Seoul Subway Line 8
| Line 8 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | |||
| Overview | |||
| Native name | 8호선(八號線) Pal Hoseon | ||
| Type | Rapid transit | ||
| System | Seoul Metropolitan Subway | ||
| Status | Operational | ||
| Termini | Amsa Moran | ||
| Stations | 17[2] | ||
| Daily ridership | 87,722,000 (2013)[1] | ||
| Operation | |||
| Opened | 23 November 1996[3] | ||
| Operator(s) | Seoul Metro | ||
| Depot(s) | Moran Staton[2] | ||
| Technical | |||
| Line length | 17.7 km (11.0 mi) | ||
| Number of tracks | 2 | ||
| |||
Seoul Subway Line 8 of the Seoul Metropolitan Rapid Transit Corporation was built 1990–99 and mainly serves the southeastern parts of Seoul and Seongnam. Moran to Amsa was opened July 1999. Its color is rose.
In 2014 construction was planned to begin to extend the line north of the Han River through Guri Station to Byeollae Station on the Gyeongchun Line. The extension will add 11.37 km of line to the already existing 17.7 km. Construction is set to finish in 2023.[4] Potentially the southern end will be extended 3.9 km to Pangyo Station around 2023.
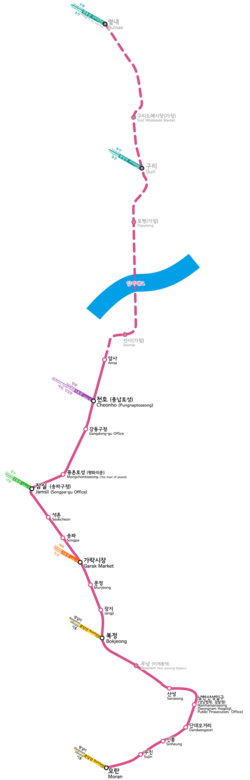
Stations
Station number | Station name English | Station name Hangul | Station name Hanja | Transfer | Line name | Distance in km | Total distance | Location | |
804 | Byeollae (October 2023) | 별내 | 別內 | Gyeongchun | Line 8 (Byeollae Line) | --- | 0.0 | Gyeonggi-do | Namyangju-si |
805 | Jingeon (October 2023) | 진건 | 眞乾 | 3.0 | 3.0 | ||||
806 | Donggureung (October 2023) | 동구릉 | 1.8 | 4.8 | Guri-si | ||||
807 | Guri (October 2023) | 구리 | 九里 | Gyeongui–Jungang | 1.2 | 6.0 | |||
808 | Topyeong (October 2023) | 토평 | 土坪 | 1.8 | 7.8 | ||||
809 | Seonsa (October 2023) | 선사 | 先史 | 3.5 | 11.3 | Seoul | Gangdong-gu | ||
810 | Amsa | 암사 | 岩寺 | Line 8 | 1.1 | 12.4 | |||
811 | Cheonho (Pungnaptoseong) | 천호 (풍납토성) | 千戶 (風納土城) | 1.3 | 13.7 | ||||
812 | Gangdong-gu Office | 강동구청 | 江東區廳 | 0.9 | 14.6 | ||||
813 | Mongchontoseong (World Peace Gate) | 몽촌토성 (평화의문) | 夢村土城 (平和의門) | 1.6 | 16.2 | Songpa-gu | |||
814 | Jamsil (Songpa-gu Office) | 잠실 (송파구청) | 蠶室 (松坡區廳) | 0.8 | 17.0 | ||||
815 | Seokchon | 석촌 | 石村 | 1.2 | 18.2 | ||||
816 | Songpa | 송파 | 松坡 | 0.9 | 19.1 | ||||
817 | Garak Market | 가락시장 | 可樂市場 | 0.8 | 19.9 | ||||
818 | Munjeong | 문정 | 文井 | 0.9 | 20.8 | ||||
819 | Jangji | 장지 | 長旨 | 0.9 | 21.7 | ||||
820 | Bokjeong | 복정 | 福井 | Bundang | 0.9 | 22.6 | |||
821 | Sanseong | 산성 | 山城 | 2.7 | 25.3 | Gyeonggi-do | Seongnam-si | ||
822 | Namhansanseong (Seongnam Court & Public Prosecutor's office) | 남한산성입구 (성남법원·검찰청) | 南漢山城入口 (城南法院·檢察廳) | 1.3 | 26.6 | ||||
823 | Dandaeogeori | 단대오거리 | 丹岱오거리 | 0.8 | 27.4 | ||||
824 | Sinheung | 신흥 | 新興 | 0.8 | 28.2 | ||||
825 | Sujin | 수진 | 壽進 | 0.9 | 29.1 | ||||
826 | Moran | 모란 | 牡丹 | Bundang | 1.0 | 30.1 | |||
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Seoul Subway Line 8. |
- Subways in South Korea
- Seoul Metropolitan Rapid Transit Corporation
- Seoul Metropolitan Subway
References
^ "Subway Passenger Transportation" (in Korean). City of Seoul. Retrieved 2014-07-14..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ ab "Operation Status". Seoul Metropolitan Rapid Transit. Retrieved 2014-08-15.
^ "History". Seoul Metropolitan Rapid Transit. Retrieved 2014-07-25.
^ Bak, Yongson (2011-05-04). "경기북부 연장 광역전철 '윤곽 잡혔다'". Yonhap News. Retrieved 7 September 2011.