Spitalfields
| Spitalfields | |
|---|---|
 Brushfield Street, looking towards Christ Church, Spitalfields | |
 Spitalfields Spitalfields shown within Greater London | |
| Population | 10,286 (2011 Census. Spitalfields and Banglatown Ward)[1] |
| OS grid reference | TQ335815 |
| London borough |
|
| Ceremonial county | Greater London |
| Region |
|
| Country | England |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | LONDON |
| Postcode district | E1 |
| Dialling code | 020 |
| Police | Metropolitan |
| Fire | London |
| Ambulance | London |
| EU Parliament | London |
| London Assembly |
|
Spitalfields /ˈspɪtəlfiːldz/ is a district and former parish in London, England. It is within Central London and located in the East End and part of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. The Liberty of Norton Folgate and the neighbouring Liberty of the Old Artillery Ground were merged into Spitalfields in 1921.
The area straddles the locale around Commercial Street and west of Brick Lane, and is home to several markets, including Spitalfields Market, the historic Old Spitalfields Market, Brick Lane Market and Cheshire Street. Petticoat Lane Market lies on the area's south-western boundaries. It is close to Liverpool Street station.
Contents
1 Toponymy
2 History
2.1 Origins
2.2 Huguenots
2.3 Victorian era
2.4 Modern Spitalfields
3 Culture
4 Notable people
5 Transport
6 See also
7 References
8 Further reading
9 External links
9.1 Images
Toponymy
The name Spitalfields appears in the form Spittellond in 1399; as The spitel Fyeld on the "Woodcut" map of London of c.1561; and as Spyttlefeildes, also in 1561.[2] The land belonged to St Mary Spital, a priory or hospital (a lodging for travellers run by a religious order) erected on the east side of the Bishopsgate thoroughfare in 1197, from which its name is thought to derive.[3][4] An alternative, and possibly earlier, name for the area was Lolsworth.[2]
History
Origins
The area that is Spitalfields was covered with fields and nursery gardens until late in the 17th century when streets were laid out for Irish and Huguenot silk weavers.[5] The Romans had a cemetery to the east of the Bishopsgate thoroughfare, which roughly follows the line of Ermine Street: the main highway to the north from Londinium.[6] The cemetery was noticed by the antiquarian John Stow in 1576 and was the focus of a major archaeological excavation in the 1990s, following the redevelopment of Spitalfields Market.[6][7] In 2013 lead isotope analysis of tooth enamel, by Dr Janet Montgomery of Durham University, led to the identification of the first person from Rome known to have been buried in Britain. She was a 25-year-old woman who was buried in a lead-lined stone sarcophagus, with unique jet and intricate glass grave goods, around the middle of the 4th century A.D.[8]

Coat of arms attributed to Walter Brunus, the founder of the priory in 1197

A map showing the Spitalfields wards of Stepney Metropolitan Borough as they appeared in 1916.
In 1197, a priory, "The New Hospital of St Mary without Bishopsgate", latterly known as St Mary Spital, founded by Walter Brunus and his wife Roisia, was built on the site of the cemetery.[9] It was one of the biggest hospitals in medieval England and had a large medieval cemetery with a stone charnel house and mortuary chapel. The chapel has been uncovered by archaeologists and preserved for public viewing. The priory and hospital were dissolved in 1539 under Henry VIII. Although the chapel and monastic buildings were mostly demolished, the area of the inner precinct of the priory maintained an autonomous administrative status as the Liberty of Norton Folgate. The adjacent outer precincts, to the south, were re-used as an artillery ground and placed under the special jurisdiction of the Tower of London as one of its Tower liberties.[10] Other parts of the priory area were used for residential purposes by London dwellers seeking a rural retreat and by the mid-17th century further development extended eastward into the erstwhile open farmland of the Spital Field.[11]
In 1729 Spitalfields was detached from the parish of Stepney becoming as a parish (with vestry) with two churches Christchurch Spitalfields and St Stephen's Spitalfields. The church of St Stephen Spitalfields was built in 1860 by public subscription but was demolished in 1930. The adjacent vicarage is all that remains. In 1911 the parish of St Mary Spital (the merged former ex-parochial liberties of Norton Folgate and the Old Artillery Ground) became part of the civil parish of Spitalfields. Spitalfields as a civil parish was abolished in 1965 on the establishment of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets.
Huguenots

A map showing the bounds of the Parish of Spitalfields, c.1885
Spitalfields' historic association with the silk industry was established by French Protestant (Huguenot) refugees who settled in the area after the Revocation of the Edict of Nantes in 1685. By settling outside the bounds of the City of London, they hoped to avoid the restrictive legislation of the City Guilds. The Huguenots brought with them little, apart from their skills, and an Order in Council of 16 April 1687 raised £200,000 to relieve their poverty. In December 1687, the first report of the committee set up to administer the funds reported that 13,050 French refugees were settled in London, primarily around Spitalfields, but also in the nearby settlements of Bethnal Green, Shoreditch, Whitechapel and Mile End New Town.[12]
The late 17th and 18th centuries saw an estate of well-appointed terraced houses, built to accommodate the master weavers controlling the silk industry, and grand urban mansions built around the newly created Bishops Square which adjoins the short section of the main east-west street known as Spital Square. Christ Church, Spitalfields on Fournier Street, designed by the architect Nicholas Hawksmoor, was built during the reign of Queen Anne to demonstrate the power of the established church to the dissenting Huguenots, who had built ten chapels in the area.[13] More humble weavers dwellings were congregated in the Tenterground.[14] The Spitalfields Mathematical Society was established in 1717. In 1846, it merged with the Royal Astronomical Society.[15]
Spitalfields Market was established in 1638 when Charles I gave a licence for flesh, fowl and roots to be sold in what was then known as Spittle Fields.[16] The market currently receives around 25,000 visitors every week.[16]
Huguenots of Spitalfields is a registered charity promoting public understanding of the Huguenot heritage and culture in Spitalfields, the City of London and beyond. They arrange tours, talks, events and schools programmes to raise the Huguenot profile in Spitalfields and to raise funds for a permanent memorial to the Huguenots.[17]
From the 1730s Irish weavers came, after a decline in the Irish linen industry, to take up work in the silk trade. The 18th century saw periodic crises in the silk industry, bought on by imports of French silk – in a lull between the wars between the two rivals; and imports of printed calicos. The depression in the trade, and the prices paid to weavers, led to protests. In 1769, the Spitalfield riots occurred, when attempts were made to break up meetings of weavers, called to discuss the threat to wages, caused by another downturn in the market for silk. This resulted in an Irish and a Huguenot weaver being hanged in front of the Salmon and Ball public house at Bethnal Green.[12]
Price controls on amounts master weavers could pay journeymen for each piece were established, removing all incentive to pay higher wages during good times. During bad times workers had no work. As the price was per piece, there was no incentive for using machinery, as the master would have to pay for the machine and still pay the same price per piece to journeymen. By 1822 labour rates were so above market labour rates, that much of the employment in silk manufacture had moved away. Remaining manufacture focussed on expensive fashion items, which required proximity to court and had higher margins.[18]
Victorian era
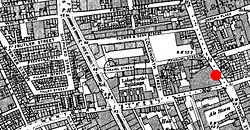
Ordnance Survey map of Spitalfields rookery, 1894
By the Victorian era, the silk industry had entered a long decline and the old merchant dwellings had degenerated into multi-occupied slums. Spitalfields became a by-word for urban deprivation, and, by 1832, concern about a London cholera epidemic led The Poor Man's Guardian (18 February 1832) to write of Spitalfields:
The low houses are all huddled together in close and dark lanes and alleys, presenting at first sight an appearance of non-habitation, so dilapidated are the doors and windows:- in every room of the houses, whole families, parents, children and aged grandfathers swarm together.
In 1860, a treaty with France allowied the import of cheaper French silks. This left the many weavers in Spitalfields, and neighbouring Bethnal Green and Shoreditch indigent. New trades such as furniture and boot making came to the area; and the large windowed Huguenot houses were found suitable for tailoring, attracting a new population of Jewish refugees drawn to live and work in the textile industry.[12]
By the later 19th century inner Spitalfields had eclipsed rival claimants to the dubious distinction of being the worst criminal rookery in London and common lodging-houses in the Flower and Dean Street area were a focus for the activities of robbers and prostitutes and in 1881 was "perhaps the foulest and most dangerous street in the metropolis".[19] Another claimant to the distinction of being the worst street in London was Dorset Street, which was highlighted by the brutal killing and mutilation of a young woman, Mary Kelly, in her lodgings here by the serial killer, Jack the Ripper in the autumn of 1888.[20] The murder was the climax of a series of slayings of prostitutes that became known as the Whitechapel Murders. The sanguinary activities of "Jack" was one of the factors which prompted the demolition of some of the worst streets in the area 1891–94.[21] Deprivation continued and was brought to notice by social commentators such as Jack London in his The People of the Abyss (1903). He highlighted 'Itchy Park', next to Christ Church, Spitalfields, as a notorious rendezvous for homeless vagrants.
Modern Spitalfields

View of Christ Church and the fruit and wool exchange.

Bishops Square, Spitalfields, west end of the exchange
In the late 20th century the Jewish presence diminished and was replaced by an influx of Bangladeshi immigrants, who also worked in the local textile industry and made Brick Lane the curry capital of London.
Another development, from the 1960s onwards, has been a campaign to save the housing stock of old merchant terraces west of Brick Lane from demolition. Many have been conserved by the Spitalfields Historic Buildings Trust which has led to gentrification and a large increase in property prices.[22]
In the 21st century large modern office blocks were built between Bishopsgate and Spitalfields Market. These represent an expansion of the City of London, northwards. A rear-guard action (contravailing planning policies) insisted on by conservationists resulted in the preservation of Old Spitalfields Market and the provision of shopping, leisure amenities and a plaza (urban square) beside the blocks.[22] Permission was granted to demolish the Fruit and Wool exchange on the edge of old Spitalfields market to provide office buildings by developer Exemplar.
Since 1998 the area has formed part of the Spitalfields and Banglatown electoral ward; the last name first arising in use in the late 20th century caused controversy between the cores of both neighboring communities but the unit boundaries less so, an effect of avoiding malapportionment, that is differing size of electorates. Communities widely accept the end of the Anglican parish-based naming.
In April 2016 the London Borough of Tower Hamlets approved and designated the Spitalfields Neighbourhood Planning Forum to monitor and enhance local planning policies[23] which has been seen in contrasting lights, as a heavily subordinated quasi-civil parish (which must defer to the council ultimately in all matters), or less favorably as narrow, deprecated "parochialism".[24]
Culture
Dennis Severs' House in Folgate Street is a "still-life drama" created by the Severs as an "historical imagination" of what life would have been like inside for a family of Huguenot silk weavers.[25][26] In 2009, Raven Row, a non-profit contemporary art centre, opened to the public at 56 Artillery Lane. Constructed in a pair of 18th-century silk merchants' houses, onto which London practice 6a Architects added two contemporary galleries, it stands on the part of the street known until 1895 as Raven Row. Whitechapel Art Gallery is at the bottom of Brick Lane.
Amongst the many well known artists living in Spitalfields are Gilbert and George, Ricardo Cinalli, Tracey Emin and Stuart Brisley. TV presenter, architecture expert and Georgian fanatic Dan Cruickshank was an active campaigner for Spitalfields, and continues to live in the area. Writer Jeanette Winterson turned a derelict Georgian house into an organic food shop, Verde's, as part of the Slow Food movement.
Spitalfields figures in a number of works of literature, including A New Wonder, a Woman Never Vexed (performed 1610–14; printed 1632) by William Rowley, a dramatisation of the foundation of St Mary Spital; The People of the Abyss (1903), the journalistic memoir by Jack London; Hawksmoor (1985) by Peter Ackroyd; Rodinsky's Room (1999) by Iain Sinclair and Rachel Lichtenstein; Brick Lane (2003) by Monica Ali; and The Quincunx (1991) by Charles Palliser.
19th century Spitalfields was recreated as the setting for the film From Hell about Jack the Ripper. This included a reconstruction (in Prague) of the notorious Ten Bells pub (still extant on Commercial Street): alleged to have been a rendezvous of some of the Ripper's prostitute victims, before they were murdered. In the film Johnny Depp (as Inspector Abberline) is seen drinking there with Ripper victim Mary Jane Kelly.
In Neil Jordan's film The Crying Game (1992), the transgender character "Dil" lives in Spitalfields.
Notable people
This section is in a list format that may be better presented using prose. (April 2013) |
Inga Beale (1963–) British businesswoman, since December 2013 the CEO of Lloyd's of London. Beal is Lloyd's first female CEO in the insurance market's 325-year history.[27][28]
Dan Cruickshank (1949–), art and architectural historian[29]
Nicholas Culpeper (1616–1654), botanist, herbalist, physician, and astrologer was born locally at the Red Lion Inn, when the area was still semi-rural.[30]
Tracey Emin (1963–), artist, resides in Fournier Street.- Sandra Esqulant (1948–), landlady of The Golden Heart, is listed among the 100 most influential people in art.[31]
Mark Gertler, (1891–1939), painter, lesser member of the Bloomsbury Group, in love with Dora Carrington whom he met at the Slade School of Art. Born in Gun St of Polish Jewish parents.
Gilbert & George (1943– ;1942– ), artists, reside in Fournier Street.[32]
Samual Gompers (1850–1924), founder of the American Federation of Labor (AFL), was born in Spitalfields in a Jewish family of cigarmakers originally from Amsterdam until emigration to New York in 1863.[33]
Thomas Helwys (c. 1575 – c. 1616), religious reformer who fled to Amsterdam in 1607/8, but returned in 1611 to found first Baptist congregation on British soil in Spitalfields. Died in prison for public advocacy of religious liberty for all, regardless of creed, even Jews, Muslims, and atheists.
Basil Henriques (1890–1961), for whom Henriques Street (formerly Berner Street) is named.
Jack the Ripper: all of his victims or presumed victims lived in Spitalfields and two (Chapman and Kelly) were murdered there (the others being murdered in nearby Whitechapel):
Annie Chapman (c. 1841 – 1888), resided at a common lodging house at 35 Dorset Street. Her body was found at 29 Hanbury Street[34]
Mary Jane Kelly (c. 1863–1888), lived and was murdered at 13 Millers Court, just off Dorset Street
Martha Tabram (1849–1888), resided at a common lodging house at 19 George Street.[35]
Mary Ann Nichols (1845–1888), resided at a common lodging house at 18 Thrawl Street.[36][37]
Elizabeth Stride (1843–1888), resided at a common lodging house at 32 Flower and Dean Street.
Catherine Eddowes (1842–1888), resided with her partner John Kelly at Cooney's common lodging house at 55 Flower and Dean Street.[38]
Keira Knightley, (1985– ), actress, lived for a while on Wilkes Street.
Joe Loss LVO OBE (1909–1990), born locally, founder of the Joe Loss Orchestra.[39]
Wolf Mankowitz (1924–1998), writer, playwright and screenwriter, of Russian Jewish descent, was born in Fashion Street.
Keith Mansfield, writer and publisher, lives locally.
Samantha Morton, actor, lived on Wilkes Street.[40]
John Nicolson MP, one time journalist and broadcaster and since 2015 an MP for the Scottish National Party; owns a house on Fournier Street which he has restored and renovated himself.
George Peabody (1795–1869), established the Peabody Donation Fund, which continues to this day, as the Peabody Trust, to provide good quality housing "for the deserving poor" in London: the fund's first block of dwellings opened in Commercial Street in 1864.
Sian Phillips, (1933–), actress
Jonathan Pryce, (1947– ), actor and singer
Lutfur Rahman, first directly elected Mayor of Tower Hamlets and former ward councillor
Dennis Severs (1944–1999), lived at 18 Folgate Street 1979–1999.
Jack Sheppard (1702–1724), highwayman and multiple absconder, born in New Fashion Street, now known as White's Row.[41]
Obadiah Shuttleworth (died 1734), musician- Sir Benjamin Truman (1699/1700–1780), brewer.
Arnold Wesker (1932–2016), playwright, author, poet, born in Mother Levy's Maternity Home, Underwood Rd. With his family took refuge during WW2 in "Mickey's Shelter" below the Fruit & Wool Exchange.
Jeanette Winterson (1959–), writer, lives on Brushfield Street where she also runs a delicatessen.[42]
Mary Wollstonecraft (1759–1797), early feminist, born locally, possibly at 21 Hanbury Street.[34]
Joe Wright (1972–), film director, bought a house on Wilkes Street but in 2013 sold it to actor Jonathan Pryce
Transport
The nearest London Underground stations are Aldgate East station (which is in the district) and Liverpool Street station. London Liverpool Street is also a National Rail station.
The nearest London Overground station is Shoreditch High Street
See also
- Bethlem Royal Hospital
- List of schools in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets
Old Truman Brewery – The Black Eagle Brewery on Brick Lane, and into surrounding streets.- Spitalfields riots
- Spitalfields Festival
- Stepney Historical Trust
References
^ "Tower Hamlets Ward population 2011". Neighbourhood Statistics. Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 17 October 2016..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ ab Gover, J. E. B.; Mawer, Allen; Stenton, F. M. (1942). The Place-Names of Middlesex. English Place-Name Society. 18. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 151–2.
^ B. Lambert (1806). The history and survey of London and its environs. T. Hughes. p. 79. Retrieved 1 April 2013.
^ F. H. W. Sheppard (1957). The Priory of St Mary Spital | Survey of London: volume 27 (pp. 21–23). Retrieved 1 April 2013.
^ F. H. W. Sheppard (1957). General introduction | Survey of London: volume 27 (pp. 1–13). british-history.ac.uk. Retrieved 25 November 2012.
^ ab Thomas Christopher (2004). Life and Death in London's East End: 2000 years at Spitalfields. Museum of London Archaeology Service. pp. 7–29. ISBN 1-901992-49-7.
^ Discovering people at Spitalfields market Archived 12 March 2007 at the Wayback Machine.
^ "Pagans of Roman Britain". bbc.co.uk. 7 January 2014. Retrieved 7 January 2014.
^ Thomas, Sloane and Phillpotts (1997) Excavations at the Priory and Hospital of St Mary Spital, London. Museum of London: London: 19–20
^ Thomas: pp. 30–75
^ Fiona Rule (2008) The Worst Street in London. Hersham, Ian Allan: 18–26
^ abc Industries: Silk-weaving, A History of the County of Middlesex: Volume 2: General; Ashford, East Bedfont with Hatton, Feltham, Hampton with Hampton Wick, Hanworth, Laleham, Littleton (1911), pp. 132–137. Date accessed: 4 March 2009
^ Fiona Rule (2008) The Worst Street in London. Hersham, Ian Allan: 28
^ Thomas: pp. 76–95
^ Dreyer, Joseph (1920). History of the Royal Astronomical Society. p. 99.
^ ab Old Spitalfields Market Published 2008. Retrieved 17 June 2009.
^ User, Super. "Huguenots of Spitalfields heritage tours & events in Spitalfields - Huguenot Public Art Trust". www.huguenotsofspitalfields.org.
^ Observations on the ruinous tendency of the Spitalfields Act to the silk manufacture, books.google.com
^ White, Jerry (4 January 2007). London in the Nineteenth Century: A Human Awful Wonder of God. Jonathan Cape. p. 323. ISBN 978-0-224-06272-5.
^ The Worst Street in London Fiona Rule (Ian Allan Ltd, 2008)
ISBN 978-0-7110-3345-0
^ White: p. 331
^ ab Taylor, Wi (24 May 2001). This Bright Field: A Travel Book in One Place. Methuen Publishing. ISBN 978-0-413-74690-0.
^ London Borough of Tower Hamlets, Planning, Spitalfields http://www.towerhamlets.gov.uk/lgnl/environment_and_planning/planning/planning_guidance/neighbourhood_planning/Spitalfields.aspx
^ Brooke, Mike (6 April 2016). "Spitalfields planning forum gets legal recognition in bid to halt City encroachment". Docklands and East London Advertiser. Retrieved 18 August 2016.
^ Dennis Severs. "The Tour". p. 3. Retrieved 25 November 2012.
^ Gavin Stamp (10 January 2000). "Dennis Severs | News | The Guardian". The Guardian. London: GMG. ISSN 0261-3077. OCLC 60623878. Retrieved 25 November 2012.
^ Gray, Alistair (20 December 2013). "Inga Beale, the steely trailblazer shaking up a masculine bastion". Financial Times.
^ Susannah Butter (2016). "Lloyd's CEO Inga Beale on coming out as bisexual in a job interview". London Evening Standard. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
^ Gould, Mark (10 December 2013). "Dan Cruikshank: London's East End is threatened by 'creeping and ghastly greed'". the Guardian.
^ Fiona Rule (2008) The Worst Street in London. Hersham, Ian Allan: 20-1
^ "One day Gilbert & George walked into the bar, and my life changed" Published 17 December 2006. Retrieved 5 October 2009.
^ "Well, that's Gilbert and George for you". independent.co.uk. 26 August 1995.
^ Swierenga, Robert P. (2000). Faith and Family. New York: Holmes & Meier. p. 197. ISBN 0-8419-1319-6.
^ ab (ed.) Sheppard, F. H. W. (1957). 'The Wood-Michell estate: Hanbury Street west of Brick Lane' Survey of London: volume 27 – Spitalfields and Mile End New Town. pp. 189–193. Retrieved 2 June 2008.CS1 maint: Extra text: authors list (link)
^ Stewart Evans and Donald Rumbelow (2006) Jack the Ripper: Scotland Yard Investigates: 51–55
^ Stewart Evans and Donald Rumbelow (2006) Jack the Ripper: Scotland Yard Investigates: 56–62
^ Paul Begg (2006) Jack the Ripper: The Facts: 42
^ Stewart Evans and Donald Rumbelow (2006) Jack the Ripper: Scotland Yard Investigates: 114-40
^ "Joe Loss - Biography & History - AllMusic". AllMusic.
^ Today, Realty (17 September 2013). "Pirates of the Caribbean Actress Keira Knightly Lists London Townhouse for $4.7 Million". realtytoday.com.
^ Fiona Rule (2008) The Worst Street in London. Hersham, Ian Allan: 30
^ Winterson, Jeanette (12 June 2010). "Once upon a life: Jeanette Winterson". the Guardian.
Further reading
John Timbs (1867), "Spitalfields", Curiosities of London (2nd ed.), London: J.C. Hotten, OCLC 12878129
External links
This article's use of external links may not follow Wikipedia's policies or guidelines. (November 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Spitalfields Life Daily blog that tells the stories of Spitalfields residents, past and present.- The Priory of St Mary Spital
spitalfields.org TH Council website- Brief History of Spitalfields
- Spitalfields City Farm
19 Princelet Street Unrestored Huguenot Master weaver's house, with synagogue. Rarely open to the public at present, but eventually to become a museum of immigration & diversity.
Dennis Severs' House 18th century time capsule- Kinetica Museum
Archives relating to Spitalfields at The National Archives (United Kingdom)
Spitalfields Life Mickey Davis at the Fruit & Wool Exchange- Huguenots of Spitalfields
Images
Images of Spitalfields at the English Heritage Archive
Images of Spitalfields at the Country Life Picture Library
London Metropolitan University East End Archive: The Paul Trevor Collection – photographs of the Spitalfields area from the 1970s to the 1990s.
Nighttime photos of Spitalfields, Whitechapel, etc.; a German language website, but mostly photos
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Spitalfields, London. |
