Particle decay
Particle decay is the spontaneous process of one unstable subatomic particle transforming into multiple other particles. The particles created in this process (the final state) must each be less massive than the original, although the total invariant mass of the system must be conserved. A particle is unstable if there is at least one allowed final state that it can decay into. Unstable particles will often have multiple ways of decaying, each with its own associated probability. Decays are mediated by one or several fundamental forces. The particles in the final state may themselves be unstable and subject to further decay.
The term is typically distinct from radioactive decay, in which an unstable atomic nucleus is transformed into a lighter nucleus accompanied by the emission of particles or radiation, although the two are conceptually similar and are often described using the same terminology.
Contents
1 Probability of survival and particle lifetime
1.1 Table of some elementary and composite particle lifetimes
2 Decay rate
3 Two-body decay
3.1 Decay rate
3.2 From two different frames
4 Complex mass and decay rate
5 See also
6 Notes
7 External links
Probability of survival and particle lifetime
Particle decay is a Poisson process, and hence the probability that a particle survives for time t before decaying is given by an exponential distribution whose time constant depends on the particle's velocity:
- P(t)=e−t/(γτ){displaystyle P(t)=e^{-t/(gamma tau )},}
- P(t)=e−t/(γτ){displaystyle P(t)=e^{-t/(gamma tau )},}
- where
τ{displaystyle tau }is the mean lifetime of the particle (when at rest), and
γ=11−v2/c2{displaystyle gamma ={frac {1}{sqrt {1-v^{2}/c^{2}}}}}is the Lorentz factor of the particle.
Table of some elementary and composite particle lifetimes
All data is from the Particle Data Group.
Type
Name
Symbol
Mass (MeV)
Mean lifetime
Lepton
Electron / Positron
e−/e+{displaystyle mathrm {e} ^{-},/,mathrm {e} ^{+}}
0000.511
>4.6×1026 years{displaystyle >4.6times 10^{26} mathrm {years} ,}
Muon / Antimuon
μ−/μ+{displaystyle mathrm {mu } ^{-},/,mathrm {mu } ^{+}}
00105.700
2.2×10−6 seconds{displaystyle 2.2times 10^{-6} mathrm {seconds} ,}
Tau lepton / Antitau
τ−/τ+{displaystyle mathrm {tau } ^{-},/,mathrm {tau } ^{+}}
01777.000
2.9×10−13 seconds{displaystyle 2.9times 10^{-13} mathrm {seconds} ,}
Meson
Neutral Pion
π0{displaystyle mathrm {pi } ^{0},}
00135.000
8.4×10−17 seconds{displaystyle 8.4times 10^{-17} mathrm {seconds} ,}
Charged Pion
π+/π−{displaystyle mathrm {pi } ^{+},/,mathrm {pi } ^{-}}
00139.600
2.6×10−8 seconds{displaystyle 2.6times 10^{-8} mathrm {seconds} ,}
Baryon
Proton / Antiproton
p+/p−{displaystyle mathrm {p} ^{+},/,mathrm {p} ^{-}}
00938.200
>1029 years{displaystyle >10^{29} mathrm {years} ,}
Neutron / Antineutron
n/n¯{displaystyle mathrm {n} ,/,mathrm {bar {n}} }
00939.600
885.7 seconds{displaystyle 885.7 mathrm {seconds} ,}
Boson
W boson
W+/W−{displaystyle mathrm {W} ^{+},/,mathrm {W} ^{-}}
80400.000
10−25 seconds{displaystyle 10^{-25} mathrm {seconds} ,}
Z boson
Z0{displaystyle mathrm {Z} ^{0},}
91000.000
10−25 seconds{displaystyle 10^{-25} mathrm {seconds} ,}
Decay rate
Note that this section uses natural units, where c=ℏ=1.{displaystyle c=hbar =1.,}
The lifetime of a particle is given by the inverse of its decay rate, Γ{displaystyle Gamma }

- dΓn=S|M|22MdΦn(P;p1,p2,…,pn){displaystyle dGamma _{n}={frac {Sleft|{mathcal {M}}right|^{2}}{2M}}dPhi _{n}(P;p_{1},p_{2},dots ,p_{n}),}
- dΓn=S|M|22MdΦn(P;p1,p2,…,pn){displaystyle dGamma _{n}={frac {Sleft|{mathcal {M}}right|^{2}}{2M}}dPhi _{n}(P;p_{1},p_{2},dots ,p_{n}),}
- where
n is the number of particles created by the decay of the original,
S is a combinatorial factor to account for indistinguishable final states (see below),
M{displaystyle {mathcal {M}},}is the invariant matrix element or amplitude connecting the initial state to the final state (usually calculated using Feynman diagrams),
dΦn{displaystyle dPhi _{n},}is an element of the phase space, and
pi{displaystyle p_{i},}is the four-momentum of particle i.
The factor S is given by
- S=∏j=1m1kj!{displaystyle S=prod _{j=1}^{m}{frac {1}{k_{j}!}},}
- S=∏j=1m1kj!{displaystyle S=prod _{j=1}^{m}{frac {1}{k_{j}!}},}
- where
m is the number of sets of indistinguishable particles in the final state, and
kj{displaystyle k_{j},}is the number of particles of type j, so that ∑j=1mkj=n{displaystyle sum _{j=1}^{m}k_{j}=n,}
.
The phase space can be determined from
- dΦn(P;p1,p2,…,pn)=(2π)4δ4(P−∑i=1npi)∏i=1nd3p→i2(2π)3Ei{displaystyle dPhi _{n}(P;p_{1},p_{2},dots ,p_{n})=(2pi )^{4}delta ^{4}left(P-sum _{i=1}^{n}p_{i}right)prod _{i=1}^{n}{frac {d^{3}{vec {p}}_{i}}{2(2pi )^{3}E_{i}}}}
- dΦn(P;p1,p2,…,pn)=(2π)4δ4(P−∑i=1npi)∏i=1nd3p→i2(2π)3Ei{displaystyle dPhi _{n}(P;p_{1},p_{2},dots ,p_{n})=(2pi )^{4}delta ^{4}left(P-sum _{i=1}^{n}p_{i}right)prod _{i=1}^{n}{frac {d^{3}{vec {p}}_{i}}{2(2pi )^{3}E_{i}}}}
- where
δ4{displaystyle delta ^{4},}is a four-dimensional Dirac delta function,
p→i{displaystyle {vec {p}}_{i},}is the (three-)momentum of particle i, and
Ei{displaystyle E_{i},}is the energy of particle i.
One may integrate over the phase space to obtain the total decay rate for the specified final state.
If a particle has multiple decay branches or modes with different final states, its full decay rate is obtained by summing the decay rates for all branches. The branching ratio for each mode is given by its decay rate divided by the full decay rate.
Two-body decay
Note that this section uses natural units, where c=ℏ=1.{displaystyle c=hbar =1.,}
@media all and (max-width:720px){.mw-parser-output .tmulti>.thumbinner{width:100%!important;max-width:none!important}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsingle{float:none!important;max-width:none!important;width:100%!important;text-align:center}}
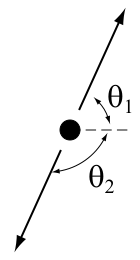

Decay rate
Say a parent particle of mass M decays into two particles, labeled 1 and 2. In the rest frame of the parent particle,
- |p→1|=|p→2|=[(M2−(m1+m2)2)(M2−(m1−m2)2)]1/22M,{displaystyle |{vec {p}}_{1}|=|{vec {p}}_{2}|={frac {[(M^{2}-(m_{1}+m_{2})^{2})(M^{2}-(m_{1}-m_{2})^{2})]^{1/2}}{2M}},,}
which is obtained by requiring that four-momentum be conserved in the decay, i.e.
- (M,0→)=(E1,p→1)+(E2,p→2).{displaystyle (M,{vec {0}})=(E_{1},{vec {p}}_{1})+(E_{2},{vec {p}}_{2}).,}
Also, in spherical coordinates,
- d3p→=|p→|2d|p→|dϕd(cosθ).{displaystyle d^{3}{vec {p}}=|{vec {p}},|^{2},d|{vec {p}},|,dphi ,dleft(cos theta right).,}
Using the delta function to perform the d3p→2{displaystyle d^{3}{vec {p}}_{2}}

- dΓ=|M|232π2|p→1|M2dϕ1d(cosθ1).{displaystyle dGamma ={frac {left|{mathcal {M}}right|^{2}}{32pi ^{2}}}{frac {|{vec {p}}_{1}|}{M^{2}}},dphi _{1},dleft(cos theta _{1}right).,}
From two different frames
The angle of an emitted particle in the lab frame is related to the angle it has emitted in the center of momentum frame by the equation
- tanθ′=sinθγ(β/β′+cosθ){displaystyle tan {theta '}={frac {sin {theta }}{gamma left(beta /beta '+cos {theta }right)}}}
- tanθ′=sinθγ(β/β′+cosθ){displaystyle tan {theta '}={frac {sin {theta }}{gamma left(beta /beta '+cos {theta }right)}}}
Complex mass and decay rate
Note that this section uses natural units, where c=ℏ=1.{displaystyle c=hbar =1.,}
The mass of an unstable particle is formally a complex number, with the real part being its mass in the usual sense, and the imaginary part being its decay rate in natural units. When the imaginary part is large compared to the real part, the particle is usually thought of as a resonance more than a particle. This is because in quantum field theory a particle of mass M (a real number) is often exchanged between two other particles when there is not enough energy to create it, if the time to travel between these other particles is short enough, of order 1/M, according to the uncertainty principle. For a particle of mass M+iΓ{displaystyle scriptstyle M+iGamma }


See also
- Relativistic Breit-Wigner distribution
- Particle physics
- List of particles
- Weak interaction
Notes
^ "The Particle Adventures"
External links
J. D. Jackson (2004). "Kinematics" (PDF). Particle Data Group..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em} - See page 2.
Particle Data Group.- "The Particle Adventure" Particle Data Group, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.






















![{displaystyle |{vec {p}}_{1}|=|{vec {p}}_{2}|={frac {[(M^{2}-(m_{1}+m_{2})^{2})(M^{2}-(m_{1}-m_{2})^{2})]^{1/2}}{2M}},,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/fbc7c73c02bf1575e86be1fea87fbd954fb29e8f)



