Cella
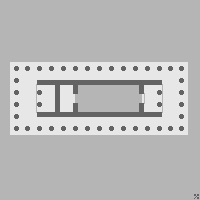
Temple layout with cella highlighted.
A cella (from Latin for small chamber) or naos (from the Greek ναός, "temple") is the inner chamber of a temple in classical architecture, or a shop facing the street in domestic Roman architecture, such as a domus. Its enclosure within walls has given rise to extended meanings, of a hermit's or monk's cell, and since the 17th century, of a biological cell in plants or animals.
Contents
1 Greek and Roman temples
2 Etruscan temples
3 Egyptian temples
4 Christian churches
5 See also
6 References
7 External links
Greek and Roman temples

Greek Temple of Apollo at Paestum with centrally located cella.

The Maison Carrée at Nîmes with its cella offset behind the hexastyle portico.
In Ancient Greek and Roman temples the cella is a room at the centre of the building, usually containing a cult image or statue representing the particular deity venerated in the temple. In addition the cella may contain a table or plinth to receive votive offerings such as votive statues, precious and semi-precious stones, helmets, spear and arrow heads, swords, and war trophies. The accumulated offerings made Greek and Roman temples virtual treasuries, and many of them were indeed used as treasuries during antiquity.
The cella is typically a simple, windowless, rectangular room with a door or open entrance at the front behind a colonnaded portico facade. In larger temples, the cella was typically divided by two colonnades into a central nave flanked by two aisles. A cella may also contain an adyton, an inner area restricted to access by the priests—in religions that had a consecrated priesthood—or by the temple guard.
With very few exceptions Greek buildings were of a peripteral design that placed the cella in the center of the plan, such as the Parthenon and the Temple of Apollo at Paestum. The Romans favoured pseudoperipteral buildings with a portico offsetting the cella to the rear. The pseudoperipteral plan uses engaged columns embedded along the side and rear walls of the cella. The Temple of Venus and Roma built by Hadrian in Rome had two cellae arranged back-to-back enclosed by a single outer peristyle.
Etruscan temples
According to Vitruvius (Book IV.7), the Etruscan type of temples (as, for example, at Portonaccio near Veio) had three cellae, side by side, conjoined by a double row of columns on the facade. This is an entirely new setup with respect to the other types of constructions found in Etruria and the Tyrrhenian side of Italy, which have one cell with or without columns, as seen in Greece and the Orient.
Egyptian temples
In the Hellenistic culture of Ptolemaic Egypt the cella referred to that which is hidden and unknown inside the inner sanctum of a temple, existing in complete darkness, meant to symbolize the state of the universe before the act of creation. The cella, also called the naos, holds many box-like shrines. The Greek word naos has been extended by archaeologists to describe the central room of the pyramids. Towards the end of the Old Kingdom, naos construction went from being subterranean to being built directly into the pyramid, above ground. The naos was surrounded by many different paths and rooms, many used to confuse and divert thieves and grave robbers.
Christian churches
In early Christian and Byzantine architecture, the cella or naos is an area at the centre of the church reserved for performing the liturgy.
In later periods a small chapel or monk's cell was also called a cella. This is the source of the Irish language cill or cell (Anglicised as Kil(l)-) in many Irish place names.
See also
- List of Greco-Roman roofs
References
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
- Trachtenberg and Hyman, Architecture:From Prehistory to Post Modernity (second edition)
External links
- Vitruvius, De architectura, Book IV. ch 7 : translation, plans and reconstructions of Tuscan cellae
| Look up cella in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |