2010 Ukrainian presidential election
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
 Results of the February 7 run-off. | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Ukraine |
|---|
 |
This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Ukraine |
Constitution |
Government
|
Judiciary
|
Elections
|
|
The Ukrainian presidential election of 2010 was Ukraine's fifth presidential election since declaring independence from the Soviet Union in 1991. The first round was held on January 17, 2010. The run-off between Prime Minister Yulia Tymoshenko and opposition leader Viktor Yanukovych followed on February 7, 2010.
On February 14, Viktor Yanukovych, with 48.95% of the popular vote, was declared President-elect and winner of the 2010 Ukrainian presidential election. According to Article 104 of Ukraine's Constitution, the President must be sworn into office within 30 days from the official declaration of the poll before the Ukrainian parliament.[1] The Ukrainian Parliament scheduled Yanukovych's inauguration for February 25.[2]
On February 17, 2010, the Supreme Administrative Court of Ukraine, suspended the results of the election on appeal from Tymoshenko. The court suspended the Central Election Commission of Ukraine ruling that announced that Viktor Yanukovych won the election, but did not postpone or cancel Yanukovych's inauguration.[3][4][5] On February 20, Tymoshenko withdrew her appeal.[6]
The 2010 election was the last Ukrainian election Crimea participated in, as it was annexed by the Russian Federation prior to the 2014 election.
Contents
1 Summary
1.1 Public opinion
2 Background
3 Law on presidential elections
4 Costs
5 Timetable
6 Nominated candidates
6.1 Excluded candidates
7 Electoral campaign
8 First round ballot
9 Second round ballot
9.1 Exit Polls
10 Issues
10.1 Fraud suspicions and accusations
11 Opinion polls
11.1 Progressive opinion polls table
12 International observers
13 Results
13.1 Electoral maps
14 References
15 External links
Summary
Early-vote returns from the first round of the election held on 17 January showed Yanukovych in first place with 35.8% of the vote.[7] He faced a 7 February 2010 runoff against Tymoshenko, who finished second (with 24.7% of the vote).
Analysts predicted a slight advantage for Tymoshenko in the second (and final) round as she was more likely to attract voters from the other 16 candidates who did not proceed to the second round.[8] Viktor Yanukovych refused to hold debates with his opponent before the second round of voting, saying Yulia Tymoshenko should either take responsibility for every word as prime minister, or go to the kitchen.[9] After all ballots were counted, the Ukrainian Central Election Commission declared that Yanukovych won the election with 48.95% of the vote compared with 45.47% for Tymoshenko.[10]Yulia Tymoshenko Bloc members immediately claimed that there was systematic and large-scale vote rigging in this run-off.[11][12][13][14]
On 10 February 2010, Yanukovych called on Tymoshenko to abandon her protests and resign as Prime Minister.[14] On 9 February 2010, Yanukovych had stated that Borys Kolesnykov was his preferred next Prime Minister of Ukraine. According to him pre-term parliamentary elections will be imminent if the Ukrainian parliament would not work effectively. Yanukovych also stated that, as the largest faction in the parliament at the time, his party was entitled to nominate the premier.[15] On 15 February, Yanukovych stated "I do not rule out the candidature of Tigipko (as next Prime Minister). Tigipko is on the list which, in my opinion, will be discussed next week in parliament".[16]
On 16 February 2010, Ukraine's parliament had fixed 25 February 2010 for the inauguration of Yanukovych as president.[17] On 17 February 2010, "the Higher Administrative Court of Ukraine", suspended the results of the election on Yulia Tymoshenko's appeal.[18][19]
On 20 February 2010, Tymoshenko withdrew her appeal after "the Higher Administrative Court of Ukraine" rejected her petition to scrutinize documents:[20]
— about 300,000 voters who voted but were not in the "Register of Voters of Ukraine";
— about 1.3 million voters who "without right" voted in their homes;
— about falsification in the election in the eastern regions (Donetsk, Luhansk, Kharkiv region, Crimea, etc.) — fixed by law-enforcement officials.[6]
Tymoshenko stated, "I and my political party will never recognize Yanukovych as the legitimately elected president of Ukraine", and "an honest court will assess that Yanukovych was not elected President of Ukraine, and that the will of the people had been rigged".[21]
Public opinion
Public Opinion Polls predicted the Party of Regions and Viktor Yanukovych's win in the 2010 Presidential election. in February 2010. According to an article in Kyiv Post in November 2009, Yanukovych's popularity in the Donbass was fading and Donbass voters voted mainly for Yanukovych to keep Tymoshenko from power.[22]
Background
In Ukraine, the previous two presidential first round ballots have traditionally occurred in October.
According to the Constitution of Ukraine, regular elections of the President of Ukraine are held on the last Sunday of the last month of the fifth year of the term of authority of the President of Ukraine. In the event of pre-term termination of authority of the President of Ukraine, elections of the President of Ukraine are held within ninety days from the day of termination of the authority.
Early presidential elections can be held in case of presidential resignation, ill-health, impeachment or death.
The President of Ukraine is elected by the citizens of Ukraine for a five-year term, on the basis of universal, equal and direct suffrage, by secret ballot.
A candidate seeking election must be a citizen of Ukraine who has attained the age of thirty-five, has the right to vote, has resided in Ukraine for the past ten years prior to the day of elections, and has command of the state language as required by Article 103 of Ukraine's Constitution.
On April 1, 2009, the Verkhovna Rada designated October 25, 2009, as the date for the first round of voting. Within a week, President Yushchenko filed an appeal with the Constitutional Court against Verkhovna Rada's October 25 date. The President's appeal argued that his inauguration on January 23, 2005, was the commencement of his five-year term of office and as such the next presidential election must be set for the last Sunday before January 23, 2010, in accordance with Article 103.[23]
On May 13, 2009, the court ruled in Yushchenko's favor, striking out the October 25th date for the elections.[24] On May 14, 2009, the Party of Regions leader Viktor Yanukovych stated that the presidential elections should now be held on January 17, 2010.[25][26][27]
On June 23, 2009, the Parliament rescheduled the date for the election for Sunday January 17, 2010, with 399 lawmakers out of 442 lawmakers registered in the session hall voted "for" the resolution "On appointing of regular election of President of Ukraine".
Minister of Internal Affairs Yuriy Lutsenko said on September 21, 2009, that he believes that the lists of voters at this presidential election will be more qualitative and more "clear" than it was at previous elections because "double names" were removed from the list.[28] The same day the Party of Regions complained about a lot of mistakes in that list and that the number of voters fell in the Southern Ukraine and Eastern Ukraine and increased by 0.5–1% in Western Ukraine.[29] It is the first time the state register of voters will be used in a Ukrainian election.[29]
Law on presidential elections
Ukraine's President is elected by a two-round first-past-the-post voting system. The first round of voting was held on January 17, 2010. As no candidate in the first round ballot had 50% or more votes the two highest polling candidates faced off in a second round ballot[30] which was held on February 7, 2010. Victor Yanukovych received the highest vote (48.96%) and is expected to be declared the winner.[31] Under Ukrainian law president elect must take the oath within 30 days of the declaration of the poll which must be made before February 17, 2010.
On July 24, 2009, the Verkhovna Rada (Ukrainian parliament) amended the law on presidential elections reducing the official presidential campaign from 120 to 90 days.[32][33][34] Outgoing President Viktor Yushchenko refused to sign the new law and lodged an appeal in Ukraine's Constitutional Court, but failed to outline in detail the grounds for any appeal.[35] The speaker of the parliament, Volodymyr Lytvyn, signed the amended law into existence following the President's refusal to sign it.
Maryna Stavniychuk, deputy head of the presidential secretariat and the President's spokesperson on legal matters stated "It is obvious that there are no serious political or legal grounds to consider the issue of the possible disruption of the presidential elections in Ukraine"
[36]
The amended law on the presidential elections required candidates to pay a 2,500,000 hryvnias (~308,000 USD) nomination deposit which will only be refunded to the two highest polling candidates that progressed to the second round of voting.
On October 19, 2009, the Central Election Commission of Ukraine formed the 225 territorial election districts needed for carrying out the election.[37]
October 20, 2009, Ukraine's Constitutional Court announced its ruling declaring unconstitutional five aspects of the new law of the presidential election. Voters abroad will no longer have to be registered with the Ukrainian consulate in order to cast a vote. The courts will retain the right to consider without limitations any application or appeal in respect to a candidate's registration or the conduct of the election. The cancellation of absentee ballots remains as does the 90-day election period and the 2.5 million hryvnia deposit. The ruling of the Constitutional Court is not expected to impact seriously on the election as the amended legislation remains in place.[38][39]
On December 21, 2009, the Central Election Commission of Ukraine formed 113 foreign polling stations.[40]
Voters are permitted to vote at home during the presidential election.[41]
Costs
The Central Election Commission has estimated the budget of the holding of regular presidential elections in Ukraine at 1.5 billion hryvnias[42] (approximately 200 million US dollars) with additional costs required by candidates to fund their campaigns.
Each candidate is required to pay an election deposit of 2.5 million hryvnias (Approximately 300,000 US dollars) The deposit will be refunded to the two highest polling candidates who progress to the second round of elections.
On November 26 the Central Election Commission stated a total of 1.314 billion hryvnias is required to hold the presidential election, including 192.2 million in 2009 and 1.122 billion in 2010.[43]
Assessments by political analysts show that each presidential candidate will have to spend at least US $150–200mn to promote himself; this includes buying story lines in the media, visual advertising, canvassing, printing political material and, work with electoral commissions.[44]
Chairman of the Committee of Voters of Ukraine, Oleksandr Chernenko, also commented that presidential candidates will spend 1 billion US dollars on the election campaign[45]
The cost of the run-off ballot is estimated to cost US$119 million[46]
Timetable
Ukraine's Central Electoral Commission (CEC) has set the following timetable for the conduct of the election:[47][48]
- October 19: Official 90-day Election Campaign period commences
- October 20 to November 6: Nominations open
- November 9: Deadline for nomination document/submissions
CEC has five days to assess and approve or reject nominations
- November 11: Deadline for candidates to submit any corrections to documentation
- November 13: CEC to finalize registration of nominations
- November 15: CEC to publish nomination lists of candidates
CEC provides certified copies of the voters list to all candidates. Within Three days of registration Candidates must provide a statement of assets and income. Candidates allowed to commence official campaign one day after registration is finalized.
- December 9: Foreign polling stations to be set up.[49]
- December 15: CEC to approve ballot paper format ready for printing.
- December 21: Deadline for withdrawals of candidature.
- January 2: Last day for public opinion polls to be published prior to election.
- January 9: All ballot papers to be printed and ready for distribution to polling stations/districts.
- January 15: Last day of public campaigning before polling day
- January 17: Election (First round ballot) Polling commences 8 am and closes 10 pm
- January 22: Tabulation of overseas and territorial polling place to be completed
- January 27: Determination of voting results and declaration of poll
As no single candidate had 50% or more of the total recorded vote the two highest polling candidates faced off in a second round ballot. The candidate with the highest vote in the second round will win the election.
- February 7: Final round run-off ballot
- February 17: Declaration of the election must be made within 10 days following the ballot or within 3 days of receipt of the official election protocols.
According to Article 104 of Ukraine's Constitution the President-elect within 30 days of the declaration of the poll must be sworn into office before Ukraine's parliament
- February 25: Viktor Yanukovych is sworn into office.
Nominated candidates
The following candidates nominated for the presidential elections (in ballot paper order)[50] A total of 18 candidates ran for president.[51]
Inna Bohoslovska, member of Verkhovna Rada, unaffiliated (block Party of Regions)[52][53][54]
Mykhaylo Brodskyy, leader of the Party of Free Democrats[55][56]
Anatoliy Hrytsenko, member of Our Ukraine, former Minister of Defense[57][58][59]
Yuriy Kostenko, Ukrainian People's Party deputy of Verkhovna Rada for Our Ukraine–People's Self-Defense Bloc[60][61]
Volodymyr Lytvyn, parliamentary speaker[62][63]
Oleksandr Moroz, Socialist Party of Ukraine, former chairman of the Verkhovna Rada[64][65]
Oleksandr Pabat, Peoples' Salvation Army[56][66]
Vasily Protyvsih, Independent[65]
Serhiy Ratushniak, Mayor of Uzhhorod[67]
Oleh Riabokon, Independent lawyer, Managing Partner in Magisters law firm from 1997 to 2009[68][69]
Petro Symonenko, Leader of the Communist Party of Ukraine[60][70]
Liudmyla Suprun, People's Democratic Party[71][72]
Yulia Tymoshenko, Incumbent Prime Minister leader of Yulia Tymoshenko Bloc[73][74]
Sergei Tigipko, former CEO of the National Bank of Ukraine endorsed by Labour Ukraine[75][76][77][78]
Oleh Tyahnybok, All-Ukrainian Union "Freedom", deputy of the Lviv Regional Council[79][80]
Viktor Yushchenko, Incumbent President and member of Our Ukraine[81][82]
Viktor Yanukovych, Party of Regions former Prime Minister and runner-up candidate in the 2004 presidential election[83][84]
Arseniy Yatsenyuk, former Chairman of the Verkhovna Rada member of Our Ukraine and Front for Change party[85][86][87][88]
Excluded candidates
All together the Central Election Commission had rejected sixteen applications for candidate registration[89]
The Central Election Commission refused to register Oleksandr Hordiichuk, Olena Osnach, Oleksandr Luzan, Hanna Kostiv, Oleksandr Vaschenko, Oleksandr Ohorodnikov, Vasyl Handula, Yurii Petlevana, Petro Rekalo, Anatolii Polischuk, Mykhailo Hamaniuk, Oleksandr Vretyk, Artem Polezhaka, Oleh Omelchenko, Natalia Vitrenko,[71]Mykola Melnychenko, Serhii Martyian and Serhiy Schetinin. The reason stated was due to errors in their documentation, qualifications or failure to pay the required 2.5 million hryvnia nomination deposit.[90][91][92][93]
Nominations closed on November 9, 2009. The Central Election Commission had until November 11 to process nomination documentations and November 13 to finalize the election list.
Electoral campaign

Yatsenyuk promotion (August 2009)

"She Works" billboard (August 2009)
Нет Ворюле!, anti-Tymoshenko placard,
rally Dnipropetrovsk, 25 Dec 2009
Concert and rally for Yanukovych,
Dnipropetrovsk, 25 Dec 2009
The official presidential campaign commenced on October 19, 2009, with nominations opening on October 20 through to November 6. The "unofficial" campaign had already started during the summer of 2009 with tents of Front for Change distributing campaign material for Arseniy Yatsenyuk Front for Changes and large scale and billboards stating Others make problems. She Works (in the colors and letter type of Bloc Yulia Tymoshenko), and photos of Sergei Tigipko displayed in most Ukrainian towns and TV-adds of Yulia Tymoshenko and Volodymyr Lytvyn shown on national TV.[94][95] According to Tymoshenko the "She Works" billboards were paid for by the Fatherland Party, and therefore they were also "social". Party of Regions deputy Andry Paruby officially requested that the prosecutor-general's office investigates the sources of financing of Tymoshenko's advertisements. He suggested that public money might have been used.[95]
Ukraine has proven more than once the degree to which the success of an election campaign depends on the level of professionalism and political spin techniques applied in election campaigns.[96]
The most popular candidates are former Prime Minister and leader of the Opposition party Viktor Yanukovych and current Prime Minister Yulia Tymoshenko.
Incumbent President Viktor Yushchenko's support has slumped from a high of 52% in 2004 to below 3% in Ukrainian public opinion polls. Most political commentators regard him as a heavy underdog who stands little chance of being re-elected to a second term of office.[97] A recent public opinion poll indicated that 83% of Ukrainians will not vote for Yushchenko.[98]
On April 5, 2009, Arseniy Yatseniuk, former Chairman of the Verkhovna Rada, announced his intention to run in the election.[99] His popularity has slowly risen to around 12–14% and is now in third place behind Yanukovych and Tymoshenko.[100]
According to Oxford Analytica the working relationship between President Yushchenko and his Prime Minister Tymoshenko will be further complicated by the search of Yushchenko for partners other than Tymoshenko's Bloc Yulia Tymoshenko who will ensure his re-election.[101] Since Yushchenko dismissed Tymoshenko as Prime Minister on September 8, 2005, the relations between Tymoshenko and Yushchenko,[102][103][104][105] including the Secretariat of the President of Ukraine,[106] have been hostile.[107] In an interview with the Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung of 11 February 2009 Tymoshenko said her recent conflict with the President is a political competition and not ideological antagonisms and she emphasized that the "election struggle for the next presidential elections has virtually begun."[108] During a visit to Brussels on February 10, 2009, Chairman of the Verkhovna Rada Volodymyr Lytvyn seconded that.[109] In late February 2009, President Yushchenko called on all Ukrainian politicians to "stop the presidential election campaign until July 1."[110][111]
On June 16, 2009, Tymoshenko accused Yushchenko, Yatseniuk and Yanukovych of having the same campaign headquarters financed by (businessman and) RosUkrEnergo owner Dmytro Firtash.[112][113][114]
Tymoshenko stated on June 22, 2009: "There is a team work on solving these issues between the President and the Prime Minister. Professional advice and support of the President will help the government during difficult times".[115]
On August 11, 2009 Russian President Medvedev in an open letter[116] directed at Viktor Yushchenko, raised a number of issues of concern related to the perceived "anti-Russian position of the current Ukrainian authorities". The Russian President's comments[117] were considered by analysts and others including the President of Ukraine as Russia's interference in Ukraine's domestic affairs.[118][119][120][121][122][123][124]
On September 12, 2009, a tour called "With Ukraine in Heart" in support of Yulia Tymoshenko kick-started on Kiev's Maidan Nezalezhnosti. The most popular singers and bands of Ukraine took part in the tour.[125][126][127]
On September 14, 2009, the Communist Party of Ukraine, the Social Democratic Party of Ukraine (united), the Justice Party and the Union of Leftists signed an agreement on creating the bloc of leftists and center-leftists and a unitary participation in the presidential election.[128][129]
The Pechersky district court in Kiev on September 22, 2009, banned "any unfair advertisement" against Tymoshenko in response to a video (allegedly made by the Party of Regions), which claimed that Tymoshenko does not deliver on her promises. The video reportedly mocked Tymoshenko's main campaign slogan "She Works," which is frequently used in her advertisements.[95]
In October 2009 representatives of the Western Ukrainian intelligentsia called upon the candidates Yushchenko, Yatseniuk, Hrytsenko and "other representatives of national democratic forces" to withdraw in favour of Tymoshenko.[130]
On October 6, 2009, the incumbent President Yushchenko warned that there may be attempts to use regional television and radio companies to create advantages for the government in the election campaign.[131]
October 17, 2009, The Social-Democratic Party of Ukraine has backed a decision to create the bloc of left and center-left political forces and supported the leader of the Communist Party of Ukraine Petro Symonenko as a single candidate for the post of the Ukrainian president from left political forces[132]
October 19 Official start of the Elections campaign 90-day period.
October 20 Candidate nomination registration opens. Oleh Riabokon first candidate to officially nominate.
October 20, Ukrainian Parliament voted to amend Ukraine's Constitution (390 out of 438 in favor) to remove provision related to Parliamentary immunity that prevents a member of parliament from being criminally liable, detained or arrested without the consent of the Verkhovna Rada. An earlier proposal to only remove immunity from the Parliament was defeated. The proposed new provisions also limits presidential immunity. The president can not be detained or arrested without the consent of the parliament however on conviction of an offense the President automatically loses office. The proposed amendments have been forwarded to Ukraine's Constitutional Court for review and will need to be reaffirmed by the parliament in February 2010 [133]
Political Analyst and senior policy fellow at the European Council on Foreign Relations, Andrew Wilson, has cast doubt on Arseny Yatseniuk, currently Ukraine's third most popular candidate, ability to maintain his meteoritic rise following a decline in his ratings dropping from a high of 13% in August to 9% in October. "Yatseniuk must look to plan B"[134]
On November 6 the nominations were closed. The same day a Viktor Yushchenko aide amidst concern over the recent flu outbreak which claimed 97 lives has proposed the cancellation of the January election until May 2010 which would extend the President's term of office a further six months.[135] The World Health Organization has stated that they expect a second and third wave of infections to occur in Spring (April to June) [136] bringing into further doubt Yushchenko's proposed cancellation. Under Ukraine's Constitution the elections can be canceled if a State of Emergency is declared. Also on November 6. 2009 the Emergencies Ministry stated it saw no grounds to introduce a state of emergency in Ukraine due to the flu epidemic.[137] On November 9 President Yushchenko said the same.[138][139]
Serhy Lutsenko, the deputy head of the People's Self-Defense party expressed on November 11, 2009, concern that Viktor Yushchenko will support his past rival, Viktor Yanukovych, in a run-off election between Yanukovych and Tymoshenko.[140]
On December 3, 2009, the Ukrainian National Council on Television and Radio Broadcasting complained that certain TV channels did not give equal conditions to all presidential candidates.[141]
On December 11, 2009, the European People's Party EPP called on "Ukraine's democratic forces" to unite around the most democratic candidate who will win through to the presidential run-off. All-Ukrainian Union "Fatherland", the Our Ukraine People's Union, and the People's Movement of Ukraine (Rukh) are the EPP's partners in Ukraine.[142]
On December 11, 2009, candidate Viktor Yanukovych stated that his Party of Regions possesses information that "government representatives are currently "motivating" the chairmen of election commissions and seeking options for victory in every possible way" and called for his supporters go to the Maidan Nezalezhnosti in case of election fraud.[143]
Bloc Yulia Tymoshenko proposes a referendum on the format of Constitutional reform - Parliamentary versus Presidential system of governance.[144]
First round ballot
The first round ballot was held on January 17 and was internationally widely recognized as meeting democratic standards.
As no single candidate had received 50% or more votes in the first round ballot the two highest polling candidates, Viktor Yanukovych (35.32%) and Yulia Tymoshenko (25.05%) progressed to the second final run-off ballot which was held on February 7, 2010.
Ukraine's incumbent president, Viktor Yushchenko, with 5.45% support, came in fifth place behind Serhiy Tihipko and Arseniy Yatsenyuk who had each respectively received 13.05% and 6.69% of the vote.
Peter Simonenko, Volodymyr Lytvyn, Oleh Tyahnybok and Anatoliy Hrytsenko all scored between 4 and 1% of the votes. The remaining nine candidates for the presidency gained less than 1% of the votes.[145]
Second round ballot
The second round of voting between Viktor Yanukovych and Yulia Tymoshenko took place on February 7, 2010. Exit polls indicated that Yanukovych had been elected, with the National Election Poll placing him first at 48.7% of the vote to Tymoshenko's 45.5%.[146]
With 100% of the ballots counted, the tally was 12,481,268 votes for Yanukovich (48.95%) and 11,593,340 votes for Tymoshenko (45.47%), giving Yanukovich a lead of 3.48%.[147] There were 1.19% invalid votes and 4.36% of voters chose to vote "Against all" (candidates).[147] In Kiev, the number of voter choosing "Against all" was close to 8%.[148] 25.5 million Ukrainians voted in the second round.[149]
The Ukrainian Central Election Commission and international observers found no evidence of significant electoral fraud and said that the voting and counting was fair.[150]Tymoshenko's party said that it would challenge the result in 1,000 of the country's 30,000 ballot boxes (as many as 900,000 ballots – enough to make a difference in the final outcome[151]), claiming that the counting process was unfair.[150] Violations cited by Tymoshenko's camp included home voting and the busing of voters to polling stations,[151] which was explicitly permitted by law.
Yanukovich's party activists rallied outside the buildings of the Higher Administrative Court of Ukraine and the Kiev Administrative Court of Appeals the days after the second round of the election.[152]
A few days after the election, Yanukovich received congratulations from the leaders of Armenia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Bulgaria, China, Egypt, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Israel, Italy, Kazakhstan, Latvia, Libya, Lithuania, Republic of Macedonia, Moldova, the Netherlands, Paraguay, Poland, Portugal, Russia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Tajikistan, Turkey the United Kingdom, the United States, Uzbekistan, NATO and the European Union.[153][154][155][156][157] Still, Tymoshenko refused to concede defeat, and Tymoshenko's party promised to challenge the result.[158] On February 17, 2010 the Administrative Court of Ukraine, suspended the results of the election on Yulia Tymoshenko's appeal. The court suspended the Central Election Commission of Ukraine ruling that announced that Viktor Yanukovych won the election.[18][19] Tymoshenko withdrew her appeal on February 20, 2010 after the Higher Administrative Court in Kiev rejected her petition to scrutinize documents from election districts in Crimea and also to question election and law-enforcement officials.[6] The same day (February 20) Tymoshenko announced that she will not challenge the results of the second round of the presidential election in the Supreme Court of Ukraine since she believed there were no legal provisions for such an appeal,[159] although Tymoshenko also stated "an honest court will assess that Yanukovych wasn't elected President of Ukraine, and that the will of the people had been rigged".[21]
Voting analysis showed that during the election creases started to emerge across the traditional geographical voters patterns. Tymoshenko made inroads in Yanukovych's traditional east and south Ukraine base of support, whereas Yanukovych did the same in Tymoshenko's traditional west and central Ukraine base of support.[160] More women voted for Yanukovych than for Tymoshenko.[161]
Exit Polls
All exit polls conducted during the final round of voting reported a win for Viktor Yanukovych over Yulia Tymoshenko.[162][163][164]
Polling Agency | Viktor Yanukovych | Yulia Tymoshenko |
|---|---|---|
| National Exit Poll | 48.7 | 45.5 |
| TRK Ukraina | 48.6 | 45.7 |
| ICTV | 49.8 | 45.2 |
| SOCIS | 49.6 | 44.5 |
| FOM Center for Social and Marketing Research | 49.7 | 44.6 |
| Research & Branding group | 50.2 | 44.0 |
| Interfax-Ukraine | 51.0 | 41.0 |
Issues
The list of major issues raised in the campaign included
- The economy[165]
- Health
- Housing
- Ukraine's membership of NATO and CSTO[166]
- European Integration
Ukraine-Russia relations[167][168]
- Constitutional Reform
Euro 2012 Football Tournament- The status of the Russian language
According to the Director of the Penta Center for Political Studies Volodymyr Fesenko there were only small differences in the election programs of the various candidates.[169]
Fraud suspicions and accusations
According to all international organizations observing the election, allegations of electoral fraud in relation to the first round ballot were unfounded, they declared that the conduct of the elections was within internationally recognized democratic standards and a testament to the will of the people of Ukraine.[170][171][172]
A December 2009 poll found that 82 percent of Ukrainians expected vote rigging, those fears were shared by some election observers, both international and domestic. The latter also fearing the lack of an independent exit poll; which they see as essential to deterring vote fraud.[173]
Yulia Tymoshenko, Ukraine's Prime-minister and one of the main candidates who sought election in the poll stated that: "We will not challenge any election returns to avoid tremors, which may bring about instability in this country. If the people elect their president, and this is not Yulia Tymoshenko, I will take this choice easy, for sure"[174]
Former President Leonid Kuchma also excluded the possibility of a third round ballot. According to Kuchma, "during the election campaign in 2004 the decision about holding the third round was political and it will not be repeated. The 2004 decision was an exclusion from a rule".[175]
Viktor Baloha, former presidential secretary under Viktor Yushchenko stated:
- "Alarming declarations about the likely vote rigging directly point to organizational weaknesses of some candidates as the law allows for reliable barriers against any electoral fraud. For instance, any presidential candidate can send his two representatives to sit on local and regional electoral commissions, appoint observers to keep an eye on voting and counting of ballots. Proxies of candidates who have wide authority can also supervise the course of the voting". "There are more than enough supervisory tools. Other effective barriers to electoral fraud are the Central Election Commission [whose members are appointed by major parliamentary parties on a quota principle] and numerous international observers. Mass media and NGOs, notably, the Committee of Voters of Ukraine, will also be effective in helping to curb fraud. Of great importance for establishing the final tally are also exit polls run by respected polling companies.they will all be used during the campaign." adding that "All the more so that there are 18 presidential candidates, some having considerable weight. That is why any declarations about the likely fraud are just attempts to justify a defeat of those who make them. Note that those candidates who are selling themselves as strong-willed and tough are most given to such declarations. In fact, such declarations expose them as would-be losers and outsiders"[176]
Candidates Victor Yanukovych and Yulia Tymoshenko both accused the other of intending to use vote rigging to win the election during the election campaign.[177][178] Early January 2010 Ukrainian President Viktor Yushchenko warned that there is a real threat of "administrative pressure" being applied during the counting of votes at the presidential election. Viktor Yushchenko without providing any details has alleged that the highest threat of falsification in the first round will be applied by Yulia Tymoshenko Bloc; "because candidate Viktor Yanukovych will enter the second round in any case".[179]
Allegations were made that Viktor Yushchenko had made a deal with Viktor Yanukovych in order to secure a number of political positions for members of his team in exchange for supporting Viktor Yanukovych's campaign [180] Concern has been expressed that Viktor Yushchenko had tried to prevent news of the deal from being published by declaring it a State Secret.[181]
A joint poll conducted by Democratic Initiatives and Ukrainian Sociology Service of January 2010 showed that less than 5% of the polled believed that the presidential election would be fair with 41.4% of respondents that believed that the election results could be manipulated and 15.7% being certain that the entire vote would be rigged.[182] According to the same poll 5.8% of those polled stated they were ready to sell their votes if the sum suited them and 1.9% of the respondents were ready to sell their votes for any presidential candidates and for any funds.[183]
A voter casting more than one ballot, or selling her/his vote, could have faced as much as two years jail time.[184]
Opinion polls
January 2, 2010, was the beginning of the 15-day media blackout on reporting of election polls before the January 17 first round election.[185]
A poll released December 15, 2009, by the International Foundation for Electoral Systems has indicated that Viktor Yanukovych (31%) as the most likely to win the presidential election in a contest with Yulia Tymoshenko (19%).[186] All other candidates were below 5% with Victor Yushchenko on 3.5% with a negativity rating of 83%. The survey also indicated that Ukrainians are pessimistic about the socio-political situation in the country. Seventy-four percent believe Ukraine is on a path toward instability and more than nine in ten Ukrainians are dissatisfied with the economic (96%) and political situation (92%) in the country.
According to other recent opinion polls, the Party of Regions candidate Viktor Yanukovych (25.0% to 33.3%) was placed first among viable presidential candidates, with Prime Minister Yulia Tymoshenko (15.5% to 18.4%) coming in second, and Front for Change candidate Arseniy Yatsenyuk (6.7% to 14.5%) in third place. Incumbent President, Viktor Yushchenko (2.0% to 3.8%) following his decline in popularity with the Ukrainian public comes in at a distant sixth place behind leader of the Communist Party Petro Symonenko (3.4% to 4.5%) and Parliamentary speaker Volodymyr Lytvyn (1.4% to 5.8%).[187][188]
A survey conducted by U.S.-based International Foundation for Electoral Systems and financed by the United States Agency for International Development (November 21 to 29) lists Viktor Yushchenko as the highest negativity rating (83%) and Viktor Yanukovych with the most positive rating (42%) [189]
An opinion poll conducted by FOM-Ukraine in September/October 2009 expected the turnout to be at least 85.1%.[190] The poll carried out by the Oleksandr Yaremenko Institute for Social Research in December 2009 predicted (at least) a 70% turnout.[191]
Media were prohibited by Ukrainian law from reporting the results of public opinion polls for the election (starting) from January 2 until election day on January 17, 2010.[192]
Progressive opinion polls table
| Conducted by Candidate Party | 2004 Presidential election | FOM – Ukraine | FOM – Ukraine | Razumkov Centre | USS | SOCIS | Institute of social and political psychology | Razumkov Centre | Research & Branding Group | KMIS | FOM – Ukraine | FOM – Ukraine | Research & Branding Group | Ukrainian Project System | SOCIS | Research & Branding Group | SOCIS | FOM – Ukraine | Research & Branding Group | Research & Branding Group | KIIS | FOM – Ukraine | Research & Branding Group | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date from | 31-Oct-04 | 14-Dec-07 | 25-Jan-08 | 31-Jan-08 | 16-Apr-08 | 30-Aug-08 | 24-Nov-08 | 17-Dec-08 | 1-Apr-09 | 03-Apr-09 | 13-Apr-09 | 17-May-09 | 12-Jun-09 | 21-Jul-09 | 24-Jul-09 | 4-Aug-09 | 20-Sep-09 | 26-Sep-09 | 12-Oct-09 | 17-Nov-09 | 21-Nov-09 | 22-Nov-09 | 5-Dec-09 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Date to | 26-Dec-04 | 23-Dec-07 | 02-Feb-08 | 05-Feb-08 | 04-May-08 | 08-Sep-08 | 30-Nov-08 | 24-Dec-08 | 9-Apr-09 | 12-Apr-09 | 25-Apr-09 | 26-May-09 | 22-Jun-09 | 20-Jul-09 | 04-Aug-09 | 14-Aug-09 | 01-Oct-09 | 04-Oct-09 | 31-Oct-09 | 25-Nov-09 | 29-Nov-09 | 30-Nov-09 | 13-Dec-09 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reference | * | [193] | [194] | ** | [195] | ** | [196] | [197] | [198] | ** | [199] | [200] | [201] | [202] | ** | [203] | [204] | ** | [205] | ** | [206] | ** | [207] | [208] | ** | [209] | ** | [210] | ** | [211] | ** | [212] | ** | ||||||||||||||||
Viktor Yanukovych | PoR | 39.3 | 44.2 | 24.4 | 20.0 | 22.8 | 27.0 | 41.0 | 25.1 | 34.6 | 20.7 | 19.8 | 27.9 | 38.4 | 25.6 | 21.9 | 26.6 | 26.8 | 38.8 | 24.0 | 25.0 | 26.1 | 26.0 | 39.6 | 28.7 | 40.3 | 26.8 | 31.0 | 41.9 | 32.4 | 47.4 | 31.2 | 42.0 | 29.8 | 41.0 | 33.3 | 46.7 | ||||||||||||
Yulia Tymoshenko | BYuT | 19.8 | 24.8 | 25.9 | 26.0 | 44.0 | 26.0 | 32.7 | 17.9 | 15.8 | 15.6 | 29.3 | 14.4 | 15.3 | 16.2 | 16.8 | 28.8 | 12.8 | 20.5 | 24.4 | 16.5 | 28.0 | 19.0 | 32.6 | 15.6 | 18.4 | 29.8 | 16.3 | 28.1 | 19.1 | 28.0 | 14.8 | 25.2 | 16.6 | 30.0 | ||||||||||||||
Sergei Tihipko | 1.4 | 2.6 | 1.6 | 3.6 | 4.4 | 4.8 | 5.7 | 7.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Arseniy Yatsenyuk | Y-Front | 2.6 | 4.6 | 6.6 | 13.4 | 13.6 | 13.8 | 12.8 | 12.3 | 5.7 | 14.5 | 12.6 | 8.2 | 9.3 | 9.6 | 6.1 | 4.7 | 4.8 | 6.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Volodymyr Lytvyn | LPB | 3.1 | 3.7 | 6.0 | 4.9 | 3.8 | 5.4 | 5.5 | 2.9 | 3.5 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 8.7 | 5.9 | 4.2 | 2.8 | 1.4 | 2.3 | 4.5 | 2.8 | 2.5 | 4.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Viktor Yushchenko | OU | 39.9 | 52.0 | 12.7 | 13.1 | 14.5 | 8.0 | 6.5 | 3.9 | 4.5 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 2.2 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 2.9 | 3.8 | 2.0 | 2.8 | 2.2 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 4.3 | 3.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Petro Symonenko | CPU | 5.0 | 3.7 | 4.2 | 4.3 | 5.0 | 5.3 | 3.8 | 3.3 | 4.3 | 3.4 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.7 | 4.5 | 3.6 | 4.0 | 3.5 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 2.9 | 3.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Inna Bohoslovska | 3.0 | 1.3 | 0.8 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Oleksandr Moroz | SPU | 5.8 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.4 | <1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Oleh Tyahnybok | AUUF | 0.9 | 0.9 | 2.3 | 2.0 | 1.9 | 1.5 | 1.0 | 1.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Anatoliy Hrytsenko | OU | 0.4 | <1 | 0.7 | 0.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others | 8.0 | 1.3 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 2.1 | 6.9 | 10.4 | 2.6 | 7.3 | 0.2 | 3.0 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 3.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Against all | 2.0 | 3.8 | 7.9 | 6.1 | 6.7 | 7.9 | 9.0 | 19.0 | 11.1 | 8.0 | 16.6 | 9.9 | 19.0 | 9.4 | 17 | 15.2 | 6.8 | 7.5 | 7.9 | 18.0 | 12.7 | 20.7 | 9.0 | 13.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Will Not vote | 7.2 | 8.0 | 11.0 | 8.6 | 8.2 | 9.4 | 5.6 | 8.9 | 9.0 | 6.6 | 6.8 | 1.4 | 6.7 | 6.8 | 4.3 | 4.5 | 5.0 | 3.5 | 3.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not sure | 15.1 | 18.1 | 11.9 | 33.0 | 8.1 | 7.4 | 5.0 | 13.6 | 12.6 | 9.4 | 6.8 | 10.4 | 6.4 | 20.3 | 8.8 | 6.7 | 9.0 | 15.9 | 7.5 | 11.6 | 9.0 | 6.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| sum | 100.0 | 100.0 | 87.1 | 97.7 | 90.4 | 100.0 | 85.0 | 100.0 | 67.3 | 58.5 | 59.6 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 96.3 | 83.9 | 63.8 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 59.5 | 80.2 | 50.5 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 85.5 | 100.3 | 100.0 | 87.0 | 100.0 | 88.0 | 77.5 | 86.9 | 100.0 | 100.0 | ||||||||||||||
| balance | 0 | 0 | 12.9 | 2.3 | 9.6 | 0.0 | 15.0 | 0 | 32.7 | 41.5 | 40.4 | 0 | 0 | 3.7 | 16.1 | 36.2 | 0 | 0 | 40.5 | 19.8 | 49.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14.5 | -0.3 | 0 | 13.0 | 0 | 12.0 | 22.5 | 13.1 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||||||
| Respondents | 2000 | 2010 | 2040 | 2000 | 2017 | 2078 | 1984 | 1000 | 1000 | 2079 | 2511 | 2000 | 3011 | 5009 | 1000 | 3118 | 3108 | 1502 | 1000 | 3038 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Margin for error | 2.2% | 2.2% | 2.0% | 2.3% | ± 2.2% | ≤ 4.0% | ≤ 4.0% | ± 2.2% | 2.0% | 2.8% | ± 2.2% | ± 1.5% | 4% | ± 2.2% | ± 2.2% | ± 2.5% | ± 3.2% | ± 1.8% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| * 2004 presidential election final results. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ** Notional second round of presidential elections. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 18, 2007, Tymoshenko elected as Prime Minister of Ukraine.[213] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
International observers
The Ukrainian Foreign Ministry expected (in November 2009) that some 600 international observers will be monitoring the elections.[214] The Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) will send around 60 long-term and 600 short-term observers to Ukraine to monitor the presidential elections, Ukraine had submitted an invitation to the OSCE to monitor the elections.[215]
This electoral observation mission is headed by Portuguese politician João Soares, President of the OSCE Parliamentary Assembly. The OSCE/ODIHR long term observation mission was officially opened on November 26, 2009.[216] On January 12, 2009, the OSCE where not satisfied with the level of funding for salaries and transport services.[217]
The European Union member-states will send over 700 observers to monitor the elections.[218] The Canada Ukraine Foundation[219] (a Canadian NGO[220]) and the Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe (PACE) will also send observers.[221] The PACE delegation is led by Hungarian politician Mátyás Eörsi.[222] Late November the PACE delegation was sceptical the elections would meet the organization's standards.[222] On December 8, 2009 Renate Wohlwend, co-rapporteur of PACE stated that PACE might continue to monitor Ukrainian politics after the country's presidential election.[223] Wohlwend had also called on the Ukrainian parliament to amend a law on the presidential elections as soon as possible. Wohlwend expressed concern over the inclusion of a provision in Ukraine's electoral legislation giving the election commission the right to amend the electoral rolls on the day of the ballot. She expressed concern this could allow the rigging of the election results.[224]
The Polish European Center of Geopolitical Analysis did send 20 observers to monitor signs of xenophobia during the presidential election campaign.[225]
On December 9, 2009, candidate Victor Yanukovych at a meeting with an OSCE election observation mission stated that he is afraid Prime Minister Yulia Tymoshenko might rig the presidential election.[226]
A total of 450 official observers from the European Network of Election Monitoring Organizations (ENEMO) will monitor the elections.[227]
Paweł Kowal lead the delegation of the European Parliament's observers; this delegation included ten people, who cooperated closely with the delegations of observers from the OSCE Parliamentary Assembly, the Council of Europe, the NATO Parliamentary Assembly, and the OSCE Office for Democratic Institutions and Human Rights (ODIHR).[228]
A total of 3,149 international observers did monitor the January 17 presidential election in Ukraine.[229][230]
On January 18, 2010, the OSCE announced it would send same number of observers to monitor Ukraine's second round of the election as in the first round.[231] At the same time it called for bringing Ukraine's election laws in line with international norms[232] but nevertheless it endorsed the first round of the Ukrainian presidential poll, saying it was of "high quality" and demonstrated "significant progress".[233]
After the second round of the election international observers and the OSCE called the election transparent and honest.[158]
According to Serhiy Paskhalov, the head of presidential candidate Yulia Tymoshenko's main campaign office in Dnipropetrovsk, international observers were physically unable to register mass irregularities in the second round of the presidential election. According to Paskhalov six foreign observers had monitored the run-off presidential election at 469 polling stations in six electoral districts in Dnipropetrovsk region.[234]
Results
Nominations by parties and candidates to run in the election closed on November 6, 2009.[47] Eighteen candidates in all have been nominated. The Central Election Committee had until November 11, 2009, to process documentation and finalize the election list.
The first round of the election was held on January 17, 2010. Voter turnout was approximately 67 percent, compared to 75 percent at the 2004 presidential election. Incumbent president Viktor Yushchenko was defeated having received only 5.45% of the vote.[235][236][237]Viktor Yanukovych and Yulia Tymoshenko [238] finished first and second in the first round and faced each other in the second round ballot held on February 7. Voter turnout in the second round was approximately 69%. On February 14, with all second round votes counted, Yanukovich was officially declared a winner of the election with 48.95%, compared to Tymoshenko's 45.47%.[238]
The election has been widely recognized and endorsed as being fair and an accurate reflection of voters' intentions by all international agencies observing the election including the OSCE and PACE.[239][240]
| Candidates | Nominating Party | First round[241] | Second round[242] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | Votes | % | |||||
Viktor Yanukovych | Party of Regions | 8,686,642 | 35.32 | 12,481,266 | 48.95 | |||
Yulia Tymoshenko | All-Ukrainian Union "Fatherland" | 6,159,810 | 25.05 | 11,593,357 | 45.47 | |||
Serhiy Tihipko | Self-nominated | 3,211,198 | 13.05 | |||||
Arseniy Yatsenyuk | Self-nominated | 1,711,737 | 6.96 | |||||
Viktor Yushchenko | Self-nominated | 1,341,534 | 5.45 | |||||
Petro Symonenko | Communist Party of Ukraine | 872,877 | 3.54 | |||||
Volodymyr Lytvyn | People's Party | 578,883 | 2.35 | |||||
Oleh Tyahnybok | All-Ukrainian Union "Freedom" | 352,282 | 1.43 | |||||
Anatoliy Hrytsenko | Self-nominated | 296,412 | 1.20 | |||||
Inna Bohoslovska | Self-nominated | 102,435 | 0.41 | |||||
Oleksandr Moroz | Socialist Party of Ukraine | 95,169 | 0.38 | |||||
Yuriy Kostenko | Ukrainian People's Party | 54,376 | 0.22 | |||||
Liudmyla Suprun | People's Democratic Party | 47,349 | 0.19 | |||||
Vasily Protyvsih | Self-nominated | 40,352 | 0.16 | |||||
Oleksandr Pabat | Self-nominated | 35,474 | 0.14 | |||||
Serhiy Ratushniak | Self-nominated | 29,795 | 0.12 | |||||
Mykhaylo Brodskyy | Self-nominated | 14,991 | 0.06 | |||||
Oleh Riabokon | Self-nominated | 8,334 | 0.03 | |||||
| Against all | 542,819 | 2.20 | 1,113,055 | 4.36 | ||||
| Invalid | 405,789 | 1.65 | 305,837 | 1.19 | ||||
Total | 24,588,268 | 100.00 | 25,493,529 | 100.00 | ||||
| Source: Central Election Commission of Ukraine | ||||||||
Electoral maps
 |  |  |
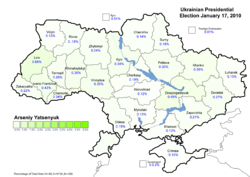 |  |  |
 |  |
Note: The above maps are based on the percentage of the national vote and as such is an accurate representation of the results of the election as each region is shown in relation to the overall result.
References
^ CEC official declaration of the 2010 Presidential election[permanent dead link], Central Election Commission of Ukraine
^ Update: Yanukovych to be sworn in, rival fights on, Kyiv Post (February 14, 2010)
^ https://www.nytimes.com/2010/02/18/world/europe/18ukraine.html High Court in Ukraine Weighs Appeal on Election
^ Ukrainian election results suspended on appeal
^ Ukrainian election result suspended after PM's appeal
^ abc Ukraine Prime Minister Drops Election Challenge, New York Times (February 20, 2010)
^ Marson, James (18 January 2010). "Ukrainian Presidential Election Set for Runoff". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 2010-01-18..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Analysts say exit poll results favor Tymoshenko win on Feb. 7, Kyiv Post (18 January 2010)
^ [1], The Financial (1 February 2010)
^ (in Ukrainian)Regular elections of the President of Ukraine 17/01/2010 Archived 2010-01-21 at the Wayback Machine, Central Election Commission of Ukraine
^ Turchynov: vote rigging in favor of Yanukovych was systematic, large-scale, Kyiv Post (10 February 2009)
^ Nataliya Korolevska: victory will be ours Archived 2014-08-15 at the Wayback Machine, Yulia Tymoshenko official website (8 February 2009)
^ Andriy Shevchenko: whole gamut of fraud in Donbas Archived 2014-08-15 at the Wayback Machine, Yulia Tymoshenko official website (8 February 2009)
^ ab Ukraine election: Yanukovych urges Tymoshenko to quit, BBC News (10 February 2009)
^ "Yanukovych opts for Borys Kolesnykov to become premier", Z I K (9 February 2010)
^ Yanukovych does not rule out Tigipko as prime minister, Kyiv Post (15 February 2010)
^ Update: Ukraine's Yanukovych to be sworn in on Feb. 25, Kyiv Post (16 February 2010)
^ ab ["Ukrainian election results suspended on appeal". Google News. Associated Press. 17 February 2010. Archived from the original on 21 February 2010.
^ ab "Ukrainian election result suspended after PM's appeal". BBC News. 17 February 2010. Retrieved 18 January 2016.
^ Yulia Tymoshenko will not challenge election results in Supreme Court Archived 2015-10-18 at the Wayback Machine, Official website of Yulia Tymoshenko (20 February 2009)
^ ab "Yulia Tymoshenko: sooner or later an honest court will assess the fraudulent 2010 elections". Yulia Tymoshenko Official website. 20 February 2010. Archived from the original on 25 February 2010.
^ "Voting for Yanukovych, but unenthusiastically", Kyiv Post (26 November 2009)
^ Yushchenko appeals parliament's decision to call presidential election for Oct. 25, UNIAN (April 8, 2009)
^ Ukraine court rules election date unconstitutional, PR-inside.com (May 13, 2009)
^ Yanukovych agrees with Yushchenko on presidential election date, Interfax-Ukraine (May 14, 2009)
^ Court declares unconstitutional parliament's resolution calling presidential polls for October 25, 2009, Interfax-Ukraine (May 13, 2009)
^ Constitutional Court rules against presidential poll date, UNIAN (May 13, 2009)
^ All doubles are eliminated – Lutsenko, UNIAN (September 21, 2009)
^ ab Regions Party worried about numerous inaccuracies in state register of voters, Interfax-Ukraine (September 21, 2009)
^ Presidential election gets under way in Ukraine, Kyiv Post (January 17, 2010)
^ "Law on the election of the President of Ukraine article 85 (16)". Ukrainian legislature. Central Election Commission of Ukraine. Retrieved 2009-08-21.
^ Law on Presidential Elections, Central Election Commission of Ukraine (Ukrainian)
^ Law on Presidential Elections, Venice Commission
^ VR reduced term of presidential campaign from 120 to 90 days, UNIAN (July 24, 2009)
^ Law on presidential elections will be amended during election campaign, says Yuschenko's secretariat, Kyiv Post (August 21, 2009)
^ Ukraine's presidential elections will not be disrupted, Kyiv Post (September 25, 2009)
^ CEC formed 225 territorial election districts, UNIAN (October 19, 2009)
^ Constitutional court rules on Law of President elections, UNIAN (October 20, 2009)
^ Ruling 26/2009 Compliance with the Constitution of Ukraine (constitutionality) of certain provisions of laws of Ukraine "On elections of President of Ukraine" On State Register of Voters, "" On Amending Certain Legislative Acts of Ukraine on the presidential elections in Ukraine and the Code of Administrative Procedure Ukraine, Constitutional Court of Ukraine (October 19, 2009)
^ Ukraine's CEC forms 113 foreign polling stations for presidential elections, Kyiv Post (December 22, 2009)
^ Tymoshenko to appeal against CEC decision permitting home voting during presidential election, Kyiv Post (January 5, 2010)
^ Presidential direct election to cost Ukraine over 1.5 billion UAH Archived 2011-07-11 at the Wayback Machine, For-ua (July 29, 2009)
^ Central Election Commission cuts expenditure on presidential election by Hr 17.3 million, Kyiv Post (November 26, 2009)
^ How much for today's president?, proUa (August 26, 2009)
^ Presidential candidates will spend at least USD 1 billion on election campaign in Ukraine Archived 2011-07-11 at the Wayback Machine, ForUm (October 20, 2009)
^ Run-off to take UAH 448.581, 119 million – CEC , UkrInform (January 28, 2010)
^ ab Ukraine's presidential candidates to be nominated from Oct. 20 to Nov. 6, Kyiv Post (October 2, 2009)
^ Official text (Ukrainian), CEC
^ Foreign polling stations for Ukrainian presidential elections to be set up by Dec. 9, Kyiv Post (November 20, 2009)
^ Candidates to be numbered in ballot paper for voting at elections Archived 2011-02-01 at the Wayback Machine, Kyiv Post (December 16, 2009)
^ CEC registers seven more presidential candidates, including Poroshenko, Tymoshenko, Interfax-Ukraine (31 March 2014)
^ MP Bohoslovska quits Party of Regions, UNIAN (May 25, 2009)
^ MP Bohoslovska nominates herself for president, Kyiv Post (October 20, 2009)
^ "Bohoslovska Applies CEC For Registering Her President Candidate". Ukrainian News. UkraNews. Retrieved 2009-10-23.
^ "Leader Of Free Democrats Party Brodskyi Applies To CEC To Register Him Candidate For President". Ukrainian News. UkraNews. Archived from the original on 2009-10-31. Retrieved 2009-10-20.
^ ab "CEC registered two more candidates for the President UKRAINE". Central Election Commission of Ukraine. Central Election Commission of Ukraine. Retrieved 2009-11-02.
^ "Hrytsenko joins the fight for the presidency". URA-Inform (in Russian). May 28, 2009. Archived from the original on July 17, 2011. Retrieved 2009-06-15.
^ On October 16, 2009, Anatoliy Hrytsenko claimed he had collected the UAH 2.503 million required for him to register as a presidential candidate. Source: Hrytsenko collects UAH 2.5 million to register as presidential candidate, Interfax-Ukraine (October 16, 2009)
^ Hrytsenko submits documents to register as presidential nominee, Interfax-Ukraine (October 21, 2009)
^ ab Run-off in Ukraine's presidential election inevitable – analysts, ITAR-TASS (October 19, 2009)
^ Ukrainian People's Party nominates its leader Kostenko for president, Kyiv Post (October 24, 2009)
^ http://www.etaiwannews.com/etn/news_content.php?id=984544&lang=eng_news
^ "Lytvyn Requests CEC To Register Him Candidate For President". Ukrainian News. UkraNews. Retrieved 2009-10-23.
^ http://kyivpost.com/news/politics/detail/51285/, Kyiv Post (October 25, 2009)
^ ab "CEC registered two more candidates for the President UKRAINE". Central Election Commission of Ukraine. Central Election Commission of Ukraine. Retrieved 2009-11-06.
^ http://photo.unian.net/eng/themes/15200, Unian.net (October 31, 2009)
^ Central Election Commission registers Uzhgorod mayor as presidential candidate, Kyiv Post (November 13, 2009)
^ Who is Oleh Riabokon: The biography of a Presidential Candidate , Who is who in Ukraine (October 27, 2009)
^ First contender for Ukraine's presidency submits documents to CEC, Kyiv Post (October 20, 2009)
^ "Communist leader Symonenko asks Central Election Commission to register him as presidential candidate". Ukrainian News. Kyiv Post. Retrieved 2009-10-21.
^ ab CEC registers two more candidates for Ukraine's president, Interfax-Ukraine (November 6, 2009)
^ (in Ukrainian) Народно-демократическая партия подала в ЦИК документы для регистрации лидера НДП Людмилы Супрун кандидатом в президенты, People's Democratic Party (November 6, 2009)
^ "PM Tymoshenko Applies CEC To Register Her Candidate For President". Ukrainian News. Ukrainian News. Retrieved 2009-10-27.
^ "CEC registered CANDIDATE PRESIDENT OF UKRAINE Yulia Tymoshenko". Central Election Commission of Ukraine. Central Election Commission of Ukraine. Retrieved 2009-10-31.
^ "Tihipko may unite with Yatseniuk, Hrytsenko and Bohoslovska to nominate single candidate for presidential election". KyivPost. Kyiv Post. August 19, 2009. Retrieved 2009-08-19.
^ "Tigipko at the presidential elections will be supported by the Labour Party" (in Russian). Persho Dzherelo. Archived from the original on 2013-05-06. Retrieved 2009-06-15.
^ "Tigipko files documents at Central Election Commission to register as presidential candidate". Interfax-Ukraine. Kyiv Post. Retrieved 2009-10-23.
^ Sylna Ukrayina party to support Tihipko in presidential elections, Kyiv Post (November 28, 2009)
^ "Nationalists put Tyahnybok out to become president". TSN.ua (in Ukrainian). May 24, 2009. Retrieved 2009-06-15.
^ "Tiahnybok files documents at CEC to register as presidential candidate". Interfax (in Ukrainian). Kyiv Post. October 27, 2009. Retrieved 2009-10-27.
^ "Homepage". The Next Big Step. nashkrok.org.ua. Archived from the original on 2009-04-09. Retrieved 2009-06-15.
^ "Yushchenko registered as a nominee for presidential election". ForUm. Archived from the original on 2009-11-03. Retrieved 2009-10-27.
^ Party Of Regions Nominates Yanukovych As Its Presidential Candidate Archived 2012-08-14 at the Wayback Machine, Ukrainian News (October 23, 2009)
^ CEC to consider Yanukovych's registration as presidential candidate on Wednesday, Kyiv Post (October 27, 2009)
^ "Arseniy Yatsenyuk will be on the ballot for the President of Ukraine". Lenta.ru (in Russian). Rambler Media Group. June 4, 2009. Retrieved 2009-06-15.
^ Taras Kuzio (4 April 2009). "Yatsenyuk, a Yushchenko clone, will bring stagnation". Kyiv Post. Retrieved 18 January 2016.
^ "The Rise And Fall (And Rise?) Of Arseniy Yatsenyuk". Andrew Wilson. Radio Free Europe. Retrieved 2009-09-18.
^ "Yatseniuk registers as presidential candidate". Interfax-Ukraine. Kyiv Post. Retrieved 2009-10-21.
^ 16 applications have been rejected for registration as presidential candidates, Kyiv Post (November 13, 2009)
^ CEC Refuses To Register Kulychenko, Subbotin, Polyschuk, Honcharenko, Melnyk As Presidential Candidates, Ukrainian News (October 30, 2009)
^ CEC denies registration to four more contenders for Ukraine's presidency, Kyiv Post (November 3, 2009)
^ (in Russian) Украина обречена либо на распад, либо на революцию. Для украинской власти Конституция Украины – туалетная бумажка. Заявление Лидера ПСПУ Наталии Витренко, Official website of Natalia Vitrenko (November 11, 2009)
^ Eighteen to run for Ukraine's presidency, Interfax-Ukraine (November 12, 2009)
^ (in Ukrainian) Від анти-кризи до армійських наметів та "фашистської загрози", Ukrayinska Pravda (September 3, 2009)
^ abc Eurasia Daily Monitor, The Jamestown Foundation—October 1, 2009—Volume 6, Issue 180, The Jamestown Foundation (October 01, 2009)
^ See how they run, proUA (September 2, 2009)
^ "Surviving the Crisis in Ukraine (American Progress Forum Video)". Center for American Progress. July 30, 2009
^ "Poll: Ukraine president's chances of re-election slim". Kyiv Post. October 20, 2009. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
^ "Yatsenyuk will be on the ballot for the office of President of Ukraine". Korrespondent.net. April 5, 2009. Retrieved 2009-04-07.
^ "Presidential race: Young candidate so far not candidate of the young". Kyiv Post. August 13, 2009. Retrieved 2009-08-13.
^ Yushchenko plots his premier's removal, Oxford Analytica (March 11, 2008)
^ Tymoshenko accuses Yuschenko of obstructing executive authorities' teamwork, Interfax-Ukraine (February 6, 2009)
^ Yuschenko demands immediate amendments to 2009 budget to save Ukraine's economy – televised address to nation, Interfax-Ukraine (January 30, 2009)
^ Yushchenko, Tymoshenko criticize each other (photo-report), UNIAN (February 11, 2009)
^ Agreement with Russia threatens Ukraine's security – President, UNIAN (February 10, 2009)
^ Presidential secretariat considers PM's report "theatrical performance", Interfax-Ukraine (February 5, 2009)
^ Yushchenko calls on Oblast leaders to work out joint plan of actions, UNIAN (June 10, 2009)
^ Tymoshenko: Political Competition Accounts For Conflict With Yuschenko Archived 2012-03-15 at the Wayback Machine, Ukrainian News Agency (February 11, 2009)
^ Ukrainian speaker condemns Kyiv's internal bickering, UNIAN, (February 11, 2009)
^ Yuschenko Called On Politicians To Stop Presidential Election Campaign Until July, Ukrainian News Agency (February 27, 2009)
^ Interview with the president, Kyiv Post (February 25, 2009)
^ Tymoshenko: Yushchenko, Yatseniuk, and Yanukovych have one headquarters for three, UNIAN (June 16, 2009)
^ Yuschenko and Yatseniuk are 'technical candidates' for Yanukovych, says Tymoshenko, Interfax-Ukraine (June 16, 2009)
^ Tymoshenko Says Yuschenko To Be Yatseniuk's Technical Candidate, Ukrainian News Agency (June 16, 2009)
^ Tymoshenko says "there is team work" between her and President, UNIAN (June 22, 2009)
^ Address to the President of Ukraine Victor Yushchenko Archived 2009-08-15 at the Wayback Machine, Kremlin.ru (August 11, 2009)
^ Relations between Russia and Ukraine: a New Era Must Begin Archived 2009-04-30 at the Wayback Machine, Video – Russian President (August 11, 2009)
^ UPDATE 3-Russia's Medvedev wades into Ukraine polls, Reuters (August 11, 2009)
^ Medvedev lambasts Ukraine leader , BBC News (August 11, 2009)
^ No hope for normalizing relations with Russia under current leadership, says Ukraine's opposition leader, Interfax-Ukraine (August 11, 2009)
^ Medvedev's statement shows Russia wants to impact presidential campaign in Ukraine, says pro-Yuschenko MP, Interfax-Ukraine (August 11, 2009)
^ Yatseniuk says Yuschenko has given grounds to call his policy anti-Russian, Interfax-Ukraine (August 11, 2009)
^ Medvedev's statement may be 'to Yuschenko's advantage,' says Tihipko, Interfax-Ukraine (August 11, 2009)
^ Medvedev's message to Yuschenko could be used in election campaign to split Ukraine, says speaker, Interfax-Ukraine (August 11, 2009)
^ Artist included Ruslana, Oleksandr Ponomaryov, Ani Lorak, Potap and Nastia Kamenskikh, Tina Karol, Natalia Mogilevska, Iryna Bilyk, TIK, TNMK, "Druha Rika", Mad Heads XL. See the concert here Archived 2009-09-22 at the Wayback Machine
^ Events by themes: Allukrainian round "With Ukraine in a heart!". UNIAN
^ Mogilevska went to Tymoshenko, UNIAN (September 11, 2008)
^ Four parties unite to participate in presidential election, Interfax-Ukraine (September 14, 2009)
^ Bloc of left and center-left forces to nominate CPU Leader for Ukraine's president, Interfax-Ukraine (October 3, 2009)
^ Western Ukrainian intelligentsia calls on candidates for president to withdraw in favor of Tymoshenko, Interfax-Ukraine (October 1, 2009)
^ Vannykova: Yuschenko warns against attempts to monopolize radio and TV broadcasting, Kyiv Post (October 6, 2009)
^ Social-Democratic Party supports Symonenko as single candidate for president post from left political forces, Kyiv Post (October 17, 2009)
^ Parliament votes to remove Immunity, UNIAN (October 20, 2009)
^ Yatseniuk loses fresh-face label, popularity after his financial backers exposed, Kyiv Post (October 22, 2009)
^ Flu epidemic in Ukraine may require postponement of elections, Kyiv Post (November 6, 2009)
^ WHO experts forecast three waves of A/H1N1 flu in Ukraine, Kyiv Post (November 6, 2009)
^ Emergency ministry sees no grounds for state of emergency, Kyiv Post (November 6, 2009)
^ Yushchenko: there are no grounds for state of emergency, UNIAN (November 9, 2009)
^ Ukraine president: no reason to delay vote over flu, UNIAN (November 9, 2009)
^ Yushchenko to back Yanukovych in runoffs, ZIK (November 11, 2009)
^ National Council: Ukrainian TV and radio companies not giving equal conditions to presidential candidates, Kyiv Post (December 3, 2009)
^ EPP calls on Ukraine's democratic forces to unite around most democratic candidate, Interfax-Ukraine (December 9, 2009)
^ Yanukovych vows to gather people on Maidan if election results are rigged, Interfax-Ukraine (December 11, 2009)
^ BYT proposes discussing form of government, constitutional amendments to referendum Kyiv Post February 15, 2010
^ (in Ukrainian) ЦВК оприлюднила офіційні результати 1-го туру виборів, Gazeta.ua (January 25, 2010)
^ Ukrainian elections: anything possible
^ ab "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2010-01-21. Retrieved 2010-02-10.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ Vote spoils Ukraine's EU, NATO hopes, Ottawa Citizen (February 10, 2010)
^ Is Ukraine ready to vote?, Washington Post (18 May 2014)
^ ab Ukraine instability fears as Tymoshenko plans next move
^ ab Tymoshenko cries foul: What's her case?, Kyiv Post (February 10, 2010)
^ Regions Party puts activists patrol near two courts in Kyiv, Kyiv Post (February 10, 2010)
^ http://www.kyivpost.com/news/nation/detail/59306/
^ http://www.partyofregions.org.ua/eng/pr-east-west/4b72cc95d7f26/
^ NATO, EU follow U.S., welcome Yanukovych, Kyiv Post (February 12, 2010)
^ Януковича поздравили еще 5 президентов
^ Продолжается поток поздравлений в адрес Януковича
^ ab Ukraine's Tymoshenko Slams Rival, No Comment On Election Result, Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty (February 11, 2010)
^ Yulia Tymoshenko will not challenge election results in Supreme Court Archived 2015-10-18 at the Wayback Machine, Official website of Yulia Tymoshenko (February 20, 2009)
^ Election winner lacks strong voter mandate, Kyiv Post (February 11, 2010)
^ Neanderthal power, Kyiv Post (March 25, 2010)
^ Exit Polls: Yanukovych wins Ukraine election, (February 7, 2010)
^ Interfax-Ukraine exit poll: Yanukovych leads among voters in Kyiv, regional capitals, (February 7, 2010)
^ ДАНІ ЕКЗИТ-ПОЛІВ (Summary Exit Polls), (February 7, 2010)
^ Ukrainians blame Yuschenko (47%) and Tymoshenko (22%) for creating economic mess, Kyiv Post (August 20, 2009)
^ Poll: over 40 percent of Ukrainians prefer Collective Security Treaty Organization, 12.5 percent favor NATO (November 26, 2009)
^ Relations between Russia and Ukraine: a New Era Must Begin Archived 2009-08-13 at the Wayback Machine, Demitry Medvedev (August 11, 2009)
^ Yushchenko calling on Medvedev to intensify Russian-Ukrainian dialog, Kyiv Post (August 19, 2009)
^ Experts: Presidential campaign characterized by poor programs of candidates, Kyiv Post (November 23, 2009)
^ EU endorses Ukraine election result, euobserver (February 8, 2010)
^ International observers say Ukrainian election was free and fair, Washington Post (February 9, 2010)
^ European Parliament president greets Ukraine on conducting free and fair presidential election, Kyiv Post (February 9, 2010)
^ Election watchers worried by lack of independent exit poll; survey essential to deterring vote fraud, Kyiv Post (December 11, 2009)
^ Tymoshenko will not protest presidential election outcome, ForUm (September 25, 2009)
^ Ex-president excludes third round of presidential elections, National Radio Ukraine (September 25, 2009)
^ Wolf-crying about likely vote rigging presidential candidates try to justify their future defeat, ZIK (November 24, 2009)
^ Yanukovych sure Tymoshenko will try to rig results of presidential election, Kyiv Post (December 17, 2009)
^ Tymoshenko says she will prevent Yanukovych from rigging presidential election, Kyiv Post (December 17, 2009)
^ Yuschenko warns of significant threat of administrative pressure during counting of votes, Interfax-Ukraine (January 5, 2010)
^ President's office ex-official blows Yushchenko-Yanukovych secret deal, Zik (January 8, 2010)
^ [http://www.jamestown.org/single/?no_cache=1&tx_ttnews[tt_news]=35871&tx_ttnews[backPid]=7&cHash=e9627f75db Yushchenko and Yanukovych Forge an Electoral Alliance – Taras Kuzio, Jamestown Foundation (January 8, 2010)
^ Poll: Less than 5% Ukrainians believe presidential election will be fair, Kyiv Post (January 12, 2010)
^ Poll: Most Ukrainians not planning to sell their votes in presidential election, Kyiv Post (January 12, 2010)
^ Ukraine presidential candidates trade warnings, promises – Summary, Earth Times (January 13, 2010)
^ "Public reporting of poll results is prohibited in final 15 days before presidential election". Inter-Fax Ukraine. Kyiv Post. January 2, 2010. Retrieved 2010-01-02.
^ (PDF) (Press release). International Foundation for Electoral Systems. 15 December 2009 http://www.ifes.org/publication/9c648aca6bb32dc209a4384513da12d2/IFES_UkraineSurvey2009_PR.pdf. Retrieved 16 December 2009. Missing or empty|title=(help)
^ "Yushchenko approval rating". FOM-Ukraine. Retrieved 22 May 2009.
^ Taras Kuzio (24 October 2009). "With or without Baloha, Yushchenko's unelectable". Kyiv Post. Retrieved 1 March 2016.
^ (in English)"Voters unhappy with choices, want jobs", (November 21–29) U.S.-based International Foundation for Electoral Systems
^ Survey: most Ukrainians ready to vote in presidential polls, Kyiv Post (October 12, 2009)
^ Pollster predicts 70% turnout for presidential election, Kyiv Post (December 23, 2009)
^ Public reporting of poll results is prohibited in final 15 days before presidential election, Kyiv Post (January 3, 2010)
^ 24.4% of Ukrainians ready to support Yanukovych at presidential election, UNIAN (December 27, 2007)
^ Опрос: наилучшие шансы стать президентом – у Тимошенко и Януковича / NEWSru.ua
^ Press release on the results sociological research—September 2008 SOCIS
^ (in Ukrainian)Фонд громадської думки Президентський рейтинг Тимошенко впав, gazeta.ua (December 24, 2008)
^ (in Ukrainian)Думка громадян України про підсумки 2008 р. (опитування) Archived 2012-09-13 at Archive.today, Razumkov Centre (December 26, 2008)
^ Poll: "CHANGE OF ELECTORAL SITUATION IN UKRAINE – April 2009", Research & Branding Group (April 2009)
^ Poll: Yanukovych, Tymoshenko, Yatseniuk have best chances to be elected president – April 18, 2009, KMIS (April 2009)
^ Українці готові зробити Януковича президентом. 15% голосуватимуть "проти всіх"
^ Yanukovych tops list of presidential candidates in Ukraine – poll, UNIAN (June 2, 2009)
^ Poll: "CHANGE OF ELECTORAL SITUATION IN UKRAINE – June 2009", Research & Branding Group (June 2009)
^ Poll: Yanukovych, Tymoshenko still top presidential ratings, Interfax-Ukraine (August 4, 2009)
^ Socis Poll: 25% Of Ukrainians Prepared To Support Yanukovych For President, 20.5% To Vote For Tymoshenko Archived 2009-08-19 at the Wayback Machine, Ukrainian News (August 17, 2009)
^ Poll: "CHANGE OF ELECTORAL SITUATION IN UKRAINE – August 2009", Research & Branding Group (August 2009)
^ Socis Poll: President of Ukraine candidates rating. 100 days before elections, SOCIS (October 8, 2009)
^ Yanukovych leads polls as a candidate for presidency, ForUm (October 13, 2009)
^ Poll: Yanukovych could beat Tymoshenko in run-off by a wide margin, Research & Branding Group (August 2009)
^ Electoral Situation in Ukraine: 50 days to go Archived 2012-09-07 at Archive.today, Research & Branding Group (November 27, 2009)
^ Voters unhappy with choices, want jobs, U.S.-based International Foundation for Electoral Systems (December 17, 2009)
^ Yanukovych leads presidential race in Ukraine – polls, Interfax (December 7, 2009)
^ Electoral Situation in Ukraine: 30 days to go[permanent dead link], Research & Branding Group (December 17, 2009)
^ (in Ukrainian)Гонка рейтингів: нові тенденції / Українська правда
^ PACE, OSCE election observers are arriving in Ukraine, Kyiv Post (November 23, 2009)
^ Over 600 OSCE observers to monitor presidential elections in Ukraine, Kyiv Post (October 13, 2009)
^ OSCE/ODIHR officially opens election observation mission for presidential election in Ukraine, Kyiv Post (November 26, 2009)
^ OSCE observer: Ukrainian election lacks funding for salaries, transport services, Kyiv Post (January 12, 2010)
^ European Union to send over 700 observers to monitor Ukraine's presidential elections, Kyiv Post (November 17, 2009)
^ Election Observer Mission 2010, Canada Ukraine Foundation
^ About us, Canada Ukraine Foundation
^ PACE delegation to pay visit to Ukraine on November 24–26, UNIAN (November 23, 2009)
^ ab European lawmakers' hopes low for Ukraine vote, Kyiv Post (November 26, 2009)
^ PACE may keep monitoring Ukraine after presidential poll, Kyiv Post (December 8, 2009)
^ PACE rapporteur calling on Ukraine's parliament to amend law on presidential elections, Kyiv Post (December 9, 2009)
^ Polish observers to arrive in Ukraine to monitor signs of xenophobia during election campaign, Kyiv Post (December 4, 2009)
^ Yanukovych claims to OSCE that Ukrainian government intends to rig presidential election, Kyiv Post (December 9, 2009)
^ 450 observers from ENEMO international mission to monitor Ukrainian elections, Kyiv Post (December 15, 2009)
^ Kowal to head delegation of European Parliament's observers for elections, Kyiv Post (December 16, 2009)
^ Central Election Commission fails to register over 2,000 official observers from Georgia, Interfax-Ukraine (January 11, 2010)
^ Over 3,000 international observers registered for Ukrainian presidential election, Kyiv Post (January 11, 2010)
^ OSCE to send same number of observers to monitor Ukraine's runoff, Kyiv Post (January 18, 2010)
^ OSCE observers: Ukraine's election laws should be brought in line with international norms, Kyiv Post (January 18, 2010)
^ Ukraine election: And then there were two, BBC News (January 18, 2010)
^ BYT: International observers were physically unable to record mass irregularities in run-off vote, Kyiv Post (February 11, 2009)
^ (in Ukrainian) Central Election Commission Candidate Results Archived 2010-01-21 at the Wayback Machine, Central Election Commission of Ukraine (January 19, 2010)
^ TABLE-Ukraine's presidential election results, Kyiv Post (January 18, 2010)
^ Ukraine's Orange leader Yushchenko loses election, BBC News (January 18, 2010)
^ ab Yulia Timoshenko received 45.47 percent, or 11.6 million votes
^ Ukraine's Tymoshenko bloc 'contesting election result', BBC News (February 9, 2010)
^ Run-off confirms that Ukraine's presidential election meets most international commitments, Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe (February 8, 2010)
^ (in Ukrainian) ЦВК оприлюднила офіційні результати 1-го туру виборів, Gazeta.ua (January 25, 2010)
^ Yulia Timoshenko received 45.47 percent, or 11.6 million votes
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ukrainian presidential election, 2010. |
"Main" (in Ukrainian). Central Election Commission of Ukraine. Retrieved 2009-06-14.
Maps of election by polling places(in Ukrainian)
"Parliament" (in Ukrainian). Official website of the Ukrainian Parliament (Rada). Archived from the original on 2007-12-23. Retrieved 2009-09-22.
"Parliament". Official website of the Ukrainian Parliament (Rada). Archived from the original on 2009-06-10. Retrieved 2009-09-22.
"Interactive Ukraine election maps". Kyiv Post. Retrieved 2010-01-18.
- Serhiy Vasylchenko: Electoral Geography of Ukraine 1991–2010






