1788–89 United States presidential election
1788–89 United States presidential election
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
69 electoral votes of the Electoral College 37 electoral votes needed to win | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 11.6%[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
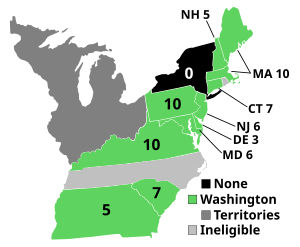 Presidential election results map. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. (Note: New York had ratified the Constitution but its legislature failed to appoint Presidential electors on time. North Carolina and Rhode Island had not yet ratified. Vermont governed itself as a republic.) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The United States presidential election of 1788–89 was the first quadrennial presidential election. It was held, from December 15, 1788 to January 10, 1789, under the new Constitution ratified in 1788. George Washington was unanimously elected for the first of his two terms as president, and John Adams became the first vice president.
Under the Articles of Confederation, ratified in 1781, the United States had no head of state. Separation of the executive function of government from the legislative was incomplete, as in countries that use a parliamentary system. Federal power, strictly limited, was reserved to the Congress of the Confederation, whose "President of the United States in Congress Assembled" was also chair of the Committee of the States, which aimed to fulfill a function similar to that of the modern Cabinet.
The Constitution created the offices of President and Vice President, fully separating these offices from Congress. The Constitution established an Electoral College, based on each state's Congressional representation, in which each elector would cast two votes for two different candidates, a procedure modified in 1804 by ratification of the Twelfth Amendment. Different states had varying methods for choosing presidential electors.[2] In five states, the state legislature chose electors. The other six chose electors through some form involving a popular vote, though in only two states did the choice depend directly on a statewide vote in a way even roughly resembling the modern method in all states.
The enormously popular Washington was distinguished as the former Commander of the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. After he agreed to exit retirement, it was known that he would be elected by virtual acclaim. Washington did not select a running mate, as that concept was not yet developed. No formal political parties existed, though an informally organized consistent difference of opinion already manifested between Federalists and Anti-Federalists. Thus, the contest for the Vice-Presidency was open. Thomas Jefferson predicted that a popular Northern leader like Governor John Hancock of Massachusetts or John Adams, a former minister to Great Britain who had represented Massachusetts in Congress, would be elected vice president. Anti-Federalist leaders like Patrick Henry, who did not run, and George Clinton, who had opposed ratification of the Constitution, also represented potential choices.
All 69 electors cast one vote for Washington, making his election unanimous. Adams won 34 electoral votes and the vice presidency. The remaining 35 electoral votes split among 10 different candidates, including John Jay, who finished next with nine electoral votes. Washington was inaugurated in New York City in April 1789 about two months after the First Congress convened.
Contents
1 Candidates
1.1 Federalist candidates
1.2 Anti-Federalist candidates
2 General election
2.1 Results
2.1.1 Popular vote
2.1.2 Electoral vote
3 Results by state
3.1 Popular vote
3.2 Electoral vote
4 Electoral college selection
5 See also
6 References
7 Bibliography
8 External links
Candidates[edit]
Though no organized political parties yet existed, political opinion loosely divided between those who had more stridently and enthusiastically endorsed ratification of the Constitution, called Federalists or Cosmopolitans, and Anti-Federalists or Localists who had only more reluctantly, skeptically, or conditionally supported, or who had outright opposed, ratification. Both factions supported Washington for President. Limited, primitive political campaigning occurred in states and localities where swaying public opinion might matter. For example in Maryland, a state with a statewide popular vote, unofficial parties campaigned locally, advertising platforms even in German to appeal and drive turnout by a German-speaking rural population. Organizers elsewhere lobbied through public forums, parades, and banquets.
Federalist candidates[edit]
John Adams, former Minister to Great Britain from Massachusetts
John Jay, United States Secretary of Foreign Affairs from New York
John Rutledge, former Governor of South Carolina
John Hancock, Governor of Massachusetts
Samuel Huntington, Governor of Connecticut
Benjamin Lincoln, former U.S. Secretary of War from Massachusetts
George Washington, former Commander-in-Chief of the Continental Army from Virginia

General
George Washington
from Virginia

John Adams
from Massachusetts

Secretary
John Jay
of New York

Governor
John Rutledge
of South Carolina

Governor
John Hancock
of Massachusetts

Governor
Samuel Huntington
of Connecticut

Maj. General
Benjamin Lincoln
from Massachusetts
Anti-Federalist candidates[edit]
George Clinton, Governor of New York

Governor
George Clinton
of New York
General election[edit]

Results by county explicitly indicating the percentage of the winning candidate in each county. Shades of yellow are for the Federalists.
No nomination process existed. The framers of the Constitution presumed that Washington would be elected unopposed. For example, Alexander Hamilton spoke for national opinion when in a letter to Washington attempting to persuade him to leave retirement on his farm in Mount Vernon to serve as the first President, he wrote that "...the point of light in which you stand at home and abroad will make an infinite difference in the respectability in which the government will begin its operations in the alternative of your being or not being the head of state."
Uncertain was the choice for the vice presidency, which contained no definite job description beyond being the President's designated successor while presiding over the Senate. The Constitution stipulated that the position would be awarded to the runner-up in the Presidential election. Because Washington was from Virginia, then the largest state, many assumed that electors would choose a vice president from a northern state. However, the stipulation that the President and Vice-President must be from different states dates only to the Twelfth Amendment of 1804. In an August 1788 letter, U.S. Minister to France Thomas Jefferson wrote that he considered John Adams and John Hancock, both from Massachusetts, to be the top contenders. Jefferson suggested John Jay, John Rutledge, and Virginian James Madison as other possible candidates.[3]
Voter turnout comprised a low single-digit percentage of the adult population. Though all states allowed some rudimentary form of popular vote, only six ratifying states allowed any form of popular vote specifically for Presidential electors. In most states only white men, and in many only those who owned property, could vote. Free black men could vote in four Northern states, and women could vote in New Jersey until 1807. In some states, there was a nominal religious test for voting. For example, in Massachusetts and Connecticut, the Congregational Church was established, supported by taxes. Though such tests and establishments were outlawed by the new Constitution, the concept of an un-Constitutional law dates to 1803 and incorporation, or application of the Constitution to the states, dates to 1868. However, in 1789, a religious test disenfranchised few among eligible voters. Test acts protected Protestants, sometimes of specific sects, but Catholicism and Judaism were rare in the newly independent United States. Catholicism was confined mainly to a minority in Maryland while both Catholicism and Judaism were further limited to a subset of urban populations in the largest, most cosmopolitan port cities, including Philadelphia, New York, Charleston, and Newport. For example, of 55 delegates to the Constitutional Convention, one from Maryland was Catholic, with the rest Protestant, which was only mildly less diverse than the American population of the time. States where public opinion endorsed such a test typically lacked meaningful religious diversity or a sizable religious minority to oppress by disqualification, and further did not necessarily vigorously enforce the test. Finally, public opinion regardless of gender, race, creed, or even political bias was known to favor Washington to the point of virtual unanimity.
Voting was hampered by poor communications and infrastructure and the labor demands imposed by farming. It took two months for Washington to be notified that he had been elected before spending one week traveling from Virginia to New York for inauguration. Similarly, Congress took weeks to assemble.
As the electors were selected, politics intruded, and the process was not free of rumors and intrigue. For example, Hamilton aimed to ensure that Adams did not inadvertently tie Washington in the electoral vote.[4] Also, Federalists spread rumors that Anti-Federalists plotted to elect Richard Henry Lee or Patrick Henry President, with George Clinton as vice president. However, Clinton received only three electoral votes.[5]
Results[edit]
Popular vote[edit]
| Popular Vote(a), (b), (c) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Count | Percentage | |
Federalist electors | 39,624 | 90.5% |
Anti-Federalist electors | 4,158 | 9.5% |
Total | 43,782 | 100.0% |
Source: U.S. President National Vote. Our Campaigns. (February 11, 2006).
(a)Only six of the 11 states eligible to cast electoral votes chose electors by any form of popular vote.
(b)Less than 1.8% of the population voted: the 1790 Census would count a total population of 3.0 million with a free population of 2.4 million and 600,000 slaves in those states casting electoral votes.
(c)Those states that did choose electors by popular vote had widely varying restrictions on suffrage via property requirements.
Electoral vote[edit]
| Presidential candidate | Party | Home state | Popular vote(a), (b), (c) | Electoral vote(d), (e), (f) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | Percentage | ||||
George Washington | Independent | Virginia | 43,782 | 100.0% | 69 |
John Adams | Federalist | Massachusetts | — | — | 34 |
John Jay | Federalist | New York | — | — | 9 |
Robert H. Harrison | Federalist | Maryland | — | — | 6 |
John Rutledge | Federalist | South Carolina | — | — | 6 |
John Hancock | Federalist | Massachusetts | — | — | 4 |
George Clinton | Anti-Federalist | New York | — | — | 3 |
Samuel Huntington | Federalist | Connecticut | — | — | 2 |
John Milton | Federalist | Georgia | — | — | 2 |
James Armstrong(g) | Federalist | Georgia(g) | — | — | 1 |
Benjamin Lincoln | Federalist | Massachusetts | — | — | 1 |
Edward Telfair | Anti-Federalist | Georgia | — | — | 1 |
| Total | 43,782 | 100.0% | 138 | ||
| Needed to win | 37 | ||||
Source: "Electoral College Box Scores 1789–1996". National Archives and Records Administration. Retrieved July 30, 2005..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}Source (Popular Vote): A New Nation Votes: American Election Returns 1787–1825[6]
(a)Only 6 of the 10 states casting electoral votes chose electors by any form of popular vote.
(c)Those states that did choose electors by popular vote had widely varying restrictions on suffrage via property requirements.
(d)The New York legislature failed to appoint its allotted 8 electors in time, so there were no voting electors from New York.
(e)Two electors from Maryland did not vote.
(f)One elector from Virginia did not vote and another elector from Virginia was not chosen because an election district failed to submit returns.
(g)The identity of this candidate comes from The Documentary History of the First Federal Elections (Gordon DenBoer (ed.), University of Wisconsin Press, 1984, p. 441). Several respected sources, including the Biographical Directory of the United States Congress and the Political Graveyard, instead show this individual to be James Armstrong of Pennsylvania. However, primary sources, such as the Senate Journal, list only Armstrong's name, not his state. Skeptics observe that Armstrong received his single vote from a Georgia elector. They find this improbable because Armstrong of Pennsylvania was not nationally famous—his public service to that date consisted of being a medical officer during the American Revolution and, at most, a single year as a Pennsylvania judge.
Results by state[edit]
Popular vote[edit]
This section does not cite any sources. (July 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| George Washington Federalist | George Washington Anti-Federalist | State Total | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | electoral votes | # | % | electoral votes | # | % | electoral votes | # | ||||||||
Connecticut | 7 | no popular vote | 7 | no popular vote | - | CT | ||||||||||
Delaware | 3 | 685 | 100 | 3 | no ballots | 685 | DE | |||||||||
Georgia | 5 | no popular vote | 5 | no popular vote | - | GA | ||||||||||
Maryland | 8 | 5,539 | 71.63 | 6 | 2,193 | 28.37 | - | 7,732 | MD | |||||||
Massachusetts | 10 | 17,740 | 100 | 10 | no ballots | 17,740 | MA | |||||||||
New Hampshire | 5 | 5,909 | 100 | 5 | no ballots | 5,909 | NH | |||||||||
New Jersey | 6 | no popular vote | 6 | no popular vote | - | NJ | ||||||||||
| New York | 8 | legislature did not choose electors on time | - | NY | ||||||||||||
| North Carolina | 7 | did not yet ratify Constitution | - | NC | ||||||||||||
Pennsylvania | 10 | 6,711 | 90.90 | 10 | 672 | 9.10 | - | 7,383 | PA | |||||||
| Rhode Island | 3 | did not yet ratify Constitution | - | RI | ||||||||||||
South Carolina | 7 | no popular vote | 7 | no popular vote | - | SC | ||||||||||
Virginia | 12 | 3,040 | 70.16 | 10 | 1,293 | 29.84 | - | 4,333 | VA | |||||||
| TOTALS: | 91 | 39,624 | 90.50 | 69 | 4,158 | 9.50 | 0 | 43,782 | US | |||||||
| TO WIN: | 37 | |||||||||||||||
Electoral vote[edit]
| State | Washington | Adams | Jay | Harrison | Rutledge | Hancock | Clinton | Huntington | Milton | Armstrong | Telfair | Lincoln |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Connecticut | 7 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Delaware | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Georgia | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Maryland | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Massachusetts | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| New Hampshire | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| New Jersey | 6 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pennsylvania | 10 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| South Carolina | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Virginia | 10 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 69 | 34 | 9 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Source: Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections[7]
Electoral college selection[edit]
The Constitution, in Article II, Section 1, provided that the state legislatures should decide the manner in which their Electors were chosen. Different state legislatures chose different methods:[8]
| Method of choosing electors | State(s) |
|---|---|
| electors appointed by state legislature | Connecticut Georgia New Jersey New York(a) South Carolina |
| Massachusetts |
| each elector chosen by voters statewide; however, if no candidate wins majority, state legislature appoints electors from top two candidates | New Hampshire |
| state divided into electoral districts, with one elector chosen per district by the voters of that district | Virginia(b) Delaware |
| electors chosen at large by voters | Maryland Pennsylvania |
| state had not yet ratified the Constitution | North Carolina Rhode Island |
(a)New York's legislature did not choose electors on time.
(b)One electoral district failed to choose an elector.
See also[edit]
- 1st United States Congress
- First inauguration of George Washington
- History of the United States (1789–1849)
- United States House of Representatives elections, 1788 and 1789
- United States Senate elections, 1788 and 1789
References[edit]
^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press.
^ See "Alternative methods for choosing electors" under Electoral College.
^ Meacham 2012
^ Chernow, 272-273
^ "VP George Clinton". www.senate.gov. Retrieved 2016-04-15.
^ "A New Nation Votes".
^ "1789 Presidential Electoral Vote Count". Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. Dave Leip. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
^ "The Electoral Count for the Presidential Election of 1789". The Papers of George Washington. Archived from the original on September 14, 2013. Retrieved May 4, 2005.
Bibliography[edit]
.mw-parser-output .refbegin{font-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul{list-style-type:none;margin-left:0}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>dd{margin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100{font-size:100%}
- Bowling, Kenneth R., and Donald R. Kennon. "A New Matrix for National Politics." Inventing Congress: Origins and Establishment of the First Federal Congress. Athens, O.: United States Capitol Historical Society by Ohio U, 1999. 110-37. Print.
- Chernow, Ron (2004). "Alexander Hamilton". London, UK: Penguin Books.
ISBN 978-1101200858. - Collier, Christopher. "Voting and American Democracy." The American People as Christian White Men of Property:Suffrage and Elections in Colonial and Early National America. N.p.: U of Connecticut, n.d, 1999.
DenBoer, Gordon, ed. (1990). The Documentary History of the First Federal Elections, 1788–1790. University of Wisconsin Press. ISBN 978-0-299-06690-1.
- Dinkin, Robert J. Voting in Revolutionary America: A Study of Elections in the Original Thirteen States, 1776–1789. Westport, CT: Greenwood, 1982.
Ellis, Richard J. (1999). Founding the American Presidency. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 978-0-8476-9499-0.
McCullough, David (1990). John Adams. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-1-4165-7588-7.
Meacham, Jon (2012). Thomas Jefferson: The Art of Power. Random House. ISBN 978-1-4000-6766-4.
- Novotny, Patrick. The Parties in American Politics, 1789–2016.
- Paullin, Charles O. "The First Elections Under The Constitution." The Iowa Journal of History and Politics 2 (1904): 3-33. Web. February 20, 2017.
- Shade, William G., and Ballard C. Campbell. "The Election of 1788-89." American Presidential Campaigns and Elections. Ed. Craig R. Coenen. Vol. 1. Armonk, NY: Sharpe Reference, 2003. 65-77. Print.
External links[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to United States presidential election, 1789. |
United States presidential election of 1789 at Encyclopædia Britannica
Presidential Election of 1789: A Resource Guide from the Library of Congress- A New Nation Votes: American Election Returns, 1787–1825
"A Historical Analysis of the Electoral College". The Green Papers. Retrieved February 17, 2005.
- Election of 1789 in Counting the Votes
Categories:
- George Washington
- John Adams
- History of the United States (1789–1849)
- 1789 United States presidential election
- Presidency of George Washington
- Unanimity
(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function(){mw.config.set({"wgPageParseReport":{"limitreport":{"cputime":"0.812","walltime":"1.116","ppvisitednodes":{"value":6092,"limit":1000000},"ppgeneratednodes":{"value":0,"limit":1500000},"postexpandincludesize":{"value":209004,"limit":2097152},"templateargumentsize":{"value":14357,"limit":2097152},"expansiondepth":{"value":15,"limit":40},"expensivefunctioncount":{"value":7,"limit":500},"unstrip-depth":{"value":1,"limit":20},"unstrip-size":{"value":36668,"limit":5000000},"entityaccesscount":{"value":1,"limit":400},"timingprofile":["100.00% 791.665 1 -total"," 32.51% 257.347 1 Template:Infobox_Election"," 26.82% 212.327 1 Template:Infobox"," 15.95% 126.264 3 Template:Infobox_election/row"," 12.55% 99.338 7 Template:Cite_web"," 9.39% 74.342 1 Template:National_Archives_EV_source"," 8.65% 68.515 1 Template:Refimprove"," 8.04% 63.620 2 Template:Ambox"," 7.72% 61.129 1 Template:Commons_category"," 7.03% 55.620 1 Template:Federalist/meta/color"]},"scribunto":{"limitreport-timeusage":{"value":"0.231","limit":"10.000"},"limitreport-memusage":{"value":7514203,"limit":52428800}},"cachereport":{"origin":"mw1276","timestamp":"20190327231923","ttl":2592000,"transientcontent":false}}});});{"@context":"https://schema.org","@type":"Article","name":"1788u201389 United States presidential election","url":"https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/1788%E2%80%9389_United_States_presidential_election","sameAs":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q697949","mainEntity":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q697949","author":{"@type":"Organization","name":"Contributors to Wikimedia projects"},"publisher":{"@type":"Organization","name":"Wikimedia Foundation, Inc.","logo":{"@type":"ImageObject","url":"https://www.wikimedia.org/static/images/wmf-hor-googpub.png"}},"datePublished":"2002-02-23T18:08:40Z","dateModified":"2019-03-27T23:19:24Z","image":"https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/b6/Gilbert_Stuart_Williamstown_Portrait_of_George_Washington.jpg","headline":"first United States presidential election"}(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function(){mw.config.set({"wgBackendResponseTime":136,"wgHostname":"mw1267"});});









