Saint-Maurice River
| Saint-Maurice River Rivière Saint-Maurice Tapiskwan sipi | |
|---|---|
 Saint-Maurice River at Grandes-Piles | |
 | |
| Location | |
| Country | |
| Province | |
| Region | Mauricie |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Gouin Reservoir |
| - coordinates | 48°21′15″N 74°06′00″W / 48.35417°N 74.10000°W / 48.35417; -74.10000 |
| - elevation | 404 m (1,325 ft) |
| Mouth | Saint Lawrence River |
- location | Trois-Rivières |
- coordinates | 46°20′55″N 72°31′40″W / 46.34861°N 72.52778°W / 46.34861; -72.52778Coordinates: 46°20′55″N 72°31′40″W / 46.34861°N 72.52778°W / 46.34861; -72.52778 |
- elevation | 3 m (9.8 ft) |
| Length | 563 km (350 mi)[1] |
| Basin size | 43,300 km2 (16,700 sq mi)[1] |
| Discharge | |
| - average | 730 m3/s (26,000 cu ft/s) |
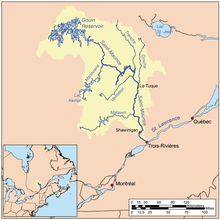
The Saint-Maurice River (Atikamekw: Tapiskwan sipi) flows North to South in central Quebec from Gouin Reservoir to empty into the Saint Lawrence River at Trois-Rivières, in province of Quebec, in Canada.[2] From its source at Gouin Reservoir, located at the same latitude as the Lac Saint-Jean, the river has a total drop of about 405 meters, to finally reach the river Trois-Rivières. The river is 563 km in length and has a drainage basin of 43,300 km² (16,700 mile²).[3] Saint-Maurice river is one of the most important tributaries of St. Lawrence river.
The main tributaries of the Saint-Maurice River are:
Matawin River, whose mouth is at Matawin (Hamlet);
Vermillon River (La Tuque) which empties about 23 km (by water) upstream (north) of the Beaumont generating station in La Tuque;
Manouane River (La Tuque) which empties about 115 km (by water) upstream (north) of La Tuque;
La Trenche River (La Tuque) which empties near the La Trenche Generating Station;
Croche River (La Tuque) which empties at north of La Tuque.
Between Weymontachie and Trois-Rivières, the St-Maurice River has 27 tributaries identified as significant enough for downhill wood:[4] Weymontachingue, Manouane, Little Rock, Little Flamand, Windigo, Flamand, Coucoucache, Grande Pierriche (Great Pierriche), Petite Pierriche (Little Pierriche), "La Trenche", Vermillion, Croche, Rivière-au-Lait, Bostonnais, Little Bostonnais, Small Stream, Mountain, Caribou, Rivière-aux-Rats, Wessonneau, Little Batiscan River, l'Oiseau (Bird), Bête Puante (Beast Puante), Mattawin, Mekinac, River "au Lac des Pêches" and Shawinigan River.
During the 18th century, early fur traders travelled along the river. During the second half of the 19th century, logging became an important industry in the surrounding Mauricie region. For much of the 20th century, the river was used to transport logs to mills down river and it was, and still is, a major source of hydroelectric power.
First communication channel in this region, the river was used by local Native Americans long before the arrival of Europeans on the spot. Early explorations by religious conversion in pain and trappers in search of furs for the trade, it was one of the primary routes of rivers in Quebec.
Several municipalities have been established on its banks, thereby taking advantage of its hydroelectric power where the falls were high enough to install a dam integration an electrical generating station. Among other cities, La Tuque, Shawinigan and Trois-Rivières are the best known, are themselves located along the Route 155 which connects the St. Lawrence River to Lake St. John.
Contents
1 Origin of name
2 Communities along the river
3 Bridges and other cross structures
4 Hydroelectric power stations and other dams
5 Timber transportation on river
6 Wildlife fish
7 See also
8 References
9 External links
Origin of name

Saint-Maurice River in Trois-Rivières.
The original name of the river was "Métabéroutin", the name given by Algonquin, which means "discharge of the wind" and in turn, the Attikameks of Haute-Mauricie still call "Sipi Tapiskwan", the "river of the threaded needle". The Abenaki the call for their "Madôbaladenitekw" or the "river that ends". Jacques Cartier named it "River Fouez" in honor of the House of Foix in 1535. However, this name was abandoned in the early seventeenth century to the name of "Three Rivers". Its current name was given in the early eighteenth century in reference to the "fief of Saint-Maurice", the common name of lordship on the west bank granted about 1668 to Maurice Poulin in La Fontaine, government prosecutor of Three Rivers. He was the owner of some property along the river in the 17th century.[5] The name "St. Maurice" is attested for the first time in a judgment dated 1723 and definitely supplanted the "Three Rivers" between 1730 and 1740.
The river gave its name to the administrative region of Mauricie.
Communities along the river
Communities on the river include, from the mouth of the river:
- Trois-Rivières
- Shawinigan
- Grand-Mère
- Grandes-Piles
- Saint-Roch-de-Mékinac
- Grand-Anse (hamlet)
- Rivière Matawin (hamlet)
- Rivière-aux-Rats (hamlet)
- La Tuque
- Wemotaci
- Sanmaur
Bridges and other cross structures
Order from downstream (Trois-Rivières, Quebec|Trois-Rivières) toward upstream:
- Railway Bridge Railway Quebec-Gatineau connecting the east bank to the island Pottery, Trois-Rivières
- Bridge linking the Saint-Quentin Island to Saint-Christophe Island, Trois-Rivières
- Bridge linking the Caron island to Saint-Christophe Island, Trois-Rivières
Duplessis Bridge, Trois-Rivières
- Railroad Bridge Railway Quebec-Gatineau, Trois-Rivières
Radisson Bridge, Trois-Rivières
La Gabelle Generating Station, linking Saint-Étienne-des-Grès to Notre-Dame-du-Mont-Carmel
- Railway Bridge Railway Quebec-Gatineau linking Saint-Étienne-des-Grès to Notre-Dame-du-Mont-Carmel
Territory of Shawinigan
- Railway Bridge Railway Quebec-Gatineau linking Shawinigan (sector Shawinigan-Sud to Shawinigan)
Marc Trudel Bridge, Shawinigan
Shawinigan Bridge, Shawinigan
- Banana Bridge linking the "Île Banane" (Banana island) to Melville Island, Shawinigan
- CNR Railway Bridge, linking the two shores, Shawinigan
Grand-Mère Bridge, Shawinigan
Bac bicycle and pedestrian, Shawinigan
Bridge of Piles, Shawinigan
Bac, bicycle and pedestrian Shawinigan to Grandes-Piles
Bridge Mekinac, Lac-Normand (West shore) to Trois-Rives (East shore) at the level of Rivière Matawin (Hamlet)
Territory of La Tuque
Bridge of Rivière-aux-Rats, La Tuque
La Tuque Generating Station, La Tuque
La Tuque West shore bride, La Tuque
Rivière-au-Lait bridge, La Tuque
Beaumont generating station, La Tuque
La Trenche Generating Station, La Tuque
Rapide-Blanc bridge, La Tuque
Rapide-Blanc Generating Station, La Tuque
Rapides-des-Coeurs Generating Station, La Tuque
- CNR Railway Bridge, linking the two shores, La Tuque
Chute-Allard Generating Station, La Tuque
- CNR Railway Bridge, linking the two shores, Wemotaci
Wemotaci bridge, linking the two shores Wemotaci
- La Loutre Bridge, linking the two shores, La Tuque
Gouin Dam, La Tuque
Hydroelectric power stations and other dams
Order from downstream (Trois-Rivières) to upstream:
- La Gabelle Generating Station
Shawinigan-2 Generating Station and Shawinigan-3 Generating Station (same falls)
Rocher-de-Grand-Mère Generating Station and Grand-Mère Generating Station (same falls)- La Tuque Generating Station
- Beaumont generating station
- La Trenche Generating Station
- Rapide-Blanc Generating Station
- Rapides-des-Coeurs Generating Station
- Chute-Allard Generating Station
- Gouin Dam
All plants on the St. Maurice are the property of Hydro-Québec.
Timber transportation on river
In 1996, the Saint-Maurice River was the last river in Quebec to stop the transportation of timber by flotation. For nearly 150 years, companies in forestry have used the current of the river and its tributaries for timber transportation. Before being stacked on the ice in Upper-Mauricie, logs were identified in order to be recovered downstream where baunes were implemented, including Grandes-Piles, in Grand-Mère, Shawinigan or Trois-Rivières.
Each spring, an army of loggers cleaned the river banks for delivering timbers which were hung on the shores, bays, rocks or in riparian wood. The loggers sorted the timbers for relaunching them into the water for redirecting them to Pulp paper plant downstream.
Wildlife fish
In the last 174 kilometers, between Trois-Rivières and La Tuque, the experts found 42 fish species frequenting the river.[6] The density of fish biomass is generally low, which is characteristic of rivers in Canadian Shield.[7]
See also
- List of Quebec rivers
- 1663 Charlevoix earthquake
- Île Anselme-Fay
References
^ ab Natural Resources Canada > Atlas of Canada > Rivers
^ Toponymy Commission. "Gender (male or female) names of rivers when their generic (river, stream ...) are omitted". Archived from the original on October 7, 2009. Retrieved November 11, 2008..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "Rivière Saint-Maurice". The Canadian Encyclopedia
^ Journals of the Legislative Assembly of Canada, 11 (1852).
^ "Rivière Saint-Maurice". Topos Web. Toponymy Commission. Retrieved September 28, 2008.
^ "The diversity of fishes: Watershed of the Saint-Maurice River". Ministry of Sustainable Development, Environment and Parks. Retrieved November 27, 2008.
^ Saint-Jacques, Nathalie & Richard, Yvon. "The basin of the Saint-Maurice River: fish communities and the biotic integrity of the environment, 1996" (PDF). Ministry of the Environment. p. 59. Retrieved November 27, 2008.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Rivière Saint-Maurice. |
Tourisme Mauricie Regional tourist office