Papers (Oxford: University of Oxford). pp. 9–13. SSRN 2804554.
^ Burns, John F. (May 9, 1984). "Moscow will keep its team from Los Angeles Olympics; Tass cites peril, U.S. denies it; Protests are issue". The New York Times.
^ "1984 Olympics". infoplease.com. Archived from the original on June 18, 2006. Retrieved June 11, 2006.
^ "Bryan Fogel talks 1984 Summer Olympics boycott on The Jim Rome Podcast". jimrome.com. Archived from the original on November 22, 2017. Retrieved November 23, 2017.
^ ab Andrew H. Levin (April 27, 2007). "No Olympics, No Problem: New York City's Political Regime after the Bid for the 2012 Games" (PDF). p. 27. Retrieved July 24, 2009.
^ "Let Boston 2024 pay for the Olympics". The Boston Globe. Retrieved July 28, 2015.
^ Mariel Garza (July 30, 2015). "Opinion: Some credit for the little-known figure behind L.A.'s 1984 Olympic Games deal". Los Angeles Times.
^ Shoval, Noam. "A New Phase in the Competition For The Olympic Gold: The London and New York Bids For The 2012 Games." Journal of Urban Affairs 24.5 (2002): 583–99.
^ Hollie, Pamela G. (August 10, 1984). "Advertising; Big Mac's Olympic Giveaway". The New York Times. Retrieved April 20, 2010.
^ "Ignition". NCIS: Naval Criminal Investigative Service. Season 7. Episode 11. January 5, 2010. 43 minutes in. CBS.
^ Stern, Jesse. The Future is Now: NCIS meets the jet pack (NCIS: The Seventh Season (Disc 3 special features)). CBS Studios.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 1984 Summer Olympics. |
"Los Angeles 1984". Olympic.org. International Olympic Committee.
"Results and Medalists — 1984 Summer Olympics". Olympic.org. International Olympic Committee.
Olympic Review 1984 – Official results- Official Report Vol. 1
- Official Report Vol. 2
Video of President Reagan declaring games open, and torch-lighting by Rafer Johnson on YouTube
Further reading
Whitakers Olympic Almanack. 2004. ISBN 0-7136-6724-9.
Henry, Bill. An Approved History of the Olympic Games. ISBN 0-88284-243-9.
Andranovich, Greg; Burbank, Matthew J.; Charles H. Heying (2001). "Olympic cities: lessons learned from Mega-Event Politics". Journal of Urban Affairs. 23–2.
| Preceded by Moscow | Summer Olympic Games Los Angeles XXIII Olympiad (1984) | Succeeded by Seoul |
