Digital terrestrial television
| List of digital television broadcast standards |
|---|
DVB standards .mw-parser-output .nobold{font-weight:normal} (countries) |
|
ATSC standards (countries) |
|
ISDB standards (countries) |
|
DTMB standards (countries) |
|
DMB standard (countries) |
|
Codecs |
|
Frequency bands |
|
Digital terrestrial television (DTTV or DTT) is a technology for broadcast television in which land-based (terrestrial) television stations broadcast television content by radio waves to televisions in consumers' residences in a digital format. DTTV is a major technological advance over the previous analog television, and has largely replaced analog which had been in common use since the middle of the last century. Test broadcasts began in 1998 with the changeover to DTTV (aka Analog Switchoff (ASO) or Digital Switchover (DSO)) beginning in 2006 and is now complete in many countries. The advantages of digital terrestrial television are similar to those obtained by digitising platforms such as cable TV, satellite, and telecommunications: more efficient use of limited radio spectrum bandwidth, provision of more television channels than analog, better quality images, and potentially lower operating costs for broadcasters (after the initial upgrade costs).
Different countries have adopted different digital broadcasting standards; the major ones are:[1]
ATSC DTV – Advanced Television Standards Committee (System A)- ATSC-M/H – Advanced Television Systems Committee Mobile & Handheld
- ChinaDTV
DVB-H – Digital Video Broadcasting Handheld
DVB-T/DVB-T2 – Digital Video Broadcasting Terrestrial (System B)
ISDB-T – Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting Terrestrial (System C)- DMB-T/H
ISDB-TSB – Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting-Terrestrial Sound Broadcasting – (System F)
FLO – Forward Link Only (System M)
Contents
1 Transmission
2 Reception
3 DTT around the world and digital television transition
4 Asia
4.1 Afghanistan
4.2 Bangladesh
4.3 India
4.4 Israel
4.5 Japan
4.6 Malaysia
4.7 Philippines
4.8 Thailand
5 Oceania
5.1 Australia
5.2 New Zealand
6 Europe
6.1 European Union
6.1.1 Bulgaria
6.1.2 Denmark
6.1.3 Finland
6.1.4 France
6.1.5 Germany
6.1.6 Greece
6.1.7 Hungary
6.1.8 Ireland
6.1.9 Italy
6.1.10 Luxembourg
6.1.11 Netherlands
6.1.12 Poland
6.1.13 Portugal
6.1.14 Romania
6.1.15 Spain
6.1.16 Sweden
6.1.17 United Kingdom
6.2 Macedonia
6.3 Russia
6.4 Switzerland
7 North America
7.1 Bahamas
7.2 Bermuda
7.3 Canada
7.4 Mexico
7.5 United States
8 Central America and the Caribbean
8.1 Costa Rica
8.2 Cuba
8.3 Dominican Republic
8.4 El Salvador
8.5 Nicaragua
8.6 Panama
9 South America
9.1 Argentina
9.2 Bolivia
9.3 Brazil
9.4 Chile
9.5 Colombia
9.6 Ecuador
9.7 Paraguay
9.8 Peru
9.9 Suriname
9.10 Uruguay
9.11 Venezuela
10 Africa
10.1 Nigeria
10.2 Tunisia
11 Analogue to digital transition by countries
12 See also
13 References
14 External links
Transmission

DTT transmitters located at Mount Zhentou in Tainan, Taiwan
DTTV is transmitted using radio frequencies through terrestrial space in the same way as the former analog television systems, with the primary difference being the use of multiplex transmitters to allow reception of multiple services (TV, radio stations or data) on a single frequency (such as a UHF or VHF channel).
The amount of data that can be transmitted (and therefore the number of channels) is directly affected by channel capacity and the modulation method of the transmission.[2]
North America uses the ATSC standard with 8VSB modulation, which has similar characteristics to the vestigial sideband modulation used for analog television. This provides considerably more immunity to interference, but is not immune to multipath distortion and also does not provide for single-frequency network operation (which is in any case not a requirement in the United States).[citation needed]
The modulation method in DVB-T is COFDM with either 64 or 16-state Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM). In general, 64QAM is capable of transmitting a greater bit rate, but is more susceptible to interference. 16 and 64QAM constellations can be combined in a single multiplex, providing a controllable degradation for more important program streams. This is called hierarchical modulation. DVB-T (and even more so DVB-T2) are tolerant of multipath distortion and are designed to work in single frequency networks.
Developments in video compression have resulted in improvements on the original H.262 MPEG 2 codec, which has been surpassed by H.264/MPEG-4 AVC and more recently H.265 HEVC. H.264 enables three high-definition television services to be coded into a 24 Mbit/s DVB-T European terrestrial transmission channel.[2] DVB-T2 increases this channel capacity to typically 40 Mbit/s, allowing even more services.
Reception
DTTV is received either via a digital set-top box (STB), TV gateway or more usually now an integrated tuner included with television sets, that decodes the signal received via a standard television antenna. These devices often now include digital video recorder (DVR) functionality.[3] However, due to frequency planning issues, an aerial capable of receiving a different channel group (usually a wideband) may be required if the DTTV multiplexes lie outside the reception capabilities of the originally installed aerial.[4] This is quite common in the UK; see external links.
Indoor aerials are even more likely to be affected by these issues and possibly need replacing.[5]
DTT around the world and digital television transition
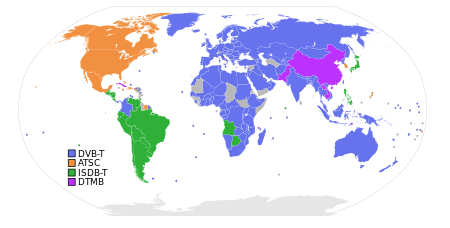
DTT broadcasting systems by country
- Main articles: List of digital television deployments by country, Digital television transition (aka Analog Switchoff (ASO) or Digital Switchover (DSO))
Asia
Afghanistan
Afghanistan officially launched digital transmissions in Kabul using DVB-T2/MPEG-4 on Sunday, 31 August 2014.[6] Test transmissions had commenced on 4 UHF channels at the start of June 2014. Transmitters were provided by GatesAir.
Bangladesh
Bangladesh had its first DTT service DVB-T2/MPEG-4 on April 28, 2016 launched by the GS Group. The service is called RealVU.
It is done with partnership with Beximco. GS Group acts as a supplier and integrator of its in-house hardware and software solutions for the operator's functioning in accordance with the modern standards of digital television.RealVu provides more than 100 TV channels in SD and HD quality.
The digital TV set-top boxes developed by GS Group offer such functions as PVR and time-shift, along with an EPG.
India
India adopted DVB-T system for digital television in July 1999.[7] The first DVB-T transmission was started on 26 January 2003 in the four major metropolitan cities by Doordarshan.[8] Currently the terrestrial transmission is available in both digital and analog formats. 4 high power DVB-T transmitters were set up in the top 4 cities, which were later upgraded to DVB-T2 + MPEG4 and DVB-H standards. An additional 190 high power, and 400 low power DVB-T2 transmitters have been approved for Tier I, II and III cities of the country by 2017. The Indian telecom regulator, TRAI, had recommended the I&B to allow private broadcast companies to use the DTT technology, in 2005.[9] So far, the Indian I&B ministry only permits private broadcast companies to use satellite, cable and IPTV based systems. The government's broadcasting organisation Doordarshan had started the free TV service over DVB - T2 to the mobile phone users from February 25 onwards and extended to cover 16 cities including the four metros from April 5, 2016.[10]
Israel
Israel started digital transmissions in MPEG-4 on Sunday, August 2, 2009, and analogue transmissions ended on March 31, 2011. Israel was the first nation in the Middle East and the first non-European nation to shut down its analogue TV distribution system. The new service which is operated by The Second Authority for Television and Radio in Israel currently offers 6 SD TV channels and 30 national and regional (private) radio services. According to government decisions, the system will expand to include two additional multiplexes that will carry new channels and HD versions of the existing channels. There is a proposition by the Ministry of Finance to run a tender in order to hand over the maintenance of the system to a private company that, in return, will receive an extended license and will be able to offer pay TV channels. In this matter nothing has been decided upon until the end on 2012.
On March 20, 2013, it was announced that Thomson Broadcast had won a major contract with The Second Authority for Television and Radio for the extension of its nationwide DVB-T/DVB-T2 network. The Second Authority's order for new infrastructure includes two new multiplexes on thirty sites including three single frequency areas. This major deal incorporates a three-year service agreement for the global transmission system.
Sixty-three high- and medium- power transmitters from Thomson's GreenPower range have been ordered together with installation and commissioning services, in a deal which follows on from the company's earlier deployment of DVB-T multiplexes over thirty transmission and sixty-two repeater sites. Equipped with dualcast-ready digital exciters, the GreenPower range offers the ability to smoothly migrate from DVB-T to DVB-T2 and to easily offer additional HDTV content. Ranging from low- to high- power, the range covers all the power requirements of The Second Authority. Thomson will also deploy its user-friendly centralized Network Management System to control and monitor the overall transmission system from a single facility.
The deal includes a new service level agreement providing The Second Authority with a high level of local services to keep its currently operating DTV transmission equipment running 24/7, 365 days a year.
Japan

Two digital terrestrial television receiving antenna on the roof, upper antenna facing Tokyo Tower and lower one to another Local Television Stations in Kantō Plain of Japan until Tokyo Skytree operates. (For ISDB-T system)

Simple and low cost ISDB-T Set-top box (tuner) with remote control
The Japanese Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications and DPA (The Association for Promotion of Digital Broadcasting-Japan) jointly set the specification and announced a guideline for "simplified DTT tuners" with price under 5,000 Japanese yen on December 25, 2007. MIAC officially solicited manufactures to put it on the market by end of March 2010 (end of fiscal year 2009). MIAC is estimating that 14 million, at maximum, traditional non-digital TV sets remain and need the "simplified DTT tuner" to be adapted even after complete transition to DTT after July 2011; it is aiming to avoid the disposal of large numbers of useless TV sets without such a tuner at one time.
On December 20, 2007, the Japan Electronics and Information Technology Industries Association published rules for Digital Rights Management for DTT broadcasting under the name "Dubbing 10". Despite the name, consumers were allowed to use Blu-ray Disc and other recorders to "dub" or copy the video and audio of entire TV programs up to 9 times, with 1 final "move" permitted.
Broadcasting with "Dubbing 10" was supposed to start at about 4:00 a.m. on June 2, 2008, but was postponed after lengthy talks with the Japanese Society for Rights of Authors, Composers and Publishers. It finally started about 4:00 a.m. on July 4, 2008. The manufacturers of DVD and DTT recorders were to make units conforming to the "Dubbing 10" rules, and some manufacturers announced plans for create firmware downloads to allow users to update their existing recorders.
On April 3, 2008, DPA announced that a total of 32.71 million of DTT (ISDB-T) TV sets capable of DTT reception (excepting 1seg receivers) had been installed in Japan as of the end of March 2008. On April 8, 2008 DPA also announced guidelines for manufacturers of DTT receiving, record and replay unit which operate with personal computers. These add-on units operate on USB or PCI BUS, and went on sale on a reservation basis from late April, appearing in retail store in mid-May 2008.
On May 8, 2008, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications announced that 43.7% of homes had DTT (ISDB-T) capable TVs and/or tuners with DVD recorder by end of March 2008.It had been 27.8% one year before, and the ministry was expecting 100% penetration by April 2011. On 27 April 2009, National Association of Commercial Broadcasters in Japan (NAB) a new official mascot, Chidejika, to replace Tsuyoshi Kusanagi after he was arrested on suspicion of public indecency.
On September 3, 2009, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications announced the procurement by tender of 5,000-8,000 sets of "simplified DTT tuners" with remote control for the citywide test transition from analogue to digital in Suzu, Ishikawa. The sets should be delivered by end November 2009.[11] The program is aiming to examine the transition problem at individuals' home in country wide such as senior and non-technical families. Based on this rehearsal plan, analog TV transmission was interrupted in Suzu and parts of Noto for 48 hours, between noon on 2010/01/22 and noon on 2010/01/24.[12][13]
On September 4, 2009, ÆON announced the low cost "simplified DTT tuners" with remote control for ISDB-T to sell at JUSCO from September 19, 2009. The tuner is produced by Pixela Corporation, and met the retail price of under 5,000 Japanese yen, which is the target price to industry by Dpa (The Association for Promotion of Digital Broadcasting (デジタル放送推進協会, dejitaru housou suishin kyōkai)). The tuner connects to an old fashioned TV though an RCA connector with SDTV quality and some other minimal functions.[14]
On September 7, 2009, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications appointed two manufacturers I-O Data and Melco among 12 bids for minimal functioning "simplified DTT tuners" with remote control for ISDB-T of free supply to Japanese Temporary Assistance for Needy Families. Tuner connects to old fashion TV though RCA connector with SDTV quality and some other minimal function.[15] On July 24, 2010, at noon, analog TV transmission officially stopped in Suzu and parts of Noto (approximately 8,800 homes) as the rehearsal plan that took place one year ahead of the nationwide shutdown, which is scheduled on July 24, 2011. Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications shall watch what type of problem arise in transition to DTT which might apply to the nationwide shutdown.

Analog television shut down in Japan at noon. All television stations broadcast a blue information screen that displayed one or more telephone numbers for digital television inquiries on the day of the shutdown until the transmitters shut off at midnight.
On April 20, 2011, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications confirmed, and made the resolution by the House of Councillors on June 8, 2011, that the analog terrestrial TV close down schedule on 24 July 2011 will be unchanged, with the exception being the close down having to be postponed by a maximum one year. Analog television shut down on March 31, 2012, in Iwate, Miyagi and Fukushima prefectures, which were heavily damaged in the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami and the nuclear accidents that followed it.[16][17] Analog television stations are required to cease normal programming at noon and shut down their signals at midnight.
Malaysia
Digital TV was available in Malaysia in June 2015 by MYTV broadcasting. Malaysia government gives free MYTV set top box if your income is under RM3000 and below or under BR1M. There are nine channels to choose from.
They launch 13 Digital TV stations nationwide which covers up to 80% household. They planned to add more Digital TV stations and covers up to 99% household by end of 2017. Malaysian Prime Minister Datuk Seri Najib Razak officially launched myFreeview's free service on 6 June 2017.[18][19]
By November 2016, MYTV set top box will be available for sale in electronics store nationwide.
They planned to switch off analog TV by 30 June 2018.
Philippines
On June 11, 2010, National Telecommunications Commission of the Philippines announced that the country will use the Japanese ISDB-T International standard.[20][21] The first fully operational digital TV channel is Channel 49 of the religious group Iglesia ni Cristo.
However, in October 2012, DZCE-TV (which occupies the channel) reopened the analog signal to relaunch as INC TV; therefore, channel 49 can only transmit digitally during off-air hours of the analog channel 49.
This was followed by state-owned television network PTV which conducted its test transmission on UHF Channel 48.
On February 11, 2015, the major TV network ABS-CBN commercially launched the digital TV box called ABS-CBN TV Plus also known as Mahiwagang Blackbox. Seven years before the commercial launch, the network initially applied for a license from NTC on digital free TV. The digital TV box was given away as a prize for the loyal viewers and listeners of ABS-CBN channel 2, DZMM (AM radio station of ABS-CBN) and DZMM TeleRadyo (TV-radio cable channel of ABS-CBN) after the initial application.
Digital television transition began on February 28, 2017, with ZOE Broadcasting Network's DZOZ-TV as the country's first station to permanently shut down analog terrestrial transmissions[22] without any test simulcast with its digital signal, and is expected to be finished by 2023.[23]
On 25 May 2018, Solar Entertainment Corp began a new digital TV service called Easy TV where most of its channels are offered to consumers through Easy TV's proprietary set-top box.
Thailand
In 2005, the Ministry of Information announced their plan to digitalise nationwide free-to-air TV broadcasts led by MCOT Public Company Limited (MCOT). Trial broadcasts were undertaken, involving one thousand households in the Bangkok Metropolitan Area from December 2000 till May 2001. According to the then-Deputy Minister of Information, the trial received "very positive" feedback, i.e. "more than 60 percent said the quality of the signal ranged from good to very good. Over 88 percent said the picture quality improved, while 70 percent said the sound quality was better."
According to Information Minister, Sontaya Kunplome, MCOT is expected to fully complete its digitalization in 2012 as part of its three-year restructuring process. Each household, once equipped with the necessary equipment (set-top box or iDTV set) is expected to receive up to 19 channels, seven of which fall under MCOT and the rest for private broadcasters such as BEC-TERO which owns its channels such as TV3. Thus far, besides simulcasting Modernine TV and Television of Thailand, MCOT is test-airing MCOT 1, MCOT 2 and MCOT 3 exclusively on the digital TV platform, transmitted at UHF channel 44, modulated at 64QAM. MCOT was also expected to launch regional channels for each province and/or territory in Thailand, making it 80 MCOT television channels. BEC-TERO was expected to commence trials in March 2009.
Thailand and the rest of ASEAN countries (with the exception of the Philippines; see above) have selected DVB-T as the final DTV standard, and are expected to switch off analogue broadcasts completely by 2015.[24] In June 2008, participants of the 6th ASEAN Digital Broadcast Meeting from seven south-east Asian countries (including Thailand) agreed to finalise the specifications of the DTV set-top box for use within ASEAN, and also set up an ASEAN HD Centre to provide training on HDTV content to broadcasters in the region.[25]
Even though MCOT's trial was a success, the future of the digital terrestrial television transition has become uncertain, especially after the end of Somchai Wongsawat's tenure as the Prime Minister and the beginning of successor Abhisit Vejjajiva's reign in favor of his concept.
In March 2011, MCOT announced that it is also possible that MCOT may be planning to switch to DVB-T2 some time in the future to replace DVB-T.
The Switch-off Date has been planned for 2020. (Only for Channel 3 (Thailand)) For now, five analogue channels has been off-air since 16 June 2018(Thai Public Broadcasting Service and Channel 7 (Thailand)), 21 June (Channel 5 (Thailand)) and 16 July (Channel 9 MCOT HD and NBT)
Oceania
Australia
Australia uses DVB-T. The transition to digital television and the phaseout of analogue television was completed on 10 December 2013.
New Zealand
New Zealand uses DVB-T. The transition to digital television and the shutdown of analogue transmissions was completed on 1 December 2013
Europe
European Union
The EU recommended in May 2005[26] that its Member States cease all analogue television transmissions by January 1, 2012. Some EU member states decided to complete the transition as early as 2006 for Luxembourg and the Netherlands, and 2007 for Finland.[27] Latvia stopped broadcasting analogue television from June 1, 2010. Poland completed the transition on 23 July 2013 and Bulgaria completed the transition on 30 September 2013. Malta switched on 1 November 2011. ASO was mostly completed in Europe in 2013 though small hilly underpopulated isolated terrain areas awaited DTT rollout beyond that date.[28][29]
Many TV-viewers TV-equipment in Europe might experience TV-interference and blocking because of 800MHz broadband usage.
Bulgaria
Bulgaria launched a free-to-air platform on Sofia region, starting in November 2004. Standards chosen are DVB-T and MPEG4 AVC/H.264 compression format. DVB-T2 will not be used at this time. The Communications Regulatory Commission (CRC) has said that it received 6 bids for the licence to build and operate Bulgaria's two nationwide DTT networks. A second licence tender for the operation of 3 DTT multiplexes was open until 27 May 2009.[30][31] Following the closing of this process, Hannu Pro, part of Silicon Group, and with Baltic Operations has secured the license to operate three DTT multiplexes in Bulgaria by the country's Communications Regulatory Commission (CRC) Bulgaria officially completed the transition to digital broadcasting on Monday, 30 September 2013.[32]
Denmark
DTT had its technical launch in Denmark in March 2006 after some years of public trials. The official launch was at midnight on November 1, 2009 where the analogue broadcasts shut down nationwide.
As of January 2013, five national multiplexes are available, broadcasting several channels in both SD and HD via both DVB-T and DVB-T2, all using the MPEG-4 codec.
MUX 1 and 2 are Free-to-air and operated by I/S DIGI-TV, a joint-venture between DR and TV 2.
MUX 3, 4 and 5 are operated by Boxer, and are for pay television only.
Finland
Finland launched DTT in 2001, and terminated analogue transmissions nationwide on 1 September 2007. Finland has successfully launched a mixture of pay and free-to-air DTT services. Digita operates the DTT and Mobile Terrestrial networks and rents capacity to broadcasters on its network on a neutral market basis. Digita is owned by TDF (France).[33][34] The pay-DTT service provider Boxer has acquired a majority stake in the leading Finnish pay DTT operator PlusTV which offers a number of commercial channels for a subscription. It started in October 2006. Boxer already provides pay-DTT services in Sweden and Denmark.[35]
Three nationwide multiplexes are granted to DNA and Anvia for DVB-T2 for High Definition and Standard Definition channel (MPEG4).
France
France's TNT (Télévision Numérique Terrestre) offers 25 free national channels and 9 pay channels, plus up to 4 local free channels. An 89% DTT penetration rate is expected by December 2008. Free-to-view satellite services offering the same DTT offer were made available in June 2007.
Since 12 December 2012, TNT has delivered ten free HD channels (TF1 HD, France2 HD, M6 HD, Arte HD, HD1, L'Equipe 21, 6ter, Numéro 23, RMC Découverte HD, Chérie 25) and one pay TNT HD channel (Canal+ HD) using the MPEG4 AVC/H.264 compression format. French consumer technology magazine Les Numériques gave the picture quality of TNT's previous 1440x1080i service a score of 8/10, compared to 10/10 for Blu-ray 1080p.[36]
Typically:
- free TNT channels are broadcast 720×576 MPEG-2 with a VBR of 3.9 Mbits (2.1 to 6.8 as measured)or a CBR of 4.6 Mbits
- pay TNT channels are broadcast 720×576 MPEG4 AVC/H.264 with a VBR of 3.0 Mbits (1.1 to 6.0 as measured)
- free TNT-HD and pay TNT-HD are broadcast 1920×1080 (1080i50) MPEG4 AVC/H.264 with a VBR of 7.6 Mbits (3 to max 15M), but were previously broadcast at the lower definition of 1440x1080.
For the audio part AC3 and AAC are used in 192 kbits for 2.0 and 384 kbits for 5.1.
Typically up to four audio part can be used:
French 5.1
VO (original language) 5.1
French 2.0
Audivision 5.1
The Prime Minister François Fillon confirmed that the final analogue switch-off date would be 30 November 2011.[37] DTT coverage had to reach 91% of a given département before analogue transmissions could be switched off. CSA announced a call to tender for more local DTT licences on 15 June 2009 and 66 new DTT sites went up since May 2009 to expand coverage to cover low population areas.[38][39]
Freesat began broadcasts from the Eutelsat Atlantic Bird 3 satellite from June 2009 as Fransat, providing for those unable to receive DTT signals for terrain reasons in preparation for ASO in 2011. Eighteen channels were broadcast initially and although free to watch, viewers needed to buy a set top box with smart card for €99 according to DVB.org article.[40]
The end dates of analogue shutdown were: 2 February 2010: Alsace, 9 March 2010: Lower Normandy, 18 May 2010: Pays de la Loire, 8 June 2010: Bretagne, 28 September 2010: Lorraine and Champagne-Ardenne, 19 October 2010: Poitou-Charentes and the middle of the country, November 2010: Franche-Comté and Bourgogne, 7 December 2010: North of the country, First quarter 2011: Picardie and Haute-Normandie, Île-de-France, Aquitaine and Limousin, Auvergne, Côte d'Azur and Corsica, Rhône, Second quarter 2011 (before November 30): Provence, Alpes, Midi-Pyrénées, Languedoc-Roussillon.[41][42]
Germany
Germany launched a free-to-air platform region-by-region, starting in Berlin in November 2002. The analogue broadcasts were planned to cease soon after digital transmissions are started. Berlin became completely digital on 4 August 2003 with other regions completing between then and 2008. Digital switchover has been completed throughout Germany as of 2 December 2008 and services are now available to 100% of the population following the update of infill for the remaining 10% of transmitters by Media Broadcast who set up broadcast antennas at 79 transmission sites and installed 283 new transmitter stations. More services are to be launched on DTT and some pay DTT channels are or have been launched in various areas such as Stuttgart and soon Leipzig.[43]
Greece
January 16,[44] 2006: Started its first pilot DTT broadcasts of 1st DTT package using five transmitters in Attica (Hymettus, Parnitha, Aegina): 48 UHF, Central Macedonia (Chortiatis): 56 UHF and Thessaly (Pelion): 53 UHF to distribute the stations Prisma+, Cine+, Sport+ and RIK Sat via its ERT Digital subsidiary, transmitting digitally terrestrial for first time in Greece.
September 26, 2007: Broadcasting of 1st DTT package from 26 UHF added in Central Macedonia region from Chortiatis, Central Macedonia (Chortiatis): 26, 56 UHF.
October 13, 2007: Broadcasting of 1st DTT package from 42 UHF added in Thessaly region from Pelion, Thessaly (Pelion): 42, 53 UHF.
October 31, 2008: Broadcasting of 1st DTT package commenced in South West Thrace (Plaka): 64 UHF.
May 6, 2009: Broadcasting of 1st DTT package from Styra added to Attica region, Attica (Hymettus, Parnitha, Aegina, Styra): 48 UHF.
October 7, 2009: Broadcasting of 1st DTT package commenced in Arcadia and Argolis (Doliana): 21 UHF.
September 27, 2010: Started broadcast of 2nd DTT package in Attica (Hymettus): 52 UHF, Central Macedonia (Chortiatis): 26 UHF (switching off 1st DTT package from 26 UHF in Central Macedonia region from Chortiatis), 1st DTT package in Central Macedonia (Chortiatis): 56 UHF only consisting of television stations Et1, NET, ET3, Vouli Tileorasi, and radio stations NET, Deftero, Trito, ERA Sport, KOSMOS.
November 19, 2010: Broadcasting of 2nd DTT package commenced in South West Thrace (Plaka): 58 UHF.
December 14, 2010: Broadcasting of 2nd DTT package from Aegina added to Attica region, Attica (Hymettus, Aegina): 52 UHF.
January 14, 2011: Broadcasting of 2nd DTT package moved frequency in Central Macedonia region from 26 UHF (switching off 26 UHF) to 23 UHF and added broadcasting also from Philippion from 23 UHF, Central Macedonia (Chortiatis, Philippion): 23 UHF.
April 26, 2011: 1st DTT package consists from now on with television stations Vouli Tileorasi, Prisma+, CineSport+ continuing Sport+ created from the merge of Cine+ and Sport+ stations and RIK Sat, all stations with temporarily MPEG-2 Compression. 2nd DTT package consists from now on with television stations ET1, NET, ET3 and a new Full High Definition television station ERT HD, all stations with H.264/MPEG-4 AVC Compression along with radio stations NET, Deftero, Trito, ERA Sport, KOSMOS.
April 27, 2011: ERT HD started pilot High Definition transmissions.
May 2, 2011: Broadcasting of 1st DTT package moved frequency in Arcadia and Argolis from 21 UHF to 39 UHF, Arcadia and Argolis (Doliana): 39 UHF.
May 27, 2011: Broadcasting of 1st DTT package commenced in Central Thessaly (Dovroutsi): 43 UHF
July 29, 2011: Broadcasting commenced in the Gulf of Corinth (Xylokastro): 55 & 61 UHF
October 27, 2011: Broadcasting commenced in Aetolia-Acarnania.
November 2011: Broadcasting commenced in Corfu.
February 3, 2012: Broadcasting commenced in Patra.
August 17, 2012: Analogue TV was switched off in Athens.
The following switch-offs are in cooperation with Digea, so the dates are the same.
Digea:
24 September 2009:The first digital broadcasting of Digea consisting of television stations Alpha TV, Alter Channel, ANT1, Makedonia TV, Mega Channel, Skai TV and Star Channel was carried out in the Gulf of Corinth from the transmitting site of Xylokastro.
14 January 2010: Digital broadcasting began in Thessaloniki - Central Macedonia from the transmitting sites of Chortiatis and Philippion.
18 June 2010: Digital broadcasting began in Athens - Attica from the transmitting sites of Hymettus and Aegina.
1 September 2010: Digital broadcasting of regional scale channels 0-6 TV, ATTICA TV, Extra 3, High TV, MAD TV, MTV Greece, Nickelodeon (Greece) and SPORT TV added in Athens - Attica from the transmitting site of Aegina.
8 February 2011: Digital broadcasting of regional scale channels BLUE SKY, CHANNEL 9, KONTRA Channel and TELEASTY added in Athens - Attica from the transmitting site of Aegina.
25 February 2011: Digital broadcasting began in Rhodes (city).
19 March 2011: Digital broadcasting began in Alexandroupoli - South West Thrace.
27 May 2011: Digital broadcasting began in Central Thessaly
December 9, 2011: Digital broadcasting began in Aitoloakarnania.
February 3, 2012: Digital broadcasting began in Patra.
July 20, 2012: Analogue TV signals were switched off in Athens.
December 14, 2012: Analogue TV signals were switched off in Thessaloniki.
June 26, 2013: Digital broadcasting began in Crete.
September 27, 2013: Digital broadcasting began in Kalamata
June 27, 2014: Analogue TV signals were switched off in Peloponnisos.
August 1, 2014: Analogue TV signals were switched off in Attica.
September 5, 2014: Analogue TV signals were switched off in East Macedonia and Thrace, Lemnos and Lesbos.
November 21, 2014: Analogue TV signals were switched off in Central Macedonia, Thessaly and Central Greece.
December 19, 2014: Analogue TV signals were switched off in West Macedonia, Epirus, Western Greece, Corfu.
February 6, 2015: Analogue TV signals were switched off in Crete, Samos, Icaria and Dodecanese.
Digital Union:
27 March 2010: The first digital broadcasting of Digital Union consisting of Regional television stations Time Channel, TV Thessaloniki, TV Chalkidiki, in Thessaloniki / Central Macedonia.
27 August 2010: Digital transmission of Regional television stations New Televisionof Chania and 4 U TV, in Iraklion - Crete Isl.
6 November 2010: Digital broadcasting began in Patra, for the Regional Channels Lepanto TV, Best TV, ORT and Ionian TV.
19 March 2011: Digital broadcasting began in Alexandroupoli - South West Thrace from the transmitting site of Plaka, for the Regional Channels Thraki NET, Delta TV, Home Shop and Rodopi TV.
27 May 2011: Digital broadcasting began in Central Thessaly from the transmitting site of Dovroutsi, for the Regional Channels Thessalia TV, Trikala TV 10, TRT and Astra TV.
ERT - NOVA (pay TV platform):
July 22, 2011: Broadcasting consisting of television stations NovaCinema1, NovaSports1 and two more satellite TV channels, that ERT will decide in the future, commenced in Attica (Hymettus): 22 UHF
Autumn 2011: Broadcasting will commence in Thessaloniki - Central Macedonia.
January 2012: Broadcasting will commence in 21 more areas.
July 11, 2014: Platform's DTT ceases to exist.
TV1 Syros started its first pilot broadcasts on November 1, 2008 in Cyclades (Syros): 60 UHF.
As of February 6, 2015, Greece has completed its transition to digital TV..
Hungary
Experimental DTT broadcast has started in December 2008. The program of Duna Televízió was broadcast during the trials. Originally analog television was planned to be shut down on 1 January 2012, but this deadline was first pushed out to 2014 then brought forward to 2013. Analogue broadcast was terminated at 12:30pm, on 31 July 2013 in the central part of Hungary, and October 2013 in the rest of the country. M1, M2, Duna TV, Duna World, RTL Klub, TV2 and Euronews are available as free-view. M1, M2 and Duna TV are also available in HD.
On both of the 2013 shutoff dates, all analog channels ceased normal programming at 12:30pm and showed a silent ASO information screen that has a phone number to call for help. It was kept on for a few days, after which the analog transmitters are permanently shut down.
Ireland
In Ireland DTT has been somewhat problematic. Responsibility for DTT, based on plans of Raidió Teilifís Éireann, was divided between two government Departments with differing views on its running. This delayed the project, took away its momentum and the economic situation deteriorated so that the opportunity to launch in good conditions was lost. When legislation finally arrived after two years to enable DTT to proceed, a private sector model was envisaged similar to the UK. A company trading as "It's TV" was the sole applicant for a digital terrestrial television license under the provisions of the Irish Broadcasting Act 2001. The "It's TV" proposed a triple play deployment with Broadband, TV and Digital Radio services, but the on air return channel (DVB-RCT system) for "interactive" use while 10s of Mbps per mast, would per user only have been 300 to 2400bit/s at peak times, they never got approval to run an Internet service. RTÉ was to have a minority stake in its network and sell its majority share. However legislative delays and economic changes made it financially difficult for RTÉ to get a good price for the network stake. "It's TV" plans raise the necessary funding failed due to the lack of approval for Internet aspect and infeasible Internet access model. Other DTT deployments in operation around that time also went bust, most particularly in the UK, Spain and Portugal. "It's TV" failed to get its license conditions varied or to get a time extension for securing funding. Its license was either never awarded (as they could not demonstrate a viable business plan & funding) or was eventually withdrawn for non-performance.
Under subsequent legislation in May 2007, RTÉ, the spectrum regulator (ComReg) and the broadcasting regulator BCI (now BAI), were mandated to invite applications during 2008 under the Broadcasting (Amendment) Act 2007. RTÉ and the BCI received licenses from ComReg for spectrum to establish DTT. The BAI advertised and invited multiplex submissions by 2 May 2008. RTÉ Networks was required to broadcast in digital terrestrial TV (aerial TV) and received an automatic license through the RTÉ Authority. It has been expanding and upgrading its transmission network to digital terrestrial during 2009 which will culminate in 98% coverage by 31 December 2011 with analog switchover to begin in Summer 2012 in concert with Northern Ireland, under the MOU signed with the UK and Irish Governments.[45]
It is also making this network available to the commercial multiplex winner for rental of capacity once negotiations are concluded, rental agreed and a security bond received.[46] It has been testing the BAI multiplexes since November 2009 across the network, which is publicly receivable with the correct DTT receivers. 1 Mux (a group of broadcast channels) will provide the services of the public service broadcaster and have 98% population coverage by 31 December 2011. The other three multiplexes will have between 90% and 92% population coverage. Following Analogue Switchover one additional PSB mux and one or more commercial muxes will be made available for DTT, mobile television, broadband and other services.
The BCI (now BAI) received three conditional applications to operate the three muxes which were presented to the public on 12 May 2008. It decided in principle to allocate the license to Boxer DTT Ltd, a consortium made up of the Swedish pay-DTT operator Boxer and the media group Communicorp at its board meeting on 21 July 2008.[47]
On 20 April 2009, the BCI revealed that Boxer had withdrawn their license, and it was instead given to the runner-up applicant OneVision.[48] At the end of April 2010 the negotiations with Onevision ended and they also decided to return the license. On April 29, 2010 the contract was offered to the only remaining applicant, Easy TV.[49][50] The Easy TV consortium informed the BAI on 12 May 2010 that it was declining their offer to pursue negotiations regarding the Commercial DTT Multiplex Licence.[51]
A Houses of the Oireachtas Channel (reportedly shelved in December 2008) and the Irish Film Channel (whose status is unclear though a company has been formed to provide the channel)[52] are enabled for establishment as public service broadcasters on Irish DTT.[53][54]
The Broadcasting Authority of Ireland replaced the Broadcasting Complaints Commission, the Broadcasting Commission of Ireland and the RTÉ Authority. The BAI includes Awards and Advisory Committees under statutory instrument 389 that gave effect to the provisions of the Broadcasting Act 2009. This legislation dissolved the BCI, vesting it and new responsibilities, assets and liabilities in a new Broadcasting Authority of Ireland on October 1, 2009.[55] This act also deals with analogue switchover.
A DTT Information Campaign was announced by the Department of Communications, Energy and Natural Resources, to launch in March 2009 ahead of the September 2009 launch of Irish DTT.[56] as of December 2009, the information campaign has not launched and has been postponed until after Saorview launches its public testing phase.[57] The Information Campaign is to be undertaken by the BAI, with support of the Department.
As of October 30, 2010 FTA DTT, which will be known as Saorview, has launched[58] following a direction from the Minister for Communications, Energy & Natural Resources, to RTÉ and the signing of the RTÉ (National Television Multiplex) Order 2010 (S.I. No. 85 of 2010) on February 26, 2010.[59] The rollout of FTA Saorview DTT will now proceed, and a commercial DTT competition may well be deferred until the economic situation improves.[60]
On 1 July 2010 RTÉ announced that Mary Curtis, RTÉ's current deputy head of TV programming, would take on the role of Director of Digital Switchover (DSO).[61]
In May 2011, RTÉ launched Saorview, which was officially opened by Minister Rabbitte.[62]
On October 14, 2011, Minister Rabbitte announced that analogue terrestrial television broadcast would be switched off on October 24, 2012. This date was chosen in consultation with the UK on its Northern Ireland analogue switchover date so that both jurisdictions on the island would switch over at roughly the same time. This was done to make it straightforward for citizens on both sides of the border.,[63] referring citizens to both Saorview's website[64] and the Department's Digital Switchover Website[65]
On 24 October 2012 all analogue television transmission in Ireland ended, leaving Saorview as the primary source of broadcast television in Ireland.
Italy
The switch-off of the analogue terrestrial network progressed region–by–region. It started on Wednesday 15 October 2008, and was completed on Wednesday 4 July 2012.
The selected broadcasting standard is DVB-T with MPEG2 video for SD and H.264 video for HD, audio is usually MPEG1. The whole frequency spectrum has been allocated with SFN in mind.
Along the original analog free to air channels that switched to digital, a few new pay per view platforms came around with the advent of DTT.
Worth mentioning is the addition of an experimental free to air HD 1080i channel from RAI which is set to broadcast important sport events like the Olympic Games or the FIFA World Cup.
Luxembourg
Luxembourg launched DTT services in April 2006. The national service launched in June 2006. On 1 September 2006, Luxembourg became the first European country to transition completely to DTT. Luxe TV, a niche theme based station, soon began broadcasting on the Luxembourg DTT platform, transmitted from the Dudelange transmitter. The aim was to reach audiences in some parts of Germany as well as in Luxembourg.[66][67]
Netherlands
The Netherlands launched its DTT service 23 April 2003, and terminated analogue transmissions nationwide on 11 December 2006. KPN owns Digitenne which provides a mix of FTA public channels and paid DTT services.[68] It also provides a mobile broadcast DVB-H service as well as an IPTV service, with DTT the most popular of its products.[69]
Poland
DTT launch in Poland was scheduled for Autumn 2009. Regulatory disagreements delayed its tender and approach until resolved and the multiplexes available for DTT were reduced to 3 and the 2nd was licensed in the Autumn of 2009. The reduction from 5 to 3 enabled mobile TV and broadband to get more spectrum allocation. Muxes 2 and 3 therefore had limited coverage until ASO. Polsat, TVN, TV4 and TV Puls have officially applied to reserve space on the countries first multiplex set to start in September. Wirtualne Media is given as the source of the story. The public broadcaster's three main channels TVP1, TVP2 and TVP Info had already been allocated capacity on the multiplex.
Poland ended its television broadcast in analogue on 23 July 2013. A mobile TV license has also been awarded in Poland to Info TV FM to use DVB-H standard.[70]
Portugal
Portugal launched its DTT service on 29 April 2009, available to around 20% of the Portuguese population and Portugal Telecom expected to reach 80% of the population by the end of the 2009. Airplus TV Portugal that was set up to compete for a licence to manage Portugal's pay-TV DTT multiplexes, dissolved as it did not get the license and a Portuguese court ruled not to suspend the process for the awarding of a licence to Portugal Telecom, based on a complaint submitted by Airplus TV Portugal. After Airplus TV Portugal was dissolved, Portugal Telecom informed that will not honour the pay-TV DTT multiplexes licence obligations. ANACOM, the Portuguese communications authority, accepted. Portugal thus has only one active multiplexer.[71]
Romania
In Romania, broadcasting regulations have been amended so that DTT service providers have only a single licence rather than the two previously required by the National Audiovisual Council (CNA). DTT services were launched in December 2009 using the MPEG-4 (H.264 AVC) compression format[72] following the Ministry of Communications publication of a strategic plan for the transition to digital broadcasting. According to Media Express, it envisaged a maximum of five national UHF multiplexes, a national VHF multiplex and a multiplex allocated to regional and local services, all in accordance with the ITU Geneva Conference RRC-06 reports BroadbandTVNews.
The Ministry of Communications (MCSI) estimated that 49% of Romania's 7.5 million households got TV from cable and 27% from DTH services in Romania while terrestrial TV was used by 18% of the TV households. 6% are reported as not able to receive TV transmissions. Subsidies were offered for those below a certain income to assist switchover for them.[73] Switchover was scheduled for January 2012.[74]
Romkatel, the local representative of Kathrein, have since been awarded the commercial Romanian DTT services license. ZF reported that Romkatel has signed a 12-month contract worth €710,420, having beaten off a challenge from France's TDF. The tender was organised by Romania's National Society for Radiocommunications (SNR).[75]
Meanwhile, the National Audiovisual Council, in charge of the public service broadcasting sector has awarded digital licences to the public channels TVR1 and TVR2.
According to Media Express, this followed a short debate at the National Audiovisual Council (CNA) about whether to also award licences to the nine remaining public channels, one of which transmits in HD and five are regional.
Romania's first DTT multiplex is likely to have the five leading commercial channels — Pro TV, Antena 1 (Romania), Prima TV, Kanal D Romania and Realitatea TV — as well as TVR1 and TVR2.
The National Authority in Communications (ANCOM), will most probably award the transmission network contract for this to the national transmission company Radiocommunicatii.[76]
In June 2013, the Romanian Government issued a Strategy to shift from analogue terrestrial to digital terrestrial that pushes ahead the until the date stopped process. According to the Strategy one of the five planned digital terrestrial multiplexes will be de facto granted to Radiocom, the state company involved in terrestrial carrying the public television signals, way before a selection for the muxes operators will be organized by ANCOM, selection with the deadline of June 17, 2015. Government is describing the Radiocom multiplex with the terms "pilot project" and "experiment". The minimum technical requirements for this project are: broadcast standard DVB-T2, ensuring the coverage of up to 40% of the population until July 1, 2014, and 70% of the population up to June 17, 2015, and the possibility of using the broadcasting premises that belongs to Radiocom.[77]
On 17 June 2015, Romania turned off analog broadcasting, and started broadcasting with DVB-T2 technology, but with very low coverage, and a very reduced number of broadcasts available. Because of low coverage, Romania will still broadcast TVR1 in analog format on VHF until 31 December 2015. DVB-T continues to be available for an undetermined period of time, only in Sibiu ( Ch 47 and Ch 54) and Bucharest ( Ch 54 and Ch 59). However, since the analogue turn-off, many people who were receiving TV on terrestrial shifted to a cable or DTH operator . To the present day, DVB-T and DVB-T2 are still in experimental broadcast. The delay of DVB-T launching is criticized by some people in Romania, as a form of sustaining the interest of cable and DTH providers, by delaying the stable launch of DVB-T and decreasing the number of channels ( once, there were available 18 channels in DVB-T, even 3 in HD) but to the present day the number has fallen to only 6, and continues to be lower, especially since TVR announced that they will reduce the number of channels (TVR news will be shut down, probably because of low audience, the same for TVR 3, and the fate of TVR HD, which is one of the channels with the largest audience in TVR Group after TVR1, is unknown). Kanal D left terrestrial platform on 2 July 2015, and, Antena 3 is the only channel except TVR's available on terrestrial in DVB-T. It is unknown whether Antena 3 will remain available on DVB-T, will shift to DVB-T2, or fully leave the terrestrial platform . Antena Group channels were once available both analogue and digital in terrestrial. Also, many people in Romania are somehow surprised by the fact that Romania had regressed in terrestrial broadcasts, because in analogue there were, once, about 8 channels ( in Bucharest), and decreasing to only 6 channels in Digital terrestrial is a regress. However, terrestrial TV was heavily surpassed both by DTH, or Cable, some people are even watching foreign FTA on satellite, because foreign broadcasts are having a more interesting content than Romanian channels. To the present day, DVB-T and T2 are still in tests. Although many TV sellers are marking DVB-T2 capable sets as being compatible with digital terrestrial television in Romania, by highlighting this feature with a sticker on the TV, buyers are mainly interested if the TV has digital cable tunner or digital satellite tuner, however TV sets without DVB-T2 continue to be sold with only DVB-T/C and sometimes S2, as cable and satellite compatibility presents most of interest.
Spain
In Spain most multiplexes closed after the failure of Quiero TV, the country's original pay DTT platform. DTT was relaunched on 30 November 2005, with 20 free-to-air national TV services as well as numerous regional and local services. Nearly 11 million DTT receivers had been sold as of July 2008. Positive approval for pay DTT services have reportedly been given by Spain's Ministry of Industry in a surprise move on 17 June of the Advisory Council on Telecommunications and the Information Society (Catsi). IT will now be included in a Royal Decree. A number of leading Spanish media players including Sogecable, Telefónica, Ono, Orange and Vodafone have apparently criticised that as according to Prisa, Sogecable's owner, "it caps a series of policy changes that benefits only a few audiovisual operators, those of terrestrial TV, to the detriment of satellite operators, cable and DSL." There may be appeals lodged against the government's decision.[78]
Sweden
In Sweden, DTT was launched in 1999 solely as a paid service. As of 2007, there are 38 channels in 5 MUXs. 11 of those are free-to-air channels from a number of different broadcasters. Switch-off of the analogue TV service started on 19 September 2005 and finished on 29 October 2007. Boxer began the deployment of MPEG-4 receivers to new subscribers. Over the next six years from 2008 Sweden will gradually migrate from MPEG-2 visual coding to using MPEG-4, H.264.
The Swedish Radio and TV Authority (RTVV) recently announced eight new national channels that will broadcast in the MPEG-4 format.
From 1 April 2008 Boxer is also responsible for approving devices to use on the network, will no longer accept MPEG-2 receivers for test and approval. Set Top Boxes must be backward compatible so that they can decode both MPEG-2 and MPEG-4 coded transmissions.[79]
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom (1998), Sweden (1999) and Spain (2000) were the first to launch DTT with platforms heavily reliant on pay television. All platforms experienced many starter problems, in particular the British and Spanish platforms which failed financially (mainly due to their encryption being compromised). Nevertheless, Boxer, the Swedish pay platform which started in October 1999, proved to be very successful.
DTT in the United Kingdom was launched in November 1998 as a primarily subscription service branded as ONdigital, a joint venture between Granada Television and Carlton Communications, with only a few channels being available free to air. ONdigital soon ran into financial difficulties with subscriber numbers below expectations, and in order to attempt to reverse their fortunes, it was decided that the ITV and ONdigital brands should align, and the service was rebranded ITV Digital in 2001. Despite an expensive advertising campaign, ITV Digital struggled to attract sufficient new subscribers and in 2002 closed the service. After commercial failure of the Pay TV proposition it was relaunched as the free-to-air Freeview platform in 2002. Top Up TV, a lite pay DTT service, became available in 2004 when Inview launched the first DTT (Freeview) EPG service.[80]
On 30 March 2005, the older analogue signals began to be phased out on a region-by-region basis (a process known as the Digital switchover, or DSO), beginning with a technical trial at the Ferryside television relay station. The first full transmitter to switch to digital-only transmission was the Whitehaven transmitter in Cumbria, which completed its transition on Wednesday 17 October 2007. The switchover to digital-only broadcasting was completed on 24 October 2012 when the transmitters in Northern Ireland turned off their analogue broadcasts (which coincided with the transition in the Republic of Ireland).
The additional transmission frequencies freed up by the shutdown of analogue signals have (among other things, such as the introduction of 4G mobile internet) allowed for the creation of a single DVB-T2 multiplex used to carry high-definition programming.[81][82] There are also plans to use one frequency to launch local television services.
Macedonia
DTT was successfully launched in November 2009. It uses MPEG-2 for 4K UHD and MPEG-4 for HD. The service was launched by ONE, and the platform is called BoomTV. It offers 42 channels including all national networks and it is available to 95% of the population.[83]
Russia
In Russia, digital television appeared in the summer of 2009, first the first multiplex was created: (Channel One Russia, Russia-1, Russia-2 (now Match-TV), NTV, Petersburg 5 channel, Russia-Culture, Russia-24, Bibigon (later - Carousel) .In the spring of 2013, added two more channels of the First multiplex: OTR and TV-Center
Digital format DVB-T on DVB-T2 was replaced on March 19, 2012
December 14, 2012 Digital TV appeared the Second Multiplex. Were part of: REN TV, TV Center (from 2013 - Spas), STS, Domashniy, Sport (from 2013 - TV-3), NTV Plus Sport Plus (then from 2015 - Pyatnica!), Zvezda, Mir, TNT and Muz -TV
In 2014, the third and fourth multiplex appeared in the Crimea. It was created after the annexation of Crimea into Russia.
January 15, 2015 in Moscow and the Moscow region appeared The third multiplex broadcast some satellite channels (for example, on 22 channel 2х2 at 12am and in the 11:59am, My planet (Moya Planeta) in the 12pm-18pm, and in the 18pm-12am - Science 2.0 (Nauka 2.0) )
On November 30, 2018, the Ministry of digital development, communications and mass communications of the Russian Federation offered them to turn off analog broadcasting in three stages (February 11, April 15, June 3)
December 3, 2018-the first region to switch from digital broadcasting to analogue broadcasting
June 3, 2019-complete transition to digital TV completed in Russia
Switzerland
Switzerland is digital.
North America
Bahamas
On December 14, 2011, national public broadcaster ZNS-TV announced it would be upgrading to ATSC digital television with mobile DTV capabilities, in line with its neighbours, the United States and Puerto Rico.[84]
Bermuda
Bermuda has plans to convert its three broadcast stations to ATSC digital terrestrial television in the future.
Canada
In Canada, analogue switch-off was mandated by regulatory authorities for all provincial capital cities and all multi-station markets. Analogue would continue in single-station markets and remote areas. With an exception, analogue switch-off in the mandated areas took place on 31 August 2011. The CBC was granted an exception in many smaller multi-station markets, due to the cost of conversion, otherwise the CBC services would have gone dark in many such markets. Most network stations are already broadcasting high-definition digital signals in Toronto, Ottawa, Montreal, Calgary, Edmonton, Winnipeg, Regina, and Vancouver. Most networks had been concerned about the August 2011 deadline as not all parts of the country were equipped to receive DTTV by the scheduled date.
Mexico
In Mexico, the digital transition is done. Digital signals are available in all cities, thus providing national coverage. Analog transmission were turned off based on population size. Tijuana was the first city to turn off analog signals and the nationwide turn off was completed on December 31, 2015.[85] On October 27, 2016, Mexico relocated all of its channels. This made Azteca 13 (now Azteca Uno) on virtual channel 1.1 nationwide, Canal de Las Estrellas (now Las Estrellas) on virtual channel 2.1 and Imagen Television on virtual channel 3.1. Border cities were not affected due signal issues across the United States. For example, in the Tijuana-San Diego area, channel 2.1 signal comes from Los Angeles and can affect television users in Oceanside, CA. Thus, Las Estrellas is on virtual channel 57.1.
United States
In the United States on 12 June 2009, all full-power U.S. television broadcasts became exclusively digital, under the Digital Television and Public Safety Act of 2005.[86][87] Furthermore, since 1 March 2007, new television sets that receive signals over the air, including pocket-sized portable televisions, include ATSC digital tuners for digital broadcasts.[88] Prior to 12 June 2009, most U.S. broadcasters were transmitting in both analog and digital formats; a few were digital only. Most U.S. stations were not permitted to shut down their analog transmissions prior to 16 February 2009 unless doing so was required in order to complete work on a station's permanent digital facilities.[89] In 2009, the FCC finished auctioning channels 52–59 (the lower half of the 700 MHz band) for other communications services,[90] completing the reallocation of broadcast channels 52–69 that began in the late 1990s.
The analog switch-off rendered all non-digital television sets unable to receive most over-the-air television channels without an external setbox receiver; however, low-power television stations and cable TV systems were not required to convert to digital until 1 September 2015. Beginning 1 January 2008, consumers could request coupons to help cover most of the cost of these converters by calling a toll-free number or via a website.[91] Some television stations had also been licensed to operate "nightlights", analog signals which consisted only of a brief repeated announcement advising remaining analog viewers how to switch to digital reception.
Central America and the Caribbean
Costa Rica
Costa Rica chose Japanese-Brazilian standard ISDB-T as 7th country on May 25, 2010,[92] and started trial transmissions by Channel 13 from Irazú Volcano on March 19, 2012[93]
Cuba
Cuba announced on March 19, 2013 that it is "prepared" to perform a digital television test using the Chinese DTMB system.[citation needed]
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic chose ATSC standards for DTT on August 10, 2010.[94]
El Salvador
El Salvador has chosen the Japanese / Brazilian standard ISDB-Tb in 2017. The Digital Switchover began on 21 December 2018, and by the year 2022 it will be completed.
[95]
Nicaragua
Nicaragua has chosen the Japanese-Brazilian standard ISDB-Tb.
Panama
Panama chose the European DVB-T standard on 12 May 2009.[96]
South America
Argentina
Argentine President Cristina Fernández signed on August 28, 2009 an agreement to adopt the ISDB-Tb system, joining Brazil, which has already implemented the standard in its big cities.[97] On air service started from 28 April 2010.[98]
Bolivia
On July 5, 2010 the Bolivian Chancellor signed an agreement with the Japanese Ambassador, selecting the Japanese system with the Brazilian modifications ISDB-T (Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting Terrestrial).[99][100]
Brazil
In Brazil, they chose a modified version of the Japanese ISDB-T standard, called ISDB-Tb (or SBTVD) in June 2006. Digital broadcast started on 2 December 2007 in São Paulo and now it is under expansion all over the country. As of 15 September 2009, metro areas of São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, Belo Horizonte, Brasília, Goiânia, Curitiba, Porto Alegre, Salvador, Campinas, Vitória, Florianópolis, Uberlândia, São José do Rio Preto, Teresina, Santos, Campo Grande, Fortaleza, Recife, João Pessoa, Sorocaba, Manaus, Belém, Aracaju, Ribeirão Preto, Boa Vista, Macapá, Porto Velho, Rio Branco, São Carlos, São José do Rio Preto, São Luís, Pirassununga, São José dos Campos, Taubaté, Ituiutaba, Araraquara, Feira de Santana, Itapetininga, Sorocaba, Presidente Prudente, Bauru, Campos dos Goytacazes, Londrina, Juiz de Fora, Campina Grande, Caxias do Sul, Franca, Rio Claro and Cuiabá have digital terrestrial broadcasting. By 2013 the digital signal was available in the whole country. Analogue shut-off is scheduled for 2023.
Chile
On September 14, 2009, president Michelle Bachelet announced that the government had finally decided, after prolonged delays, on a digital television standard. Chile will be adopting the ISDB-T Japanese standard (with the custom modifications made by Brazil). Simulcasting is expected to begin in 2010, with a projected analog switch-off in 2017.[101]
Colombia
Colombia has chosen the European DVB-T standard on 28 August 2008. However, in 2012, Colombia adopted DVB-T2 as the national standard for terrestrial television, replacing DVB-T, the previously selected standard for digital TV.
On December 28, 2010, private networks Caracol TV and RCN TV officially started digital broadcasts[102] for Bogotá, Medellín and surrounding areas on channels 14 and 15 UHF,[103] respectively. State-run Señal Colombia and Canal Institucional had started test digital broadcasts earlier in 2010.[102]
The current coverage of DVB-T2 can be consulted on the website of the organization "Tdt para Todos" which is the entity responsible for facilitating its adoption.[104]
Ecuador
Ecuador chose Japanese-Brazilian standard ISDB-T as 6th country on 26 March 2010.[105][106][107]
Paraguay
Paraguay chose Japanese-Brazilian standard ISDB-T on 1 June 2010.[108][109]
Peru
Peru has chosen on 23 April 2009 the Brazilian modified version of the Japanese standard ISDB-T. Agreed with Japan to cooperate for resource exchange and technical transfer on 21 August 2009, and on air service started on Channel 7 of TV Perú from 30 March 2010.[110][111][112] Currently, all the major stations in Lima are broadcasting in Digital and HDTV. ATV was the first station in the country to broadcast a digital signal back in 2008, testing all the systems in order to assess what was more convenient to choose. When the standard was chosen, they were already broadcasting in HD and the first live TV show to be aired in HDTV in Perú was Magaly TV on August 30, 2010. Frecuencia Latina began transmitting on September 14, 2010, and the first major HDTV show was the participation of the Peru women's national volleyball team in the 2010 FIVB Women's Volleyball World Championship. Shortly after these events, America Television started broadcasting in digital and the highest ranked TV show in Peru (Al Fondo Hay Sitio) started airing in HD on February 28, 2011.
Suriname
Suriname is currently transitioning from analogue NTSC broadcasts to digital ATSC and DVB-T broadcasts. Channel ATV started with ATSC broadcasts in the Paramaribo area in June 2014, which was followed by ATSC broadcasts from stations in Brokopondo, Wageningen and Albina. The stations in Brokopondo, Wageningen and Albina broadcast both the channels of ATV (i.e. ATV and TV2) and STVS, while the station in Paramaribo currently only broadcasts the ATV channels.[113] The Telecommunication Authority of Suriname was originally aiming at a full digital transition by June 2015,[113][114] but this was criticized by broadcasters as being unfeasible.[115] However, the ITU has documented both DVB-T and ATSC are in use].[116]
Uruguay
Uruguay had chosen the European DVB-T standard in August 2007,[117] however disproved it and decided to adopt ISDB-T on 27 December 2010 to follow neighbouring countries.[118][119][120]
Venezuela
In Venezuela, tests are being performed with full deployment to start 2008–2009. DTT will coexist with analogue standard television for some time, until full deployment of the system on a nationwide level is accomplished. 30 September 2009, decided to employ Japanese ISDB-T system under cooperation with Japan, and officially be agreed with Japan in early October 2009.[121][122]
On October 6, 2009, Venezuela has officially adopted ISDB-T with Brazilian modifications. Transition from analog to digital is expected to take place in the next 10 years.[123][124]
On March, 2012, Venezuela signed a $50M agreement to purchase 300,000 decoders from Argentina to implement TDT in Caracas and later this year in some of the most important cities, but only in the Government controlled TV Stations. NTSC and TDT will coexist. The Government hopes to reach TDT the whole country's population in 2 years. http://m.insidetele.com/index.php?article_id=-677679205374602596[permanent dead link]
Africa
On the African continent the trend is still to use the European standard "DVB-T2", which is the most modern system of broadcasting. Countries that have adopted the standard are: Algeria, Angola, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Ghana, Kenya, Lesotho, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, Nigeria, Seychelles, South Africa, Swaziland, Tanzania, Togo, Uganda, Zambia and Zimbabwe.[125][126]
Nigeria
In March 2015 Inview Technology (a UK digital switch-off company based in Cheshire and with local operations in Nigeria) was appointed by Nigeria's government run National Broadcasting Commission (NBC) to enable digital switchover from analogue[127] throughout the country and provide a Conditional Access System, set-top box software and services including full EPG, Push Video-On-Demand, a range of broadcasting applications such as news, public service information and audience measurement services over the digital terrestrial and satellite networks in Nigeria.[128]
Inview Nigeria and NCB will:
- create a free digital TV service called FreeTV (based on Freeview in the UK), rather than pay TV subscriptions
- subsidise the FreeTV STB down to an affordable retail price of N1500 ($7.50)
- fund subsidies and digital infrastructure costs through the sale of spectrum and the introduction of a BBC style licence fee (called 'digital access fee') of N1000 ($5) pa which is payable on all digital STBs including pay TV operators. The Nigerian Government will receive a digital dividend of c.$1 billion from the sale of spectrum, ensuring that the whole DSO programme is self-funding.
FreeTV will carry up to 30 free channels: the best of Nigeria TV and international channels across news, movies, kids, music and general entertainment genres.
A national standard set top box specification has been set which incorporates a common operating system created by Inview. All boxes will require this specification to view the channels and access value added services such as interactive news, programme recording, internet applications and video on demand.
As of March 2016, FreeTV is being operated by Inview and is an open platform which enables any content or pay TV provider to broadcast their content so that Nigerian consumers only have to buy one box to view all the content. Only manufacturers licensed in Nigeria will receive the Inview operating system required to access the channels and services, which will protect domestic manufacturers and consumers from illegal grey imports.
Tunisia
To follow the transition from analog to digital in the field of terrestrial television broadcasting, and to keep pace with these technological international innovations, Tunisia through the Office of National Broadcasting has planned the following phases to digitize its terrestrial broadcasting networks:
First phase: Deployment, since 2001, of an experimental digital TV broadcasting unit using DVB-T system, and MPEG-2 compression, implemented in Boukornine site, to insure the coverage of Great Tunis (25% of population). This experimental project highlighted the benefits of digitization which are : -Better quality of Video and audio signals, -Increasing the capacity of distribution networks through the transmission of a digital TV package (bouquet): a layer of digital distribution network enables the transmission of 4 to 6 programs TV instead of a single TV program in the case of an analog network -The economics of radio spectrum and the energy consumption. -Introduction of new multimedia services. In preparatory phase, ONT has prepared the frequency plan for digital terrestrial TV networks of and has signed the final acts of the Regional Radio Communication Conference 2006 in Geneva organized by the International Telecommunications Union, which recommends to switch off analog broadcasting services around 2015 and their replacement by digital broadcasting systems.
Second phase: This phase includes the completion of the two following projects:
1- First part: Digitization of the transmission network between production studios and different broadcasting stations. The network consists of 41 transmission stations spread throughout the country. This step represents the first part of the Digital Terrestrial TV network, and its deployment is completed during the period 2008-2009. The cost of this project is 27 million dinars TTC.
2- Second part: National digital terrestrial TV broadcasting Network to viewers, which consists of 17 DTTV stations spread throughout the country and will be conducted under a contract including a vendor financing agreement with the Thomson Grass Valley (France) company. The project came into force in August 2009 and will be conducted during 2009-2010. Its cost is 13 million dinars TTC.
Analogue to digital transition by countries

World map of digital television transition progress. Legend:
Transition completed, all analog signals terminated
Transition completed for full-power signals only; LPTV stations still being broadcast in analog
Transition in progress, broadcasting both analog and digital signals
Transition not yet started, broadcasting analog signals only
Does not intend to transition, broadcasting analog signals only
No information available
The broadcasting of digital terrestrial transmissions has led to many countries planning to phase out existing analogue broadcasts. This table shows the launches of DTT and the closing down of analogue television in several countries.
- Official launch: The official launch date of digital terrestrial television in the country, not the start for trial broadcasts.
- Start of closedown: The date for the first major closedown of analogue transmitters.
- End of closedown: The date when analogue television is definitely closed down.
- System: Transmission system, e. g. DVB-T, ATSC or ISDB-T.
- Interactive: System used for interactive services, such as MHP and MHEG-5.
- Compression: Video compression standard used. Most systems use MPEG-2, but the more efficient H.264/MPEG-4 AVC has become increasingly popular among networks launching later on. Some countries use both MPEG-2 and H.264, for example France which uses MPEG-2 for standard definition free content but MPEG-4 for HD broadcasts and pay services.
| Country | Officially launched | Analog closedown commenced | Analog closedown completed | DTT transmission | Interaction | AV standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Afghanistan | 2014-05 | DVB-T2 | None | H.264 | ||
| Albania[129] | 2004-07-15 | 2012/2015 | DVB-T | H.262 | ||
| Andorra[130] | 2007-09-25 | DVB-T | None (MHP abandoned) | H.262 | ||
Argentina[131] | 2010-04-28 | — | 2019-09-01 | ISDB-Tb | Ginga | H.264 |
Australia[132][133][134][135][136][137][138] | 2001-01-01 | 2010-06-30 (Mildura and Sunraysia) | 2013-12-10[139] | DVB-T (7 MHz channels 6~12 VHF and 28~69 UHF) | MHEG-5 (EPG only) | H.262[140] |
Austria[141] | 2006-10-26 | 2007-03-05[142] | 2010[143] | DVB-T | None (MHP abandoned)[144] | H.262 |
Botswana | 2013-02-26 | June 2014 | 2015-06 | ISDB-T | None | H.262, H.264 HD & SD |
Belgium[145] | 2002/2003 | 2008-11-03 (Flemish Community) | 2010 (Francophone Community) | DVB-T | None | H.262 |
Brazil[2] | 2007-12-03 | 2016-02-15 (Rio Verde) | 2023 | ISDB-Tb | Ginga | H.264 |
Bulgaria[146] | 2004-11 | 2013-03 | 2013-09-30[147] | DVB-T[148] | MHP | H.264 |
Canada[149] | 2003-01 | 2011-08-31 | ATSC | H.262, H.264 HD (ATSC 2.0) | ||
Cambodia[150] | 2011 (trial) 2013-02-04 | 2015 | 2020 | DVB-T2 | MHP | H.264 |
China[151] | 2006 | 2006 | 2015 (SARFT reported August 2005) | DMB-T/H[152] | H.262, H.264 | |
Colombia[153] | 2008-08-28 | 2019-12-31 | DVB-T ( 6 MHz ) | MHP | H.264 | |
Costa Rica | 2010-05-04 | — | 2018 | ISDB-Tb | Ginga | H.264 |
Croatia[154] | 2002-07-09 | 2002-07-09 | 2011-01-01[155] | DVB-T | H.262, H.264 | |
Czech Republic[156] | 2005-10-21 | 2005-10-21 | 2012-06-30 | DVB-T | MHP | H.262 |
Denmark[157][158][159] | 2006-03-31 | 2009-02-01 | 2009-11-01 | DVB-T | MHP | H.262, H.264 |
El Salvador | 2009-04-22 | 2018-12-21 | 2022 | ISDB-Tb | H.262, H.264 | |
Estonia[160][161][162] | 2006-12-15 | 2008-03-31 (Ruhnu island) | 2010-07-01 | DVB-T | MHP planned | H.264 |
Faroe Islands[163] | 2002-12 | 2002-12 | 2003 | DVB-T | None | H.262 |
Finland[164] | 2001-08-27 | 2007-09-01[165] | 2007-09-01 | DVB-T | None (MHP abandoned) | H.262 |
France[166][167] | 2005-03-31 FTA 2006/03/01 Pay DTT[168][169] | 2009-02-04 | 2011 (before November 30)[41][42] | DVB-T | MHP[170] | H.262, H.264[171] |
Germany[172] | 2003-03 | 2003-03 Regional rollout | 2008-12-02 completed | DVB-T | H.262 / H.264 (Stuttgart for non public channels) | |
Greece | 2006-01-16 Tests[44] | 2008-11-01[44] | 2015[173] | DVB-T | H.262 (ERT) H.264 (ERT, DIGEA) | |
Hong Kong[174][175] | 2007-12-31 | 2016-04-02 (ATV) | DMB-T/H | MHEG-5 (TVB) | H.264 | |
Hungary[177][178] | 2008-12-01 | 2013-07-31 | 2013-10-31 | DVB-T | H.264 | |
Indonesia[179] | 13 August 2008 (Trial) 20 May 2009 (Official)[180] | February 2019[181] | June 2019[181] | DVB-T2 | MPEG-2 SD, H.264/MPEG-4 AVC HD | |
Iran[182][183][184] | 2009 | 2015 | DVB-T | H.264 | ||
Ireland[53][54][185][186][187] [188][189][190][191][192][193][194][195] | 1999–2002 Licensing abandoned; 2006–2008 Trial; 31 October 2010 (90%)[196] 26 May 2011 DTT launch, December 2011 (98%)[197] Network testing, publicly receivable | 2012-10-24 with NI[198] | 2012-10-24 with NI[199][200] | DVB-T | RCT abandoned, MHEG5, | H.264 |
Israel[201][202][203][204] | 2009-08-02[205] | June 2011 | DVB-T | H.264, AAC+ V2 | ||
Italy[206] | 2004-01-01 | 2012-07-04 | DVB-T | MHP | H.262, H.264 | |
Japan[207][208] | 2003-12-01 | 2010-09-24 (some regions of Ishikawa) | 2011-07-24 (all cities except Morioka, Sendai, and Fukushima)[16] 2012-03-31 in Iwate, Miyagi and Fukushima[209] | ISDB-T | BML | H.262 |
Lithuania[210] | 2006 | 2009 (Now expanded nationwide) | 2012-10-29[211] | DVB-T | H.264 | |
Luxembourg[212] | 2006-04-04 | 2006-04-04 | 2006-09-01 | DVB-T | None | H.262 |
Republic of Macedonia[83] | 2004-05-04 | 2010-01-01 | 2013, June | DVB-T | MHP | H.264 |
Malaysia[213][214] | 6 June 2017 | 2015 (parallel running) | 1 June 2018 | DVB-T2 | MHEG-5 | H.264 |
Mexico | 2004-07-02 | 2013-07-18 (Tijuana) | 2015-12-31 | ATSC | H.262, H.264 HD (ATSC 2.0) | |
| Mongolia | 2014-07-01 | Parallel running | Unknown | DVB-T2 | ||
Morocco[215][216][217] | 2007-06-01 | 2007-03-05 | 2015 | DVB-T | ||
| Myanmar | 2013-10[218] | 2016 | 2020 | DVB-T | ||
Netherlands[219] | 2003 | 2003-11 | 2006-12-11 | DVB-T | H.262 | |
New Zealand[220][221][222] | April 2008 | 2012-09-30 | 2013-12-01 | DVB-T | MHEG-5 (EPG only) | H.264/HE-AAC |
Norway[223] | 2007-09[224] | 2008-03[225] | 2009-12-01 | DVB-T | MHP | H.264[226] |
Peru[227] | 2010-03-30 | 2023-03-01 | ISDB-Tb | Ginga | H.264 | |
Philippines | 2008-10 (trials) 2017-02-14 (DTT Launch) | 2017-02-28[22] | 2023[23] | ISDB-T | BML | H.262, H.264 |
Poland[228][229][230] | 2004 (trials) 2009-09-20 (DTT Launch) | 2011-05 | 2013-07-23[231] | DVB-T | H.264 | |
Portugal[232] | 2009-04-29[233] | 2011 | 2012-04-26[234] | DVB-T | H.264 | |
Qatar[235] | 2013-12-11 | 2015-02-13 | DVB-T2 | H.264 | ||
Romania[76][236] [237][238][239][240][241] | 2005-12-01 | 2015-06-17 (planned) | DVB-T2 | H.264 | ||
Russia[242] | 2009-06-24 | 2018-07-01 | 2018-12-31 | DVB-T2 | H.264[243] | |
Saudi Arabia | 2006-06-11 | 2015-02-13 | DVB-T/DVB-T2 | H.264 | ||
Singapore | 1 January 2006 | 16 December 2013 | 6 January 2019 | DVB-T2 | H.264 | |
Slovakia[244] | 1999–2004,2005–2009 | 2010[245] | 2012-12-31[246] | DVB-T | MHEG-5 | H.262, H.264 |
Slovenia[247] | 2007 | 2010-12-01 | 2011-06-30 | DVB-T | H.264 | |
South Africa[248][249] | 2006-03 | 2016-10-28[250] | No date yet[251][252] | DVB-T2 | MHEG-5 (Future use planned) | H.264 |
South Korea[253] | 2001 | 2010-09-01 14:00[254] (Uljin) | 2012-12-31[255] | ATSC | H.262, H.264 HD (ATSC 2.0) | |
Spain[256] | 2000–2005 (Previous and relaunch) | 2009 | 2010-04-03[257] | DVB-T | None (MHP abandoned) | H.262 SD, H.264 HD |
Sri Lanka[258][259] | 2014-09-07 | 2015-01-01 | 2020 | ISDB-T | BML | H.264 HD |
Sweden[260] | 1999-04-01[261] | 2005-09-19 | 2007-10-29 | DVB-T, DVB-T2 (HD) | MHP | H.262 SD, H.264 HD[262] |
Switzerland[263] | 2001 | 2002-03 | 2008-02-25[264] | DVB-T | ||
Taiwan[265] | 2004-01[266] | 2010-07 (Pinglin) | 2012-06[266] | DVB-T | MHP | H.262, H.264[266] |
Thailand[267] | 2013-01-25 (official) 2014-04-01 (all trials) 2014-06-01 (all official plan) | 2015-12-01[268][269] | 2020-03-25[268] | DVB-T2 | MHEG-5 | H.264 |
Turkey[270] | 2006-02 (trial services) | Not commenced.[271] | DVB-T (during trials) | |||
Ukraine[272] | 2009-04-01 | 2018-07-31 | 2018-08-31 | DVB-T2 | none | H.264 |
United Kingdom[273] | 1998-11-15 | 2007-10-17 (Whitehaven) | 2012-10-24 | DVB-T, DVB-T2 (HDTV) | MHEG-5 | H.262 SD, H.264 HD |
United States[274][275] | 1998-10-29 | 2008-09-08 (Wilmington) | 2009-06-12 (Full-power TV stations) | ATSC | H.262 | |
Vietnam | 2001 (tests) 2015 | 2020 | 2026 | DVB-T2 | MHEG-5 | H.264 |
See also
Common Interface (CI)
Conditional-access module (CAM)- Digital television transition
- Interactive television standards
- List of digital television deployments by country
- Multiplex
- 1seg
- USB stick
- WiB (Digital Terrestrial Television)
References
^ "REPORT ITU-R BT.2140" (PDF). ITU. Retrieved 2017-01-25..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ abc Webfactory www.webfactory.ie. "Digital Video Broadcasting - Standards & Technology". DVB. Retrieved 2010-09-02.
^ Blog series: Is Over-The-Air (OTA) HDTV right for you | Tablo. Tablotv.com. Retrieved on 2014-06-23.
^ BBC www.bbc.co.uk/reception (2009-06-16). "Television Aerials Factsheet" (PDF). BBC. Retrieved 2010-09-28.
^ Digea www.digea.gr (2009-06-16). "Aerials for Digital Television". Digea. Archived from the original on 2010-07-12. Retrieved 2010-09-28.
^ [1]. Afghanistan formally launches digital broadcasting system.
^ News. DVB. Retrieved on 2014-06-23.
^ [2] Archived September 5, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
^ Chapter 1 : Introduction Archived 2013-06-04 at the Wayback Machine. (PDF) . Retrieved on 2014-06-23.
^ [3]
^ "地上デジタル放送用「簡易なチューナー」購入に係る公募" [Announcement for Simplified DTT tuners bidding] (PDF). Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-16. Retrieved 2009-09-11.
^ アナログ停波実験 問い合わせ相次ぐ[dead link](lit. Analog stop experiment, inquiries arisen) 2010-01-23Asahi com(in Japanese)
^ Yomiuri Shimbun, 2010-01-25 ver.13S, pade34
^ 低価格のイオン向け地上デジタルチューナー発売のお知らせ [Announce of selling low cost tuner for Digital terrestrial television to ÆON] (in Japanese). Osaka, Japan: Pixela Corporation. Archived from the original on 2009-09-08. Retrieved 2009-09-08.
^ "「簡易なチューナー」の購入に関わる公募の結果" [The result of open bidding for "simple tuner" procurement] (PDF) (in Japanese). Tokyo, Japan: Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications and NTT-ME (NTTエムイー, enuthithi-emuī). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-10-07. Retrieved 2009-09-08.
^ ab "Japan Completed Analog Switch Off in Terrestrial Television Broadcasting Successfully". Tokyo: Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications. July 2011. Retrieved 2011-08-02.
^ Brasor, Philip, "Today is D-Day for analog television Archived 2011-08-05 at the Wayback Machine", Japan Times, 24 July 2011, p. 9.
^ "Najib launches Malaysia's foray into digital terrestrial TV via myFreeview". NST Online. 2017-06-06. Retrieved 2018-01-10.
^ "PM launches myFreeview digital broadcast, 4.2m decoders to be given free". 2017-06-06. Retrieved 2018-01-10.
^ "NTC picks Japanese model for digital TV". Manila: Malaya. 2010-06-11. Archived from the original on 2012-02-27.
^ フィリピン共和国が地上デジタルテレビ放送日本方式を採用する規則に署名 [Philippines signed the regulation to adopt Japanese DTT broadcasting system] (in Japanese). Tokyo: Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications. 2010-06-11.
^ ab Delos Reyes, Dyan (February 14, 2017). "Light Network, nasa Digital TV na!". Light Network Website. Retrieved February 28, 2017.
^ ab "Gov't wants analog TV switched off by 2023". GMA News Online. 2017-02-14.
^ "ASEAN picks DVB-T as common TV standard". 2005-06-17. Archived from the original on 2007-07-14. Retrieved 2008-06-21.
^ "Asean Broadcasters Prepare For Digital Broadcasting". Bernama (Ministry of Information). 2008-06-19. Archived from the original on 2009-02-20. Retrieved 2008-06-21.
^ "Switchover from analogue to digital broadcasting". Europa.eu. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ http://circa.europa.eu/Public/irc/infso/cocom1/library?l=/public_documents_2009/cocom09-01_switchover/_EN_1.0_&a=d Archived 2009-10-19 at the Wayback Machine
^ "eCommunications: National Switchover Plans | Europa — Information Society". Ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "DigiTAG". DigiTAG. Archived from the original on 2009-11-14. Retrieved 2010-09-02.
^ "Комисия За Регулиране На Съобщенията". Crc.bg. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ Webfactory www.webfactory.ie. "Digital Video Broadcasting — Bulgaria". DVB. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ Аналоговият ТВ сигнал спрян окончателно, 100 000 са без телевизия - Днес.dir.bg. Dnes.dir.bg. Retrieved on 2014-06-23.
^ "Digita". digitv.fi. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Digita Oy — We deliver your content". Digita.fi. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ Webfactory www.webfactory.ie. "Digital Video Broadcasting — Finland". DVB. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ Les Numériques http://www.lesnumeriques.com/. "La plus belle image pour ma TV". Retrieved 2016-12-23.
^ lefigaro.fr. "Le Figaro — Flash actu: Le passage au tout numérique en 2011". Lefigaro.fr. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "CSA — Décisions — Consultation publique sur le lancement d'appels à candidatures pour des télévisions locales". Csa.fr. 2009-06-08. Archived from the original on 2009-08-10. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "CSA — Communiqués de presse — Progression de la télévision numérique terrestre aux mois d'avril et mai 2009". Csa.fr. 2009-06-02. Archived from the original on 2009-06-16. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ Webfactory www.webfactory.ie. "Digital Video Broadcasting — France". DVB. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ ab "ATV's News Archive April 6th — April 10". Advanced-television.com. 2009-03-03. Archived from the original on 2009-10-09. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ ab "AFP: Télévision: le calendrier d'extinction de l'analogique officialisé, avec l'outre-mer". Google.com. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ Webfactory www.webfactory.ie. "Digital Video Broadcasting — Germany". DVB. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ abc "Greece to launch DTT in November". Broadband TV News. 2008-08-07. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ (PDF) http://www.culture.gov.uk/images/publications/MoU-DCMS-DCENR.pdf. Retrieved March 9, 2010. Missing or empty|title=(help)
[dead link]
^ "Back to Earth for terrestrial TV - The Irish Times - Fri, Dec 04, 2009". The Irish Times. 2009-12-04. Retrieved 2010-09-02.
^ "BCI announces Community Television Special Scheme". Bci.ie. 2008-07-21. Archived from the original on 2009-10-14. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Boxer pulls out of DTT contract — RTÉ - 20 April 2009". Rte.ie. 2009-04-20. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ McCaughren, Samantha (2010-05-02). "Digital television negotiations reach crisis point | The Post". Thepost.ie. Archived from the original on 2010-07-06. Retrieved 2010-09-02.
^ Independent.ie (2010-05-05). "Chorus-NTL renamed UPC as it rings changes with new services - Irish, Business". Independent.ie. Retrieved 2010-09-02.
^ "Irish DTT on the brink after Easy TV refuses BAI offer". Broadband TV News. 2010-05-16. Retrieved 2010-09-02.
^ "Bealach Scannán Na Héireann / Irish Film Channel Limited - Irish Company Info - Solocheck". Solocheck.ie. Retrieved 2010-09-02.
^ ab "Major changes heralded in broadcasting as new laws enacted". Department of Communications, Energy and Natural Resources. 2009-07-15. Archived from the original on July 20, 2009.
^ ab "Minister Ryan discusses the Broadcasting Act". Department of Communications, Energy and Natural Resources/Youtube.com. 2009-07-15.
^ "Broadcasting Act 2009 (Number 18 of 2009) - Tithe an Oireachtais". Oireachtas.ie. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Minister Ryan announces end of Digital Terrestrial Television trial". Digitaltelevision.ie. 2008-07-24. Archived from the original on 2009-06-09. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ New York (2009-07-09). "RTE admits digital TV launch delay - Media, Business". Independent.ie. Retrieved 2010-09-02.
^ "New digital service starts on trial basis". RTÉ News. 2010-10-29. Archived from the original on 2010-11-01. Retrieved 2010-10-29.
^ "Parliamentary Debates (Official Report - Unrevised) Dáil Éireann Tuesday, 2 March 2010 - Page 1". Debates.oireachtas.ie. Retrieved 2010-09-02.
^ "Ryan: Ireland will meet DTT deadlines". Broadband TV News. 2010-06-03. Retrieved 2010-09-02.
^ "RTÉ Appoints Director of Digital Switchover (DSO)". RTÉ Press Office. 1 July 2010. Archived from the original on 5 July 2010. Retrieved 1 July 2010.
^ "Minister Rabbitte Launches National Free to Air Digital Terrestrial Television". Digitaltelevision.ie. 2011-05-26. Retrieved 2012-01-11.
[permanent dead link]
^ "MINISTER RABBITTE ANNOUNCES DATE FOR DIGITAL TV SWITCHOVER". DCENR. 2011-10-14. Retrieved 2012-01-12.
[permanent dead link]
^ Saorview. Saorview.ie (2012-08-22). Retrieved on 2014-06-23.
^ http://www.goingdigital.ie
^ "Luxe.tv to join Luxembourg DTT | Broadband TV News". Broadband TV News<!. 2007-10-30. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ Webfactory www.webfactory.ie. "Digital Video Broadcasting — Luxembourg". DVB. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Dutch cable fights back | Broadband TV News". Broadband TV News<!. 2008-11-30. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ Webfactory www.webfactory.ie. "Digital Video Broadcasting — Netherlands". DVB. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ News. DVB. Retrieved on 2014-06-23.
^ "Low coverage start for Portuguese DTT- BroadbandTVNews-Branislav Pekic — Wednesday, 15 April 2009". Broadbandtvnews.com. 2009-04-15. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Romania unveils digital strategy". Broadband TV News. 2009-07-21. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Romania eyes DTT subsidies | Broadband TV News". Broadband TV News<!. 2009-03-26. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ Webfactory www.webfactory.ie. "Digital Video Broadcasting — Romania". DVB. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Romania awards DTT services licence". Broadband TV News. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ ab "Romania awards digital licences". Broadband TV News. Retrieved 2009-08-19.
^ Pavelescu, Mihai. "DIGITAL TERRESTRIAL-GO AHEAD-COMMENT / The Government favors state-owned Radiocom in the analogue switchover process". Media Expres. Retrieved 9 July 2013.
^ "Spain approves DTT pay-TV | Broadband TV News". Broadband TV News<!. 2009-06-18. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ Webfactory www.webfactory.ie. "Digital Video Broadcasting — Sweden". DVB. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ Technology. "Website". Website. Inview Technology. Archived from the original on 12 December 2013. Retrieved 9 December 2013.
^ Andrews, Amanda (2009-05-04). "Freeview rolls out high definition for World Cup". London: Telegraph. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ Webfactory www.webfactory.ie. "Digital Video Broadcasting — United Kingdom". DVB. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ ab "DVB in Republic of Macedonia". DVB.org<!. 2009-11-15.
^ Bahamas national TV to get multi-million dollar digital upgrade – video. The Bahamas Investor. Retrieved on 2014-06-23.
^ "DOF - Diario Oficial de la Federación".
^ Title III of the Deficit Reduction Act of 2005, Pub. L. No. 109-171, 120 Stat. 4 (8 February 2006), codified at 47 U.S.C. § 309(j)(14).
^ The deadline was originally 17 February 2009; Congress (with the signature of the President) delayed the deadline for total conversion in response to public outcry when funding for conversion DTV box coupons ran out. The bill was signed 11 February 2009
^ Bray, Hiawatha (2007-02-26). "FCC rule requires all new TVs to be digital". Boston Globe. Retrieved 2007-04-24.
^ Federal Communications Commission (2007-12-22). "Third Periodic DTV Review Report and Order" (PDF). Retrieved 2008-02-09. FCC 07-228
^ "FCC: Wireless Services: Lower 700 MHz". Federal Communications Commission. October 28, 2004. Retrieved May 9, 2007.
^ http://www.dtv2009.gov Archived 2007-12-31 at the Wayback Machine Digital Transition website accessdate= 2007-12-31
^ コスタリカ共和国における地上デジタルテレビ放送、方式採用の決定について [lit. Republic of Costa Rica decided adoption on Digital terrestrial television methodology] (PDF) (in Japanese). Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. 2010-05-26. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-22. Retrieved 2010-05-26.
^ "Costa Rica held its first broadcast on DTT ISDB-Tb". Panorama Audiovisual. 2012-03-21. Archived from the original on 2012-03-30. Retrieved 2012-03-22.
^ Advanced Television System Committee, Dominican Republic Adopts ATSC Digital Television Standard Archived August 23, 2010, at the Wayback Machine, August 12, 2010
^ "Para 2022, transmisión de TV será sólo digital: SIGET" [lit. By the year 2022, only Digital TV will be transmitted: SIGET] (in Spanish). La Prensa Gráfica. 2018-12-22. Retrieved 2018-12-30.
^ "Gaceta Oficial Digital". Gacetaoficial.gob.pa. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ Gray, Kevin (2009-08-28). "Argentina adopts Japanese digital TV standard". Reuters.
^ "Argentina started ISDB-T". Tokyo: DiBEG. Retrieved 12 June 2010.
^ "Bolivia adoptará la opción de Tv digital japonés-brasileña ·". La-razon.com. Archived from the original on June 8, 2011. Retrieved 2010-09-02.
^ "Erbol Comunicaciones - Periódico Digital". Erbol.com.bo. Archived from the original on 2011-07-06. Retrieved 2010-09-02.
^ "Gobierno de Chile adopta norma de Televisión Digital para el País". Subtel.cl. 2009-09-14. Archived from the original on 2009-09-22. Retrieved 2010-09-02.
^ ab EFE (28 December 2010). "Caracol y RCN inician emisión digital terrestre". El Espectador (in Spanish). Retrieved 30 December 2010.
^ "RESOLUCIÓN 389 DE 2010". Comisión Nacional de Televisión. 16 April 2010. Archived from the original on 7 July 2011. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
^ "TDT para Todos". TDT para Todos. TDT Televisión Digital Para Todos. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
^ "Ecuador is the sixth country to adopt the standard of ISDB-T". 2010-03-25. Retrieved 2010-04-30.
[permanent dead link]
^ "Hoy se presentó informe de la TDT y se firmó memorandos de cooperación". Superintendencia de Telecomunicaciones. Archived from the original on June 3, 2010. Retrieved 2010-03-26.
^ Ecuador is ready to migrate to Digital TV(2010-09-17)
^ "Paraguay adopts ISDB-T as the standard of the terrestrial digital TV". Tokyo: DiBEG. 2010-06-02. Retrieved 2010-06-08.
[permanent dead link]
^ "Paraguay adopta sistema japonés de televisión digital". 2010-06-01. Retrieved 2010-06-02.
^ "Peru begins digital TV transition process today". Dataxis. 2010-03-31. Retrieved 2010-09-18.
^ "Peru adopts ISDB-T". Tokyo: DiBEG. 2009-04-29. Retrieved 22 May 2010.
[permanent dead link]
^ "Peru adopts ISDB-T". Tokyo: DiBEG. Retrieved 12 June 2010.
^ ab "FAQ digitale telivisie (DTC)". Telecommunication Authority of Suriname. Retrieved 9 July 2015.
^ "TAS streeft naar digitale tv Suriname per juni". StarNieuws. 18 March 2015. Retrieved 9 July 2015.
^ "'Digitale tv in juni 2015 niet haalbaar'". Suriname Herald. 19 March 2015. Retrieved 9 July 2015.
^ https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-D/Spectrum-Broadcasting/Pages/DSO/Summary.aspx
^ Webfactory www.webfactory.ie. "Digital Video Broadcasting — Uruguay". DVB. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "DTT: Uruguay Regains Common Sense". Montevideo, Uruguay: ttv medianews. 2010-12-28. Archived from the original on 2011-07-17. Retrieved 2010-12-29.
^ "Uruguai adota padrão nipo-brasileiro de TV digital". Terra. 27 December 2010.
^ ウルグアイ東方共和国における地上デジタルテレビ放送日本方式採用の決定・欧州方式採用の決定を覆し、技術的に優れた日本方式採用を決定 [Uruguay decided to adopt Japanese DTT system in afternoon 27 December 2010, disproved European system (DVB-T), and decided to ISDB-T which is superior technically.] (in Japanese). Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications. 2010-12-28. Retrieved 2010-12-28.
^ "Venezuela adopts ISDB digital TV standard". Digitaltvnews.net. Retrieved 2010-09-02.
^ 地デジ、ベネズエラが日本方式採用へ5カ国目(Venezuela to Adopt Japanese Digital TV System, 5th country) Asahi Shimbun web site on 1 October 2009 (in Japanese) Archived October 4, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
^ Venezuela adoptó estándar japonés de televisión digital terrestre[permanent dead link](Venezuela adopted Japanese terrestrial digital television standard) Agencia Bolivariana de Noticias (in Spanish)[dead link]
^ Venezuela adopta sistema japonés para desarrollo de televisión digital Archived July 24, 2011, at the Wayback Machine(Venezuela adopts Japanese system for digital television development) TeleSUR (in Spanish)
^ Fifteen African countries finally adopted the DVB-T2 [permanent dead link]
^ http://www.tvtechnology.com/news/0002/gatesair-wins-ethiopia-tv-transition-project/278114
^ "NBC Appoints Inview Technologies for Common Set-Up-Box System". talkmedianigeria.com. Talk media Nigeria. Retrieved 23 March 2015.
^ "NATIONAL COMMON SET TOP BOX SYSTEM AGREEMNENT". nbc.gov.ng. National Broadcasting Commission of Nigeria. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 23 March 2015.
^ "The Strategy of the Republic of Albania for the Transition from Analogue to Digital Transmissions (Project). KKRT" (PDF) (in Albanian). 2008-12-05. Retrieved 2009-06-22.
[permanent dead link]
^ "Que es la TDT?". Archived from the original on 2010-02-14. Retrieved 2010-09-01.
^ es:Televisión Digital Terrestre en Argentina
^ "Oz DTV switchover in 2013". Advanced Television.com. 2008-04-07. Archived from the original on 2009-10-09.
^ "Australia to launch Freeview service". Digital Television Group.org. 2008-07-18. Archived from the original on 2015-07-25. Retrieved 2018-11-29.
^ "Legislation and research to advance digital TV switchover". Department of Broadband, Communications and the Digital Economy.gov.au. 2008-09-24. Archived from the original on 2009-07-10.
^ "Freeview Digital TV Platform Launch". australia.to. 2008. Archived from the original on March 13, 2009.
^ "Package to drive digital television transition". Department of Broadband, Communications and the Digital Economy.gov.au. 2009-01-29. Archived from the original on 2009-07-10.
^ "Digital TV Switchover Australia". Department of Broadband, Communications and the Digital Economy.gov.au. 2009-03-30.
^ "Australia". DVB.org. 2009-07-08.
^ "Digital TV Timetable by Region". Australian Government - Digital Switchover Taskforce. Archived from the original on 2013-10-21. Retrieved 2013-04-09.
^ "Digital switchover information for consumers". Archived from the original on 19 July 2008.
^ "Austria". DVB.org. 2009-04-07.
^ "DVB-T: Zeitplan". DVB-T.at. Archived from the original on 2007-06-30. Retrieved 2007-07-03.
^ "Analogue terrestrial TV switch-off in the EU - briefing — EUbusiness - European Union business news search and analysis". Eubusiness.com. Retrieved 2010-09-02.
^ "ORF stoppt im Juni digitalen Teletext". 2011-05-23. Retrieved 2012-10-13.
^ "Weg met sneeuw op je tv! (Away with snow on your TV!)".
^ "About - DVB".
^ "Bulgarian DTT woes continue". Broadband TV News. 2012-07-12. Retrieved 2012-09-05.
^ "THE NEWS — Hannu Pro (video, audio, multimedia)". Hannu Pro. 2009-04-13. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Broadcasting Public Notice CRTC 2007-53 - Determinations regarding certain aspects of the regulatory framework for over-the-air television". Canadian Radio and Television Commission. 17 May 2007. Archived from the original on 2008-04-05.
^ News. DVB. Retrieved on 2014-06-23.
^ "China". DVB.org. 2009-03-02.
^ "Bulletin of national standards". Web.archive.org. Archived from the original on 2007-06-23. Retrieved 2010-09-02.
^ "Acuerdo de la CNTV en la cual se adopta el formato DVB-T para la TDT" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-12-26.
^ "Croatia". DVB.org. 2009-07-01.
^ "HAKOM Hrvatska agencija za poštu i elektroniÄŤke komuinikacije — PoÄŤetna". Telekom.hr. Archived from the original on 2008-08-22. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Czech Republic". DVB.org. 2009-07-22.
^ "Digi TV". Digi-tv.dk. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ Webfactory www.webfactory.ie. "Barry Tew Boxer launches in Denmark — DVB.ORG - 7 April 2009". Dvb.Org. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Julian Clover Danish launch saves Boxer's bacon- BroadbandTVNews- - Wednesday 16 April 2009". BroadbandTVNews. 2009-04-16. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Launch of DTT services in Estonia". DigiTAG Web Letter. 15 December 2006. Archived from the original on 29 September 2007.
^ "Estonia — ASO to take place in 2010". DigiTAG attributed to the Estonian Government Committee for Transition to Digital Television. 2008-04-07. Archived from the original on 2008-04-11. Retrieved 2009-02-15.
^ "Ringhäälinguseadus §45¹ (15)" (in Estonian). Elektrooniline Riigi Teataja. Retrieved 2009-02-15.
^ "Faroe Islands". DVB.org. 2004-01-21.
^ "Finland will switch over to all-digital television". Finnish Ministry of Transport and Communications. 2007-08-31.
^ "Digi-tv esillä ympäri maata". Finnish Ministry of Communications. Retrieved 2007-08-15.
^ "France". DVB.org. 2009-07-06.
^ "France creates fund for ASO". BroadbandTVNews.com. 2009-07-23.
^ "Accueil TNT". Tnt-gratuite.fr. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "CSA — Communiqués de presse — L'offre de la TNT s'enrichit de 8 nouvelles chaînes et verra prochainement son déploiement étendu à de nouvelles régions françaises". Csa.fr. 2005-07-19. Archived from the original on 2009-08-25. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Archive 2005". Advanced-television.com. Archived from the original on 2009-06-16. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Orange". Wanadoo.fr. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Germany". DVB.org. 2009-07-15.
^ "Transition to the Digital Era". Minpress.gr. Archived from the original on 2009-11-11. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ OFTA(2007-06-04), Hong Kong Technical Standard for Digital Terrestrial Television Broadcasting Archived 2007-09-27 at the Wayback Machine, Hong Kong
^ (in Chinese) 望月 (2007-06-09). "獨家專訪TVB 折解數碼廣播七大疑團 (Exclusive interview with TVB on digital broadcasting)". e-zone AVzone. pp. 4–5.
^ "Hong Kong to end analogue TV services in 2020". news.rthk.hk. Retrieved 2019-02-11.
^ "Hungary starts residential phase of digital switchover". Retrieved 2013-03-13.
^ "Hungary set for digital switchover". Retrieved 2013-03-20.
^ Konsorsium TV Digital Indonesia Archived September 21, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
^ "Peluncuran TV Digital: Digital Dividend pada Pita 700 MHz untuk WiMAX". Indonesian Infocom Society - Masyarakat Telematika Indonesia (MASTEL).
^ ab Penyelenggaraan Penyiaran Televisi Digital Teresterial Penerimaan Tetap Tidak Berbayar
^ http://portal.irib.ir/web/digitaltv/main/-/asset_publisher/TY7v/content/40-%D8%AF%D8%B1%D8%B5%D8%AF-%D8%A7%D8%B2-%D8%AC%D9%85%D8%B9%D9%8A%D8%AA-%D9%83%D8%B4%D9%88%D8%B1-%D8%AA%D8%AD%D8%AA-%D9%BE%D9%88%D8%B4%D8%B4-%D8%B3%D8%A7%D9%85%D8%A7%D9%86%D9%87-%D8%AA%D9%84%D9%88%D9%8A%D8%B2%D9%8A%D9%88%D9%86-%D8%AF%D9%8A%D8%AC%D9%8A%D8%AA%D8%A7%D9%84-%D9%82%D8%B1%D8%A7%D8%B1-%D8%AF%D8%A7%D8%B1%D9%86%D8%AF?redirect=%2Fweb%2Fdigitaltv%2Fmain[permanent dead link]
^ http://portal.irib.ir/web/digitaltv/main/-/asset_publisher/TY7v/content/%D9%85%D8%B4%D8%B1%D9%88%D8%AD-%D9%85%D8%B5%D8%A7%D8%AD%D8%A8%D9%87-%D8%AF%DA%A9%D8%AA%D8%B1-%D8%B9%D9%84%DB%8C%E2%80%8C%D8%B9%D8%B3%DA%A9%D8%B1%DB%8C%D8%8C-%D9%85%D8%B9%D8%A7%D9%88%D9%86-%D8%AA%D9%88%D8%B3%D8%B9%D9%87-%D9%88-%D9%81%D9%86%D8%A7%D9%88%D8%B1%DB%8C-%D8%B1%D8%B3%D8%A7%D9%86%D9%87%D8%8C-%D8%AF%D8%B1-%D8%A8%D8%B1%D9%86%D8%A7%D9%85%D9%87-%D9%BE%D8%A7%D8%B1%DA%A9-%D9%85%D9%84%D8%AA-%D9%BE%D9%86%D8%AC%D8%B4%D9%86%D8%A8%D9%87-13-%D9%85%D8%B1%D8%AF%D8%A7%D8%AF-1390?redirect=%2Fweb%2Fdigitaltv%2Fmain[permanent dead link]
^ http://portal.irib.ir/web/digitaltv/main/-/asset_publisher/TY7v/content/%D8%AA%D9%87%DB%8C%D9%87-%D8%B7%D8%B1%D8%AD-%D8%AC%D8%A7%D9%85%D8%B9-%DA%AF%D8%B0%D8%A7%D8%B1-%D8%A7%D8%B2-%D8%A7%D9%86%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%88%DA%AF-%D8%A8%D9%87-%D8%AF%DB%8C%D8%AC%DB%8C%D8%AA%D8%A7%D9%84-%D8%AF%D8%B1-%D8%B1%D8%B3%D8%A7%D9%86%D9%87-%D9%85%D9%84%DB%8C?redirect=%2Fweb%2Fdigitaltv%2F[permanent dead link]
^ "What is Digital Television?". "Department of Communications, Energy & Natural Resources". 2008-03-04. Archived from the original on 2008-12-01.
^ "BCI DTT Licensing Policy 2008 (Revised Edition" (PDF). "Broadcasting Commission of Ireland (Broadcasting Authority of Ireland)". 2008-02-09. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-06-07. Retrieved 2009-06-22.
^ "BCI Issues Decision on DTT Multiplex Contracts". "Broadcasting Commission of Ireland" (Broadcasting Authority of Ireland)). 2008-07-21. Archived from the original on 2009-10-14.
^ "BCI DTT Licensing (DTT Multiplex Contracts: Applications received". "Broadcasting Commission of Ireland (Broadcasting Authority of Ireland (in 2009"). 2008-05-15. Archived from the original on 2012-02-10.
^ "Minimum Receiver Requirements for DTT in Ireland V1.0)(" (PDF). "Department of Communications, Energy & Natural Resources, Ireland". 2008-02-06. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-21. Retrieved 2009-06-22.
^ "Coordination issue likely to delay DTT roll-out". The (Sunday Business) Post.ie-Thomas Crosbie Holdings Limited Archives. 2008-07-27. Archived from the original on 2009-02-26.
^ "DTT Rollout". "Department of Communications, Energy & Natural Resources". 2008-03-13. Archived from the original on 2008-12-18.
^ "Minister Ryan announces end of Digital Terrestrial Television trial". "Department of Communications, Energy & Natural Resources, Ireland". 2008-07-24. Archived from the original on 2009-06-09.
^ "Broadcasting Bill Number 29 of 2008". Tithe an Oireachtais". 2009-04-03.
^ <"Boxer pulls out of DTT contract". RTÉ. 2009-04-20.
^ "BCI Awards DTT Contracts to One Vision". BCI. 2009-05-11. Archived from the original on 2009-08-17.
^ "Authority frustrated by delays in deal for digital TV". "Irish Independent". 2010-03-15.
^ "RTÉ Saorview". RTÉ.ie. Retrieved 2010-10-29.
^ "Parliamentary Debates (Official Report -(unrevised) Déil Éireann Tuesday, 2 March 2010 - Tithe an Oireachtais". Oireachtas.ie. Archived from the original on April 8, 2010. Retrieved 2010-03-15.
^ "Going Digital.ie". "goingdigital.ieQ. Retrieved 2012-01-11.
^ "Digital UK Northern Ireland". "digitaluk.co.uk". Archived from the original on 2012-01-20. Retrieved 2012-01-11.
^ "מאפייני הממיר/המקלט הדיגיטאלי לטלוויזיה" (PDF). Retrieved 2010-09-01.
^ "Israel". DVB.org. 2009-07-15.
^ "Digital Television in Israel". Godigital.co.il. 2009.
^ "Israel DTT goes nationwide". BroadbandTVNews. 2009-08-05.
^ "Israel DTT goes nationwide". Broadband TV News. 2009-08-05. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Italy". DVB.org. 2009-07-13.
^ "Digital Broadcasting Experts Group (DiBEG) promote ISDB-T". DiBEG. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ ISDB-T, Application, Present and Future Archived February 25, 2009, at the Wayback Machine, PDF File
^ On 20 April 2011, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications confirmed, and made the resolution by the House of Councillors on 8 June 2011, that the analog terrestrial TV closedown schedule on 24 July 2011 would remain unchanged, with the only exception being that the shutdown will be postponed for maximum one year in Iwate, Miyagi and Fukushima prefectures. These prefectures were heavily damaged by the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami and the nuclear accidents that followed it.
^ "Lithuania". DVB.org. 2009-04-27.
^ Webfactory www.webfactory.ie. "Digital Video Broadcasting — Lithuania". DVB. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Broadcasting Center Europe: DVB-T / TNT". Archived from the original on 2008-10-20.
^ planned to introduce DTT in 2011, then start switching off in 2012 and finish in 2015, the plan was cancelled
^ "DVB.org"%7cdate=2009-05-12 "About - DVB".
^ "DVB.org"%7cdate=2009-06-16 "About - DVB".
^ "NEC completes Morocco deal". "tradearabia.com". 2007-04-28. Archived from the original on 2009-12-16.
^ "Google Translate". "Translate.google.com". Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ Digital TV broadcasting to begin in Myanmar this week Archived 2014-01-03 at the Wayback Machine. NexTV Asia. Retrieved on 2014-06-23.
^ "DVB.org"%7cdate=2009-05-08 "About - DVB".
^ "Going Digital- When is my area going digital?". Archived from the original on 2011-10-17.
^ "TVNZ To Go HDTV For Beijing Olympics". Archived from the original on 2007-11-05.
^ "Process for analogue switch-off to digital TV".
^ "Norway". DVB.org. 2008-09-17.
^ "RiksTV — Når kommer det?". RiksTV.no. Archived from the original on 2007-04-30. Retrieved 2007-07-04.
^ "Google Translate". Translate.google.com. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "DigiTAG". DigiTAG. Archived from the original on 2009-10-09. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "La implementación de la TDT en el Perú". telecentros.pe. 2008.
[permanent dead link]
^ "Chris Dziadu Technology breakthrough for Polish DTT- BroadbandTVNews- - 31 March 2009". BroadbandTVNews. 2009-03-31. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Chris Dziadu Polish DTT nears- BroadbandTVNews- - Wednesday 15 April 2009". BroadbandTVNews. 2009-04-15. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ Webfactory www.webfactory.ie. "Poland- DVB.org — Wednesday 20 July 2009". DVB.org. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Google Translate". Translate.google.com. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Portugal". DVB.org. 2009-05-08.
^ "Google Translate". Translate.google.com. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Google Translate". Translate.google.com. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Qatar Goes DVB-T2". Digital Video Broadcasting Project (DVB). 11 Dec 2013.
^ "Romania". DVB.org. 2009-05-08.
^ "Romania unveils digital strategy". BroadbandTVNews.com. 2009-07-21.
^ "Romania opens DTT services tender". BroadbandTVNews.com. 2009-07-21.
^ "Romania awards DTT services licence". BroadbandTVNews.com. 2009-08-12.
^ "Romania approves late transition to digital terrestrial". 2013-06-24.
^ "Romania Switching to DVB-T2". 2013-10-22.
^ "Russian Federation". DVB.org. 2009-07-06.
^ "Russia sets out DTT channel strategy". Broadband TV News. 2009-06-24. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ [4]
^ "Towercom outlines DTT plans". Broadband TV News. 2009-08-18. Retrieved 2010-09-02.
^ "Éra analógového vysielania sa definitívne končí". 2012-12-28. Archived from the original on 2013-10-21. Retrieved 2012-12-28.
^ [5]
^ "South Africa". DVB.org. 25 May 2009. Archived from the original on 27 July 2009. Retrieved 14 July 2009.
^ "South Africa". DVB.org. Retrieved 7 March 2018.
^ Odendaal, Natasha (28 October 2016). "Analogue transmission switch-off starts in Northern Cape as South Africa progresses digital migration". Engineeringnews.co.za. Engineering News. Retrieved 17 July 2017.
^ van Zyl, Gareth (17 June 2015). "SA joins list of losers on digital migration". Fin24.com. Retrieved 7 March 2018.
^ Herman, Paul (23 January 2018). "Communications department needs R6.6bn to complete digital migration by 2019 deadline". News24.com. Retrieved 7 March 2018.
^ "South Korea". DVB.org. 2009-05-18.
^ "KBS WORLD". KBS World. 2010-09-01. Retrieved 2010-09-01.
^ "ATV's News Archive February 25th — February 29". Advanced-television.com. Archived from the original on 2009-10-09. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Spain". DVB.org. 2009-07-13.
^ Webfactory www.webfactory.ie. "Digital Video Broadcasting — Spain". DVB. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Sri Lanka to digitalize TV broadcasting". DailyFT. Archived from the original on 2014-09-08. Retrieved 2014-09-08.
^ "Comment of the Minister for Internal Affairs and Communications on Adoption of Japanese Terrestrial Digital TV Broadcasting System (ISDB-T) in the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka". Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications. Retrieved 2014-09-08.
^ "Sweden". DVB.org. 2009-07-13.
^ "Nya tillstånd för digitala TV-sändningar". Swedish Radio and TV Authority. 20 January 2001. Archived from the original on 8 September 2007.
^ As of June 2007, H.264 is only used for HDTV in the Mälaren Valley region.
^ "Switzerland". DVB.org. 2009-07-13.
^ "SF Info set for January DTT launch". Broadband TV News. 2008-12-16. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "Taiwan". DVB.org. 2009-07-13.
^ abc Webfactory www.webfactory.ie. "Digital Video Broadcasting — Taiwan". DVB. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
^ "About - DVB".
^ ab "NTC. Hope to take Thai step digital TV. The readiness of today .. have enough yet??". telecomjournal.net. Retrieved 2554-05-20. Check date values in:|accessdate=(help)
^ ThaiPBS Will be first to come before switching over on Analog TV than other terrestrial television stations, and Start from 1 December Same year (at first start plan in Fang (Chiang Mai), and Koh Samui (Surat Thani))
^ "Turkey". DVB.org. 2007-04-24.
^ https://technology.ihs.com/593619/the-outlook-for-digital-terrestrial-television-in-turkey
^ "International Forum 'Digital Broadcasting in Ukraine". ITK (Television Industry Committee). Archived from the original on 2008-09-11.
^ "What is Digital Switchover?". DAS TV. 2007-07-01. Archived from the original on 2007-09-10. Retrieved 2007-08-13.
^ "Commerce Department Issues Final Rule To Launch Digital-to-Analog Converter Box Coupon Program".
National Telecommunications & Information Administration. 2007-03-12.
^ "TV Comverter box Programme website". National Telecommunications & Information Administration. 2007-03-12. Archived from the original on November 4, 2009.
External links
The Future of Broadcast Television (FoBTV) is next month March 20, 2012
Future of Broadcast Television Summit Declares Global Goals for Future of Broadcasting Nov. 11, 2011- IEEE Spectrum - Does China Have the Best Digital Television Standard on the Planet?
- DigiTAG
The DVB Project - including data on DTT deployments worldwide- European Audiovisual Observatory
- MAVISE database on TV channels and TV companies in the European Union
Worldwide overview of the digital terrestrial systems ATSC, DMB-T/H, DVB-T and ISDB-T Status DTT in the world.
Digital Broadcasting, the Launching by Country Digital Broadcasting Experts Group (DiBEG)- Research in DTT
- Schedule for the implementation of Digital TV in the world