Driver's license

A license from Spain, in the format of the European driving licence
A driver's license is an official document permitting a specific individual to operate one or more types of motorized vehicles, such as a motorcycle, car, truck, or bus on a public road.
The term driver's license is American English; the Canadian English equivalent is driver's licence, the Australian English equivalent is driver licence and in British English it is driving licence. In this article, the American terminology and spelling is used except where the section refers specifically to British practice. The laws relating to the licensing of drivers vary between jurisdictions. In some jurisdictions, a license is issued after the recipient has passed a driving test, while in others, a person acquires a license before beginning to drive. Different categories of license often exist for different types of motor vehicles, particularly large trucks and passenger vehicles. The difficulty of the driving test varies considerably between jurisdictions, as do factors such as age and the required level of practice.
In some international agreements the wording driver's permit is used, for instance in the Vienna Convention on Road Traffic.
Contents
1 History
2 Driver's licenses used for identification purposes
2.1 Europe
2.2 Asia
2.2.1 Japan
2.3 North America
2.4 South America
3 Licenses for different categories of vehicles
3.1 Africa
3.1.1 Egypt
3.1.2 Ghana
3.1.3 Kenya
3.1.4 Morocco
3.1.5 Nigeria
3.1.6 South Africa
3.1.7 Tanzania
3.2 Asia
3.2.1 Hong Kong
3.2.2 India
3.2.3 Indonesia
3.2.4 Israel
3.2.5 Lebanon
3.2.6 Malaysia
3.2.7 Pakistan
3.2.8 Singapore
3.2.9 South Korea
3.2.10 Sri Lanka
3.2.11 Thailand
3.2.12 Vietnam
3.3 European Economic Area
3.3.1 Austria
3.3.2 Belgium
3.3.3 Bulgaria
3.3.4 Croatia
3.3.5 Cyprus
3.3.6 Denmark
3.3.7 Finland
3.3.8 France
3.3.9 Germany
3.3.10 Greece
3.3.11 Iceland
3.3.12 Ireland
3.3.13 Italy
3.3.14 The Netherlands
3.3.15 Norway
3.3.16 Poland
3.3.17 Romania
3.3.18 Spain
3.3.19 Sweden
3.3.20 United Kingdom
3.4 Rest of Europe
3.4.1 Albania
3.4.2 Azerbaijan
3.4.3 Macedonia
3.4.4 Russia
3.4.5 Switzerland
3.4.6 Turkey
3.5 North America
3.5.1 Canada
3.5.2 Barbados
3.5.3 Costa Rica
3.5.4 El Salvador
3.5.5 Jamaica
3.5.6 Mexico
3.5.7 Trinidad and Tobago
3.5.8 United States
3.6 Oceania
3.6.1 Australia
3.6.2 Cook Islands
3.6.3 New Zealand
3.7 South America
3.7.1 Brazil
3.7.2 Peru
3.7.3 Venezuela
4 Organ donations
5 International and interstate considerations
5.1 Issues when moving permanently from one country or one state to another
5.1.1 Australia
5.1.2 Canada
5.1.3 France
5.1.4 Germany
5.1.5 Hong Kong
5.1.6 Singapore
5.1.7 Sweden
5.1.8 United Kingdom
5.1.9 United States
6 See also
7 References
8 External links
History

The world's first license to drive a motor vehicle, issued to Karl Benz upon his request.
Karl Benz, inventor of the modern automobile, had to receive written permission from the Grand Ducal authorities to operate his car on public roads in 1888 after residents complained about the noise and smell of his Motorwagen.[1] Up until the start of the 20th century, European authorities issued licenses to drive motor vehicles similarly ad hoc, if at all.[1]
Mandatory licensing for drivers came into force on 1 January 1904[2] after the Motor Car Act 1903 received royal assent in the United Kingdom. Every car owner had to register their vehicle with their local government authority and be able to prove registration of their vehicle on request. The minimum qualifying age was set at 17. The licence gave its holder 'freedom of the road' with a maximum 20 mph (32 km/h) speed limit.[3] Compulsory testing was introduced in 1934, with the passing of the Road Traffic Act.[4]
Prussia, then a state within the German Empire, introduced compulsory licensing on September 29, 1903. A test on mechanical aptitude had to be passed and the Dampfkesselüberwachungsverein ("steam boiler supervision association") was charged with conducting these tests.[1] In 1910, the German imperial government mandated the licensing of drivers on a national scale, establishing a system of tests and driver's education requirements that was adopted in other countries.[1]
In 1909, the Convention with Respect to the International Circulation of Motor Vehicles[5] recognize the need of qualifications, examination, and authorization for international driving.
In 1929, the notion of International Driving Permit is addressed by international Convention.[6]
In 1949, the United Nations defined a convention on road traffic that standardised rules on roads, occupants, rules, signs, driver's licenses and such. It address the notion of driving license for a number of countries, under the wording "driving permit" and declares that its color should be pink.[7]

Screenshot of Annex 6 of the "Convention on Road Traffic" volume 125 of Geneva convention 1949
In 1968, the Convention on road traffic, ratified in 1977, further updated these agreements.[8]
Other countries in Europe also introduced driving tests during the twentieth century, the last of them being Belgium where, until 1977, it was possible to purchase and hold a license without having to undergo a driving test.[9]
As automobile-related fatalities soared in North America, public outcry provoked legislators to begin studying the French and German statutes as models.[10] On August 1, 1910, North America's first licensing law for motor vehicles went into effect in the US state of New York, though it initially applied only to professional chauffeurs.[11] In July 1913, the state of New Jersey became the first to require all drivers to pass a mandatory examination before receiving a license.[12]
Driver's licenses used for identification purposes
Many countries, including Australia, New Zealand, Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States, have no national identification cards. As many people have driver's licenses, they are often accepted as de facto proof of identity. Non-drivers can apply for equally valid state-issued identification-only cards. Most identity cards and driver's licenses are credit card size—the "ID-1" size and shape defined in ISO/IEC 7810.
Europe
Many European countries require drivers to produce their license on demand when driving. Some European countries require adults to carry proof of identity at all times, but a driving license is not valid for identification in every European country.[13]
In the United Kingdom most drivers are not required to carry their licence. A driver may be required by a constable or vehicle examiner to produce their licence, but may provide it in a specified police station within seven days;[14] the police issue a form for this purpose.[15]
In Denmark, Finland, Norway, Spain and Sweden, the driver's license number is the same as the citizen's ID number. Banks and authorities use the same number for customer databases, making the licence fully useful for identification purposes.
Asia
In Hong Kong a driving license carries the same number as the holder's ID card, but has no photograph. As such, a driver's license is not a legal document for proof of age for purchase of alcohol. Upon inspection both must be presented. Plans to make the newly phased in Smart ID contain driving license information have been shelved.
Similarly, the Saudi Arabian government require all drivers to carry an ID card in addition to a license and present them whenever requested. In Saudi Arabia using a license instead is only permitted if the request is made for on-site inspection/identification purposes, especially at checkpoints. Expatriates may be requested to present their visas as well.
In Japan, South Korea, and Singapore driving license cards are widely used as identification.[16]
Japan
Japanese driver's licenses bear one of the following 3 colors on the expiration date.
- Green
- New Drivers (First license in Japan) Valid for 2 to 3 years. Drivers with under one year of driving experience are required to display a "Shoshinsha mark" (Young Leaf Mark) on their vehicle. This holds true if the driver acquires a license for a different class of vehicle, regardless of the length of driving experience on their previous license. However, such a mark does not indicate necessarily the color on the driver's license. A driver with a young leaf mark on their car could very well be a gold driver. This is because the gold status does not disappear with a change in vehicle class.
- Blue
- Drivers who have fewer than 5 years of clean driving history or who do not have a clean driving record but more than 5 years of driving history. Valid for 3 to 5 years depending on age, violation history, etc.
- Gold
- In addition to the regular license, the Gold Driver's License (ゴールド免許, Gōrudo Menkyo), or Superior Drivers License (優良運転者免許証, Yūryō Untensha Menkyoshō), is a special designation of license given to "superior drivers" (優良運転者) in Japan. Holders of such licenses can be identified by the gold band printed over the expiration date of their driver's license.

Superior Driver's License, (Gold License)
The Gold License is granted to any driver who, at the point of license renewal, has at least five years of clean driving history (no driving infractions).[17][18] According to implications in the Road Traffic Laws Reforms that took place on May 10, 1995, all such licenses are marked with a gold band over the license's expiration date as well as the word 優良 (excellent) printed in black, below.
Those who hold a gold license have the added benefit of qualifying for the Superior Drivers Course at the time of renewal, a significantly shorter and less-expensive renewal process. In some cases, they can bypass the main license center and have their license renewed at a separate Superior Drivers License Renewal Center.[19]
Moreover, because such license holders are proven to have been free of accidents and moving violations for at least five years, they are deemed low-risk and qualify for optional car insurance discounts. To qualify, drivers must be accident and violation-free for 5 years and 41 days prior to their birthday on their license's expiration. The period in which the license holder's driving history is reviewed begins on the 40th day prior to their birthday of that year. Should the license holder be deemed to qualify, they will receive a decision in the mail with the word 優良 printed on it.
Even the so-called "Paper Drivers" who hold licenses but never drive, who technically are without violation or accident, can lose their eligibility to obtain a gold license for several reasons including if their car is used by a drunk driver or to support drunk driving in any way.
North America
In the United States and Canada, driver's licenses are issued by the states and provinces (or territories), respectively, and do not look the same nationwide. They are also used as a de facto or government-issued identification document for the holder. Most government issuers of driver's licenses also provide a government-issued identification card with similar attributes to a driver's license to those residents within their jurisdictions who do not have or maintain a valid driver’s license, making it easier for them to do things such as open a bank account, and perform any other activities that require official identification. Identification cards serve as government-issued photo ID but do not enable a person to operate a motor vehicle, a fact typically noted on the ID via the phrase 'Not a driver's license' or similar wording. This type of photo ID is referred to as a Photo card in some jurisdictions (for example, Ontario Photo Card). Government-issued ID cards are also issued to out-of-state residents e.g. college students enrolled in an institution of higher education outside their state of residence e.g. a domiciled Texas resident enrolled at UCLA where the individual retains their Texas driver license and holds a California state issued ID card (as mentioned above e.g. bank account and financial affairs); also applicable to those who own business assets and not domiciled in a state or city as a resident e.g. one domiciled in Los Angeles and owns either a business or real estate property in Florida). In the United States no individual can hold two valid driver licenses, e.g. a Texas and California driver license held simultaneously, since some U.S. states do not collect personal income taxes e.g. Texas, Florida while California has a personal state income tax.[clarification needed]
South America
In Venezuela, the driver's license number is the same as the citizen's ID number.
The number of a driving license issued by the Dominican Republic has the same number as the holder's Dominican Republic ID card.
Licenses for different categories of vehicles
In a number of countries (including the United States, New Zealand, Australia, UK, Ireland and sometimes Canada as well) people who drive commercially are required to have special licenses. The cost of taking the series of tests and examinations to obtain these licenses usually means that an employer would subsidize his or her drivers.
Africa
Egypt
Egyptian citizens are entitled to a driver's license once they have reached the age of 18. To obtain their licenses, applicants must pass a driving test as well as several computer tests.
In order to pass, all a person had to do was drive six meters forward and then reverse six meters. However, the test was updated to make it more difficult, now the applicant has to answer 8 out of 10 correct answers in a computer test, then pass a forward & reverse S-track test in addition to an assessment of parking skills.
Ghana
Driver's licensing in Ghana is conducted by the nation's Driver and Vehicle Licensing Authority. The legal driving age is 18.
Kenya
The legal driving age is 18 years old. The license must include:
- Id number
- Name
- Date of issue
- Class of vehicle
Morocco
The legal driving age of Moroccan citizens is 18.[citation needed]
Nigeria
In Nigeria, the minimum age to qualify for a driver's license is 18. The applicant would first attend training at an accredited driving school. Then, the driving school will present the applicant to a Vehicle Inspection Officer (VIO) for a driving test.Upon passing the driving test and the applicant would obtain a certificate of proficiency from the VIO.The applicant then completes a driver's licence application form at the Driver's Licence Centre (DLC) or download the form online.Afterwards he pays a license fee online or at the Bank and presents his application form to the Board of Internal Revenue (BIR) Officer and VIO at the DLC for endorsement. After all these he proceeds to the Federal Road Safety Corps (FRSC) Officer at the DLC for biometric data capture.He is given a temporary driver’s licence which is valid for 60 days. He picks up original driver’s licence at the BIR Office after 60 days.
South Africa
The minimum driving age in South Africa is 17, when you may drive with an adult whom holds a valid driving license, after passing your learners license theory test. At 18 you can obtain a driving license after passing the road test. Small motorcycles may be driven from the age of 16.
To obtain a license, applicants must pass a written or computer-based test to obtain a learner's license, and then pass a road test to obtain the driving license. Categories for licenses include CODE B (normal vehicles), CODE C1 (LDV), CODE EC (heavy trucks), CODE A (motorcycle).
The learners license theory test will contain three sets of questions with multiple answer options; you will have to select the correct answer. Some driving license test centres use computers for the test, whereas other centres require you to complete the test using a test paper and pen.[citation needed]
Tanzania
Driver's licenses are issued by the Tanzania Revenue Authority. The legal driving age for motor vehicles is 18 and for motorcycles is 16.[20]
Asia
Hong Kong
The minimum driving age in Hong Kong is 16 for mopeds under 50 cc (3.1 cu in), and 18 for cars and motorcycles. Access to motorcycles producing more than 50 cc (3.1 cu in) is restricted to riders aged 18 and above.[citation needed] Drivers are legally obliged to carry a valid driving license whilst driving, and must be produced if required to do so by a police officer.[citation needed]
People above 70 have to undergo strict medical tests in order to obtain a license that has limited validity and requires renewal after a certain period.
India
The minimum driving age in India is 16 for mopeds under 50 cc (3.1 cu in), and 18 for cars and motorcycles. Access to motorcycles producing more than 50 cc (3.1 cu in) is restricted to riders aged 18 and above.[21] The Regional Transport Office (RTO/RTA) issue their own driving licences in various states. Drivers are legally obliged to carry a valid driving license in India whilst driving, and must be produced if required to do so by a police officer.
In India, people aged 50 or more, have to undergo strict medical tests in order to obtain a license that has limited validity and requires renewal every five years. A commercial driving license is valid for 3 years and requires to be renewed.
Indonesia

Front side of the Indonesian Driving License card "A" class for driving normal 4 wheel car/jeep vehicle

Rear/back side of the Indonesian driving license card
In Indonesia, to drive a motor vehicle, one must own a legal Indonesian Driving License which is called (Surat Izin Mengemudi) or SIM in Indonesian. It is a card which legally permits one to drive a motor vehicle. In Indonesia, there are classes for each driving license for which is allowed to drive a type of motor vehicle:
A – to drive private passenger or cargo vehicle with weight allowed not exceeding 3,500 kg (7,700 lb)
A Public (A UMUM) - to drive commercial vehicles and goods carrier to the amount of weight that is allowed does not exceed 3,500 kg (7,700 lb)
B1 – to drive private passenger or cargo vehicle with weight allowed exceeding 3,500 kg (7,700 lb)
B1 Public (B1 UMUM) - to drive passenger vehicles and general freight allowed amount of weight over 3,500 kg (7,700 lb)
B2 - to drive heavy equipment vehicles, towing vehicles, or motor vehicles with attractive patch or trailer train individuals with severe or patches are allowed to train more than 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) trailer/s
B2 Public (B2 UMUM) - to drive commercial vehicles for towing or pull cart trailer with heavy patch that are allowed to train more than 1,000 kg trailer
C – to drive motorcycles (two-wheeled motor vehicle)
D – special vehicle for disabled person
The classes above are also allowed by the age of the driver according to the class of the driving license. The ages are accordingly issued to the different classes of the driver's choice:
- 17 years old for issue of Driving License class: A, C, and D
- 20 years old for issue of Driving License class: B1
- 21 years old for issue of Driving License class: B2
Israel
Lebanon
Malaysia

The front side of a typical Malaysian driver's license.
The minimum age for obtaining driving license varies between 16 and 21, although there is a concern about teenage driving safety.[22]
As of November 2011, any drivers could renew their license on his or her birthday, rather than expiry date.[23]
Pakistan
The minimum age for eligibility for learner's permit is 18 years ; as the driver's information is saved against the Computerized National ID Card number which is issued at the age of 18. The License Issuing Authorities vary to each district and work under the relative District Police.
New credit card format driving license has been introduced. The license bears the digital photo, signature and blood group information of card holder. The record of violation is stored automatically in the database. To obtain a driving license one must register for the learner's permit at any of the local District Police's designated license offices and after 42 days can apply for test for a regular full license.
The test phase consists of a theory based test followed by a short practical test. Only the ones who pass the theory test are allowed to take the practical test. The whole test stage is a single day process where both the tests are to be taken the same day. The driving license currently issued holds basic information of the Driver including Name, Father's Name, Date of birth, Address, Authorized Vehicle Types, Emergency Contact, Blood Group, Fingerprint Impression, Driver Photo. The license also has a magnetic strip though its viability is yet to be made public.
Singapore
Driving licences in Singapore are issued by the traffic police. The minimum age to obtain a provisional driving licence (PDL), which allows the holder to practise driving while under the supervision of an authorised driving instructor, is 18. A provisional driving licence is obtained once the individual has passed the basic theory test. PDL holders are then required to sit for and pass the final theory test before they are allowed to sit for the practical driving test. Once they have passed the practical driving test, they are issued with a driving licence which allows for driving without supervision, though new drivers are required to display probationary plates when driving for the first year after their licence is issued.
South Korea
In South Korea, one must be holding a driving license called "운전면허증" or an international driving license. The International driving license is valid for 1 years starting from the date of entry. If one is going to stay in South Korea longer than a year, it is necessary to change the international license to a local license by visiting the police office or driving license testing center.
For South Korean driving license, there are classes for each driving license for which is allowed to drive a type of motor vehicle:
Type 1 (1종) – Commercial Vehicles
Large (대형) – A license which allows one to drive every vehicle except trailers and wreckers. It allows one to drive cargo truck, passenger bus, construction equipment for commercial purposes.
Normal (보통) – Allows one to drive a vehicle with less than 15 seats, an emergency motor vehicle with less than 12 seats, a cargo truck with a load limit of 12 tonnes, a construction equipment which weighs less than 3 tonnes (doesn't include trailers and wreckers), a special motor vehicle which weighs less than 10 tonnes (doesn't include trailers and wreckers).
Small (소형) (No longer valid) – Allows one to drive a vehicle with three wheels and a motorcycle.
Type 2 (2종) – Non-Commercial Vehicles
Normal (보통) – Allows one to drive a vehicle with less than 10 seats, a cargo truck with a load limit of 4 tonnes, a special motor vehicle which weighs less than 3.5 tonnes (doesn't include trailers and wreckers).
Small (소형) – Allows one to drive a motorcycle.
Practice Licence
Type 1 (1종) – Allows one to drive a vehicle with less than 15 seats, a cargo truck with a load limit of 12 tonnes, when the driver is driving with somebody with a licence which isn't a practice licence.
Type 2 (2종) – Allows one to drive a vehicle with less than 10 seats, a cargo truck with a load limit of 4 tonnes, when the driver is driving with somebody with a licence which isn't a practice licence.
Besides the type of the licence, the licence may have a special condition. Depending on the special condition given, the driver must satisfy the condition below to be able to drive. Drving a vehicle without satisfying the given condition is considered as unlicensed driving.
A – Automatic Transmission Only
B – Drive with prosthetic hand or arm
C – Drive with prosthetic leg
D – Wear hearing aid when driving
E – Drive with Hearing-Impaired Sign + Convex Mirror
I – Drive a car with a gas pedal located in the left.
Sri Lanka
New E-Smart Card driving licenses are available in Sri Lanka. These cards are intended for the use in the proposed "Point System".
In Sri Lanka, a driving license is the official document which authorizes its holder to operate various types of motor vehicles on public roads. They are administered by the Department of Motor Traffic (DMT). The minimum age is 18 years for all vehicle types.
Thailand
Driving in Thailand without a driver's license is prohibited and is punishable by fines. Moreover, in case of a road accident, a driver without a license can be considered as the guilty party. Also, an unlicensed driver who was in road accident will be refused medical insurance payment
It isn't difficult to receive a driver's license in Thailand. In fact, it is accessible to foreigners too. When the package of documents will be collected person need to appeal to the Transport Authority and sign up for the exam. Waiting time usually is near one month.
The exam includes theoretical and practical parts held on the same day. Reaction's tests are conducted before the exam. The complainant gets a temporary ID valid for one year. It may be extended for five years, but only if the complainant lives in Thailand on non-immigrant visa. An International driver's license is recognized in Thailand. With its help it is easy to get a license without doing the exams.
There are different plastic cards for motorcycles and vehicles. Therefore, documents and exams need to be done twice.[24]
Privileges of driver's license holder:
- A driver's license can be used as ID.
- Discounts (up to fivefold discounts) for sightseeing, museums, etc. can be obtained by the license.
- Thai (5-years extended) license is valid in the following countries: Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam, Brunei, Malaysia, Indonesia, Singapore, Philippines.
- International driver's license (5-years validity) can be obtained on the basis of 5-years Thai license.
Vietnam
In Vietnam, to drive a vehicle, one must own a legal Vietnamese Driving License which is called "bằng lái". It is a card which legally permits one to drive a motor vehicle. In Vietnam, there are classes for each driving license for which is allowed to drive a type of motor vehicle:
A – to drive private passenger or cargo vehicle with weight allowed exceeding 3,500 kg (7,700 lb).
B1 – to drive private passenger or cargo vehicle with weight allowed not exceeding 3,500 kg (7,700 lb). B1 is issued to drivers who are younger than 21 years old. B1 license is valid for 5 years.
B2 - to drive private passenger or cargo vehicle with weight allowed not exceeding 3,500 kg (7,700 lb). B2 license is identical to B1 license but issued for drivers who are 21 years old or older. B2 license is valid for 10 years.
C – to drive motorcycles (two-wheeled motor vehicle)
D – special vehicle for disabled person
The classes above are also allowed by the age of the driver according to the class of the driving license. The ages are accordingly issued to the different classes of the driver's choice:
- 17 years old for issue of Driving License class: A, C
- 20 years old or younger for issue of Driving License class : B1
- 21 years old for issue of Driving License class: B2
European Economic Area
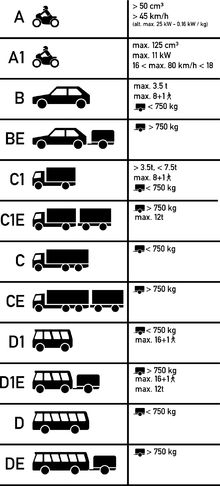
Driver's licenses within the European Union are subdivided into different categories.
The European Union has adopted a common format for driving licenses within all 31 European Economic Area member states (EU, Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway), and a common set of driving license categories. They were introduced to replace the 110 different plastic and paper driving licenses. The common format with the same information in the same place on all licenses allows the driving license to be understood, even if it is in a different language.
The system for handling the penalty points remains different in each country, for the existence of points, initial number of points, revolving, and number of points removed (or added) for each penalty.
Austria
Belgium
Bulgaria
Croatia
Cyprus
Denmark
Finland
France
Germany
Greece
Iceland
The minimum age for getting a driver's license in Iceland is 17 for a B class license, a B class license will qualify a person to drive low powered motorcycles (50 cc (3.1 cu in) two stroke or equivalent, for more powerful bikes one will have to obtain an A class license), Tractors, ATVs and Automobiles that do not exceed a GVWR of 3,500 kg (7,700 lb) or 8 passengers.
The minimum age in Iceland to get a C1 class (vehicles up to 7,500 kg (16,500 lb) GVWR) is 18, for a C class (vehicles exceeding 7,500 kg) one will have to have obtained a 12-point license (obtainable without getting a ticket for a whole year) and have reached the age of 21 years.
The minimum age in Iceland for a D1 class license is 21 years old and D class (and DE class) license is 23 years old, the same rules apply as with a C/CE class license.
Ireland
Italy
The Netherlands
Norway
The minimum age for getting a driver's license in Norway is 16 for A1, T (tractor), 18 for A-C and 21 for D. The driver's licenses are always revoked when he/she has reached an age of 100.
Poland
Romania
The minimum age for obtaining a driver's license in Romania is 18 ("Minimum legal age in Romania")
Spain
Sweden
United Kingdom
The minimum driving age in the United Kingdom is 16 for mopeds under 50 cc (3.1 cu in), and 17 for cars and motorcycles. Access to motorcycles producing more than 25 kW (34 hp) is restricted to riders with two years experience or aged 21.[25] The British Overseas Territories and the British Crown dependencies issue their own driving licences. There is no legal requirement for a non-professional driver to carry a driving licence in the UK whilst driving, although it must be produced at a police station within seven days, if required to do so by a police officer.[26]
In the United Kingdom, one must hold a Passenger Carrying Vehicle (PCV) licence to drive a vehicle with more than eight passenger seats for hire or reward, or a Large Goods Vehicle (LGV) licence to drive a vehicle with a Gross Vehicle Weight (Maximum Authorized Mass) in excess of 3,500 kg (7,700 lb). Licences and Driver Certificate of Professional Competence qualification cards must be carried whilst driving vehicles in such categories. Special licences are also required in order to transport hazardous materials.
Rest of Europe
Albania
Azerbaijan
Macedonia
Russia

Driving licence. 2014
Russia was one of the first countries to create a driving licence. Russia's first licences were issued in 1900 by Saint Petersburg authorities, and Russia joined an international convention in 1909[citation needed]. However, due to relatively small number of cars, the attempts to create a standardised Russian licence were rather sporadic and limited to major urban areas. No comprehensive system of driver licensing was present until 1936, when the Soviet government organised and standardised traffic and driving regulations, with the statewide system regulated by specialised police authorities.
Russia employs a system of driver's licenses very similar to the EU standard. Since 2014 there are 14 main categories that require a driving licence: A, A1, B, B1, C, C1, D, D1, BE, CE, C1E, DE, D1E, M[27] and two additional categories: Tm (tram) and Tb (trolleybus).
The current licence style, introduced in 1999, is a laminated plastic card similar to the European driving licence card in dimensions and outward appearance, with the bearer's photo and name (in Latin and Cyrillic scripts) to the left, place/date of issue, allowed categories and signature to the right. The reverse of the card features a detailed list of allowed categories in Russian.[28] Older booklet-style licenses are also occasionally seen although they are no longer issued and are increasingly rare as a result. The Russian driving license is also sometimes supplemented by a special card called "временное разрешение" (temporary permission), which serves for registering offense points and as a temporary licence if the primary licence has been seized by the authorities for serious traffic offences.[29] This supplement has been abolished and reinstated a countless number of times as the views of the traffic police change.
The legal driving age within the Russian Federation is 18 years (16 for motorcycles (A1 and M categories only, not A) and 20 for buses)[30] and to obtain a licence one must be physically fit to drive (including certificates of mental fitness and no record of substance abuse). One must also pass a test administered at a local traffic police authority and pay a fee. Tests are divided into theory and practice. The theory test is usually a computerized multiple-choice test on various traffic rules. Twenty multiple-choice questions are asked, only two incorrect answers allowed for a passing grade.[31] A road test is then administered which includes a demonstration of basic driving skills (steering, slope starting for manual transmission vehicles and backing-up), obstacle course as well as a skills examination for road driving. Four minor errors are allowed for the road driving examination—the obstacle course is pass-fail. The number of retries is unlimited.
Driver's license is issued by subdivisions of the General Administration for Traffic Safety of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and grants the right to drive on-road vehicles only.
The right to drive off-road vehicles is granted by tractorist-machinist's license [1], which is issued by state inspections of the supervision of the technical condition of self-propelled machines and other machinery [2] (these state inspections are parts of the regional governments of federal subjects of Russia and may have different names). The Ministry of Agriculture approves the form of the license and the procedure for issuing it. There are 9 categories in tractorist-machinist's license: AI (quad bikes, snowmobiles and other off-road vehicles with steering that is similar to motorcycle's steering), AII (wheeled cross-country vehicles weighing less than 3,500 kg, including amphibious snow-and-swamp vehicles such as TREKOL-39294, VIKING-29031, etc.), AIII (haul trucks), AIV (off-road buses), B (wheeled and caterpillar tractors with engine power less than 25,7 kW), C (wheeled tractors with engine power from 25,7 kW to 110,3 kW), D (wheeled tractors with engine power over 110,3 kW), E (caterpillar tractors with engine power over 25,7 kW), F (self-propelled agricultural machinery). To obtain the tractorist-machinist's license with AII category applicant must have at least 1-year driving experience by category B of driver's license, AIII category - category C of driver's license, AIV category - category D of driver's license. For getting the tractorist-machinist's license applicant has to pass theoretical and practice exam on the program approved by the Ministry of Agriculture. If applicant doesn’t have the driver’s license he also has to pass theoretical exam on the program approved by the General Administration for Traffic Safety of the Ministry of Internal Affairs (knowledge of traffic rules).
In the case of deprivation of driving license by court decision a citizen loses both licenses.
Switzerland
Even though Switzerland is a EFTA member state, it is not a member of the European Economic Area. Switzerland has, however, generally adopted much of the harmonised EU legislation with regard to driving licences. Swiss licences can be exchanged in most EEA countries. Switzerland has, since the 2000s, used the EU system of vehicle categories and issued EEA-style credit-card licences.
To apply for a car driving licence (category B), the applicant must be 18 years old. They must first attend first aid courses, and pass an eyesight test. Passing a theory exam is required to receive a learner's permit valid for two years. This allows holders to drive a car only if accompanied by an adult aged 23 or more who has had a full driving licence for a minimum of three years. Before passing the practical exam, the candidate must attend 10 hours of theory lessons on "sensibilisation (familiarisation) to road traffic". Practical driving lessons are not legally required, but are considered a de facto prerequisite for passing the practical exam taken with a government official Driving Test Examiner. Upon succeeding the practical exam, a probationary driving licence is issued for three years. To obtain the full, unlimited, driving licence after these three years, the candidate must not commit a serious traffic offence, and attend two days of further driving training.
For motorcycles and heavier vehicles, the regulations are different, and some agrarian vehicles can be driven without a licence. As of 2011, a 45-minute driving lesson costs around CHF 90, while the various fees and theoretical instruction costs associated with getting a car driving licence can amount to up to CHF 600, without counting the costs for the two days of further training.
The theoretical exam must be taken in either German, French or Italian. In some cantons it is possible to take it in English.
Turkey
Turkey has been an associate member since 1963, and application to accede to the European Economic Community, the predecessor of the European Union (EU), was made on 14 April 1987.[32] Turkey signed a Customs Union agreement with the EU in 1995 and was officially recognised as a candidate for full membership on 12 December 1999, at the Helsinki summit of the European Council.
On 1 January 2016 new Turkish laws concerning driving licences were implemented.[33][34] The changes are intended to bring Turkey more in line with existing EU driving regulations and concern all road users in Turkey. A foreign national can drive in Turkey with an EU license for 6 months. After 6 months he/she has to change it to a Turkish licence. Application can be made to any Traffic Registration office, and the foreign driving licences will not be returned to holders. Instead they will be sent to the issuing authority of the country of origin i.e. for British nationals, DVLA. The DVLA says that expats can drive in the UK on a Turkish licence for up to 12 months, and if they wish to settle back in the UK, the Turkish license can be exchanged for a UK license.[33]
In Turkey you must be at least 18 years old in order to drive a car and at least 17 to drive a motorbike. The driving test comprises a practical and theory test, which has been recently made tougher in order to meet European Union regulations.[35]
North America
Canada
The age to obtain a driver's license in Canada varies by province, as do the necessary procedures. The minimum age for obtaining a driver's license to drive unaccompanied in most provinces is 16.[citation needed]
Barbados
In Barbados, a person 16 years or over can apply for a Learner's Permit which allows them to drive for a specified period with an accompanying tutor. During that period they will be tested on their driving skill and their knowledge of road signs and traffic laws. On passing both the written and driving test the license is issued. Once issued a driver's license is valid for a period of one to five years depending on which period of time the driver chooses to pay for. On the expiry of the period for which the license is issued, it will become renewable on the last day of the driver's birth month and will again be valid for the time period for which payment is made. Visitors and non-nationals who are the holders of a valid driver's license issued in their country of residence or origin are not allowed to drive automatically in Barbados but must go to a police station to have a temporary local driver's license issued. The license is issued on payment of a fee and the production of the visitor's existing license.
Costa Rica
Every vehicle driver must carry a driver's license (Licencia de Conducir), which is issued by COSEVI (Consejo de Seguridad Vial) of the ministry of transportation and public infrastructure (Ministerio de Obras Públicas y Transporte).
For this license to be granted there are three needed tests, practical driving (includes driving a car in simulated streets), theoretical driving (a multiple selection written test based on booklet issued by the education department or after taking a special course), and finally a medical test performed by a medical practitioner that tests eyesight, blood pressure and attests the presence of other diseases and behavior of the driver.
Every citizen can solicit a driver's license at age 18, after being issued the first time, the license must be renewed after two years, and every successive occasion after five years.[36] Foreigners may also obtain a drivers' license if they have residency.
Besides this document the driver must carry the national identity card (Cédula de Identidad), however both documents use the same identification number, the national identity card being the basis of the driver's license number.
El Salvador
All driver's licenses are given by the government agency SERTRACEN (Servicios de Tránsito Centroamericanos S.A. de C.V.).
One needs a minimum of 15 years to receive a driver's license (a juvenile license).[37] To get a new license, one needs to pass a vision test, a written test, and a driving test. These tests are given at accredited driving schools. Foreigners with a license from another country can obtain an El Salvador license if they have residency. They will also have to pass a vision test.[38] The driver's license number is the same as the person's Tax ID number.
El Salvador licenses (as well as vehicle circulation cards) contain a chip which can be read by putting the card in a chip reader.
There are several categories of drivers' licenses in El Salvador:[39]
- Juvenil Particular—License for minors, allowing them to drive cars and pickup trucks
- Motociclista—Motorcycle license
- Particular—License for adults, for cars, vans up to 17 passengers, and pickup trucks.
- Liviana—Taxis, Light trucks up to 5 tons, and buses up to 30 passengers.
- Pesada—Buses greater than 30 passengers, and trucks greater than 5 tons.
- Pesada T—Trucks with more than 3 axles.
Jamaica
A citizen may obtain a learner's permit once he or she is age 17. A learner will get their driver's license upon being proven competent through the results of both a written and practical test. This license expires on the holder's fifth birthday after the date of issue.
Mexico
Driving licenses in Mexico are regulated by each state, and they all have different rules and requirements. However, all state driving licenses are recognized across Mexico, and international licenses with an IDP are also recognized as well.
A driver is allowed a learner's permit at the age of 15 (in some states), with the cost of approximately 100 dollars, a duration of a year, and requiring to drive with an adult at all times. At the age of 16, the fee drops to 30 dollars, and a driving permit is issued with some usage restrictions, depending on the state (like a curfew). When a driver turns 18, he or she is allowed a full license.
Trinidad and Tobago
In Trinidad and Tobago, you could obtain a learner's permit at your 17th birthday. Licenses to drive are commonly referred to in Trinidad and Tobago as Driver's Permits. Driver's Permits are issued by the Licensing Authority, which is governed by the Ministry of Works and Transport. In order to legally operate any motor vehicle in Trinidad and Tobago, whether it is on or off public-owned-roads, the operator of the motor vehicle must be in possession of a valid Driver's Permit on their person and is legally endorsed for that class of vehicle. Contravention to the aforementioned could warrant a fine of up to TT$1,500 and imprisonment.[citation needed]
United States

Age requirements to receive a restricted driver's license by US State
14 years and 3 months
15 years
15 years and 6 months
16 years
16 years and 3-4 months
16 years and 6 months
17 years
The eligible age to first obtain a driver's license varies substantially from state to state, from 14 years, three months, in South Dakota to 17 in New Jersey. In a majority of states one can obtain a license that allows driving without adult supervision by age 16, after passing the requisite tests. Since the driver's license is a commonplace document that carries much of the necessary information needed for identification, it has become the primary method of identification in the United States.[40]
In the United States, a holder of a driver's license is typically legally allowed to operate a motor vehicle up to 26,000 pounds if no hazardous materials and no more than 16 persons (driver included) are in the vehicle.
Most jurisdictions that grant driver's licenses only permit the holder to operate a roadworthy vehicle consisting of four or more wheels. To operate a two-wheel motorized vehicle with a sustainable speed greater than 30 mph (48 km/h) requires an endorsement on the license, typically after successful completion of a theory (written) and practical test.
On the federal level, motor vehicles with a curb weight of GCWR of 26,001 lb (11,794 kg) or more, a vehicle designed to transport 16 or more passengers (driver included), or a vehicle transporting hazardous materials can only be driven by an operator carrying a Commercial Driver License (Commercial Motor Vehicle Safety Act of 1986). Upon successful completion of theory and practical testing, endorsements can be applied to a CDL to allow legal transport of specialty types of goods:
- T Semi trailer Double or Triple (Written Test)
- Certain states prohibit triple trailers statewide, such as California,[41] Florida,[42] Michigan,[43] and New York[44]
- A Class A license is required to obtain the T endorsement
- Certain states prohibit triple trailers statewide, such as California,[41] Florida,[42] Michigan,[43] and New York[44]
- P Passenger Vehicle (Written and Driving Tests)
- S School Bus (Written and Driving Test, Background Check, Sex Offender Registry Check and P endorsement)
- N Tank Truck (Written Test)
- H Hazardous materials (Written Test and Background Check through the Transportation Security Administration)
- X Combination of Tank Vehicle and Hazardous Materials (Written Test)
- W Tow truck. (Written Test)
- M Motorcycle License (Written Test and practical)
Various state statutes also mandate that CDL must be held to operate vehicles not covered by federal statutes.
Oceania
Australia
The minimum driving age varies between 16 and 18 years of age in different States and Territories. After the minimum age, a graduated licensing scheme operates, with state variations.
Cook Islands
A Cook Islands "License to Drive a Motor Vehicle" is issued at police headquarters on Rarotonga, on production of a valid license from the visitor's home country. To use a scooter or motor cycle (the main hire vehicles for tourists) a short test has to be taken by anyone whose home license is only valid for cars, in which a police officer observes the applicant riding up and down the main street of the capital.
New Zealand
Since August 2011, the minimum age to obtain a learner licence is 16 years old in New Zealand; formerly it was 15 years old.[45]
There are three different types of drivers licence in New Zealand: learners, restricted and full licence. Learners licences allow the person to drive, with a wide number of restrictions.[46] Restricted licenses allow driving alone between the hours of 5am to 10pm, and require the person to be 16 1⁄2.[47] Full licences are restricted to those 18 and over, or 17 1⁄2 years if an approved advanced driving course has been successfully completed.[48] New Zealand also used DuPont's Tyvek for its driver's licenses from 1986 to 1999.[49]
There are six different classes of vehicle that are licensed:[50]
| Class Number | Vehicle | Requirements for learners licence | Requirements for restricted licence | Requirements for full licence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | Car | Must be 16 years or over | Must be 16 1⁄2 or over, must have learners licence for at least 6 months | Must be 18 or over, must have restricted licence for at least 12 months |
| Class 2 | Medium rigid vehicle | Hold a full class 1 licence for at least 6 months and pass a theory test[51] | N/A | 6 months on the class 2 learner licence plus a practical test, or immediately upon passing an approved course |
| Class 3 | Medium combination vehicle | Get a full licence in Class 1 | N/A | TBA |
| Class 4 | Heavy rigid vehicle | Hold a full class 2 licence for at least 6 months (under 25) or 3 months (25 and over). No theory test required. Apply and pay the required fee | N/A | 6 months on the class 4 learner licence plus a practical test, or immediately upon passing an approved course |
| Class 5 | Heavy combination vehicle | Hold a full class 4 licence for at least 6 months (under 25) and pass a theory test | N/A | 6 months on the class 5 learner licence plus a practical test, or immediately upon passing an approved course |
| Class 6 | Motorcycle | Must be 16 years or over | Must be 16 1⁄2 or over, must have learners licence for at least 6 months | Must be 18 or over and have had restricted licence for 18 months or must be 17 1⁄2 years or over and have had restricted licence for 12 months if an approved advanced driving course is completed |
South America
Brazil
Peru
The minimum age for a driving license is 18 years old. It is obtained via a test in a car, a computer and the applicant must present a vision test which says they are permitted to drive
Venezuela
In Venezuela there are four categories of driving licenses:
Seconde Degree License (Motorcycles): to 16 years old persons (Type "A", for motorcycles less than 150 cm3 engine capacity) and to 18 years old persons (Type "B", to drive motorcycles of any engine capacity).
Third Degree License (motor vehicles for the private transportation of persons, with a capacity of up to nine seats, including that of the driver; vehicles destined to the transport of load, whose maximum weight does not exceed two thousand five hundred (2500) kilograms): Type "A", to people over sixteen (16) years and under eighteen (18), subject to the special legal regime; Type "B", to persons over eighteen (18) years of age.
Fourth and Fifth Degree Licenses: To persons over 21 years of age to drive vehicles with a capacity of up to nine (9) seats destined for public transport of passengers and cargo vehicles, whose maximum weight does not exceed six thousand (6,000) kilograms. Persons over twenty-five (25) years old, to drive all types of vehicles whatever their capacity or use.[52]
Organ donations
Licensing bureaus in many countries add an organ donation option on license forms. Sometimes a small picture of a heart or the term Organ Donor is printed on the driver's license, to indicate that he or she has agreed to donate his or her organs in case of sudden death, such as after a collision.
In the United States, this is governed by the Uniform Anatomical Gift Act. In New Zealand and the Republic of Ireland, willingness to donate organs for transplant is also listed on driver's licenses. In Australia, the system of notating organ donation requests on licenses was replaced in July 2005 with a national registration system and the issue of special cards. In Great Britain (England, Wales and Scotland), code "115" is printed on the reverse of the licence to indicate that details are on the National Health Service (NHS) Organ Donor Register.
International and interstate considerations
Many groups of countries have agreed to recognize driver's licenses issued by authorities of any of its members. Examples include the European Union and the GCC, where holders of driver's licenses issued by any member state can drive in all member states. Most countries worldwide will also recognize the licenses of citizens of foreign states wishing to drive as visitors. All EU member countries now issue licenses in a standard format, regardless of the language of the license.[53]
The International Driving Permit (IDP) (sometimes erroneously called the International Driver's License) is a booklet which is an authorized translation of a driver's home license into many languages (especially languages with non-Latin scripts such as Russian, Arabic, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, etc.). In some cases, it is obtained from a motoring organization such as the Automobile Association or the equivalent in the driver's home country. In other cases, it is delivered by the same government services that deliver ordinary licenses. The IDP has no validity except when used in conjunction with the driver's own license. The existence of the IDP is necessitated by many countries refusing to recognize driver's licenses written in foreign languages without accompanying translations.
Temporary visitors from the United States to France (less than 90 days) are permitted to drive with a valid US state driver's license. In addition to holding a US driver's license, visitors are advised (but not required) to carry an International Driving permit, or attach a French translation to their US state driver's license.
China, at present, does not recognize IDPs and requires drivers to get an additional Chinese license before being officially allowed on all roads. Holders of foreign licenses are exempt from certain requirements when obtaining a Chinese license.
A minimum driving age often exists regardless of possession of a foreign license; an American cannot drive below the local minimum age in Europe, nor can a 17-year-old Briton drive in mainland Europe where the minimum age is 18.[54]
Many countries have established a driver's license exchange arrangement after reviews of the foreign jurisdiction's licensing processes. Where standards in the other jurisdiction are comparable in areas such as medical standards, minimum driving age, and knowledge and road testing, an exchange (or honoring) of the foreign jurisdiction's license may occur.[55] This may also be called Driver's License Reciprocity.[56]
Issues when moving permanently from one country or one state to another
Most license-issuing authorities require holders of foreign licenses taking up residence in their jurisdiction to obtain a local driver's license within a limited time, typically 6 months or 1 year. In most cases, the driver must follow the full local procedure for obtaining a license, but some jurisdictions have mutual recognition agreements and will exchange the foreign license for a local one without the need to undertake an additional driving test.
An exception is the EU, where licenses do not need to be exchanged since the introduction of the common EU-driver's-license scheme.
Australia
Each state in Australia has different rules for how long a visitor can drive on an international licence or a licence from a different state. For example, New South Wales allows three months[57] whereas Victoria allows six months.[58] Drivers that move permanently to another state must change their licence to a local state licence within the prescribed time. This is usually free. In some states, drivers with a full New Zealand licence are treated as interstate drivers.
Canada
British Columbia has a reciprocal license exchange scheme with other Canadian provinces and territories as well other countries provided the license is valid or has been expired for less than three years.[59]Ontario If you have a (7L) licensing, which is given out by British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, you are not restricted to being accompanied by a supervisor while driving in Ontario, until you get your Full License at the age of 18. Ontario has a reciprocal license exchange scheme for Canadian provinces and territories, Canadian Forces Europe, and some other countries.[60]Quebec has a reciprocal license exchange scheme for Canadian provinces and territories, Canadian Forces Europe, American states and other countries.[61]
France
US state driver's licenses can be exchanged from the 15 states below during the first year of legal residence in France: Arkansas, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Illinois, Iowa, Maryland, New Hampshire, Ohio, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, Texas, Virginia and Wisconsin.[62]
If you are a resident of France (holder of a carte de séjour or carte de résidence), you may drive in France with a valid US state driver's license for a one-year recognition period, beginning on the date of validity of the first carte de séjour (exception for students who are allowed to use their driver's license for the duration of their studies). In addition to having a US state driver's license, residents are also required to attach a French translation done by a sworn translator, or expert traducteur or traducteur assermenté.
Germany
The US Embassy, supported by the American Chamber of Commerce in Germany, continues to actively press all US states, territories, and the federal district to reach an agreement on the reciprocal recognition of driver's licenses with Germany, essentially a waiver of testing requirements.[63]
If approved, drivers from Alabama, Arizona, Arkansas, Colorado, Delaware, Idaho, Illinois, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Massachusetts, Maryland, Michigan, New Mexico, Ohio, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, Puerto Rico, South Carolina, South Dakota, Texas, Utah, Virginia, West Virginia, Washington State, Wisconsin, and Wyoming will be exempted from road and written driving tests.
If approved, drivers from Connecticut, District of Columbia, Florida, Indiana, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, North Carolina, Oregon, Tennessee will be exempted from the road tests only.
Hong Kong
As stated on the application form for direct issue of full Hong Kong driving license (Rev. 11/2008),[64] when a person has documentary evidence to the Commissioner for Transport's satisfaction that all of the following apply, the person is eligible to direct issue of a Hong Kong license:
- The person has held a full driving license (not an International Driving Permit) for three years issued by one of the following countries or territories: Australia, Austria, Bangladesh, Belgium, Bermuda, Canada, China, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Guernsey, Iceland, India, Ireland, the Isle of Man, Israel, Italy, Japan, Jersey, Luxembourg, Macao, Malaysia, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Nigeria, Norway, Pakistan, Portugal, Singapore, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, South Africa, South Korea, Namibia, Taiwan, the United Kingdom and the United States.
- The driving entitlement(s) for which one is applying must be equivalent to the class(es) which are authorized to drive by the issuing country or place; and
- The driving license was obtained by passing the relevant driving test(s) in the issuing country or territory; and
- Satisfies one of the three requirements below:
- The license was originally issued on any date during a period of residence of not less than 6 months in the country or place of issue (entry and departure stamps on a passport, school transcript or employer's testimonial with employment period specified are accepted as proof); or
- The license has been issued for not less than 5 years immediately before the application; or
- Hold a passport or an equivalent travel document of the country or territory in which the license was issued.
Singapore
A foreigner 18 years of age or older and holding a Work Pass/Dependent Pass/Student Pass may drive in Singapore with a valid class 3, 3A or 2B foreign license, for a period of not more than 12 months. A Singaporean driving licence is required after 12 months. Those on short term social visits may drive with their foreign license for up to 12 months each time they enter into Singapore. For licences not written in the English language, an International Driving Permit or translation is required.
Foreign licence conversion is only granted for class 2B and class 3 qualified driving licences.
In order to convert your foreign licence to a Singapore driving licence, you are required to pass the Basic Theory Test (BTT). Overseas theory test results are not admissible for consideration.[65]
Sweden
Residents in Sweden having a foreign license can exchange it to a Swedish license, if it is from an EU country, an EEA country, Switzerland or Japan.[66] Foreign licenses are valid if the holder has not been living in Sweden for more than a year (and some more requirements).
United Kingdom
The Driver and Vehicle Licensing Agency (DVLA), which licences drivers in Great Britain (England, Scotland and Wales), but not Northern Ireland, exchanges full licences issued by:[67]
- Northern Ireland (although being part of the UK, driving licences are issued by the Driver and Vehicle Agency (DVA) in Northern Ireland),
- Countries within the EEA and Switzerland,
- The British Crown dependencies (Guernsey, Jersey and the Isle of Man)
- Gibraltar and other British Overseas Territories,
- Australia, Barbados, the Faroe Islands, Hong Kong, Japan, Monaco, New Zealand, Singapore, South Korea, South Africa, and Zimbabwe.
- Canada (by default, Canadian driver's licences will only be exchanged for licences to drive automatic transmission cars, unless documentary evidence is provided that a manual gearbox (shift) test was passed in Canada)
United States
A Driver's License from any US state is valid for temporary use in any other US state, although most states require that a person have a license issued by their state of primary residence. Most states allow residents to convert an out-of-state license to an in-state license without any additional written or road tests.
Delaware has a reciprocal license exchange for Germany, France, and Taiwan to allow holders of those licenses to obtain a Delaware license without any additional written or road tests.[68]
A District of Columbia driver's license may be obtained while maintaining out-of-country driver's license. D.C. driver's licenses may vary for non-US citizens, depending on visa classification. The written test is required for non-US citizens who possess an out-of-country driver's license.[69]
Florida has a reciprocal license agreement with South Korea, allowing South Korea licenses to be exchanged for a Florida license, and vice versa, without taking a written or road test.[70]
A New York State driver's license may be obtained by a resident of another country. If the driver has a driver license from any nation except Canada, they must pass a written test, complete a 5-hour pre-licensing course and pass a road test to qualify for a driver's license.[71]
Texas doesn't require drivers from Canada, France, Germany, nor Taiwan to take the written and practical tests. But drivers must still agree to a vision test.[72]
Washington State has a reciprocal license exchange, allowing holders of valid licenses from any other US state, British Columbia, Germany, South Korea, and Taiwan to exchange their license for a Washington State license without taking any written or road tests.[73]
Virginia has a reciprocal agreement with Canada, France and Germany. The knowledge and skills tests may be waived if the driver meets residency and other requirements.[74]
See also
- Commercial driver's license
- Driver's Education
- Learner's permit
- International Driving Permit
- Road-traffic safety
- Vehicle category
- List of countries by minimum driving age
References
^ abcd Lutteroth, Johanna. "Der Lappen, der die Welt bedeutet". einestages (in German). Spiegel Online. Retrieved 2008-08-02..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "The Motor Car Act, 1903 - The Motor Miscellany". Retrieved 2017-05-23.
^ "A Brief History of Driver Education in the UK".
^ "A Potted History of Driving, and the UK Driving Licence".
^ "Convention with Respect to the International Circulation of Motor Vehicles". The American Journal of International Law. American Society of International Law. 4 (4 Supplement:Official Documents): 316–328. October 1910. JSTOR 2212082.
^ Paris International Convention relative to Motor Traffic (PDF). London: His Majesty's Stationery Office. 1930.
^ "United Nations Treaty Collection: Chapter XI: Transport and Communications: B. Road Traffic: 1 . Convention on Road Traffic". Act of Error: thedateoryearparameters are either empty or in an invalid format, please use a valid year foryear, and use DMY, MDY, MY, or Y date formats fordate.
^ Convention on Road Traffic (PDF). United Nations Conference on Road Traffic. 1968-11-08.
^ "Altes vom Auto: Meldungen aus 125 Jahren:Tops und Flops (a summary of the highlights and lowlights of the first 125 years of motoring history)". Auto Motor u. Sport. Heft 4 2011: Seite 16. 2011-01-27.
^ Anonymous, "Better Auto Laws Are Now Needed," New York Times, 1907-08-18, S3.
^ Frederick H. Elliott, "Working Out New Auto Law In New York," New York Times 1910-10-16, 3.
^ "New York's Auto Exports Increase-Big Jump in Cars Shipped Last Year-New Jersey Examines All Drivers" (PDF). New York Times. 1913-07-14. p. 11. Retrieved 2009-06-03.
^ "Travel documents for EU nationals". Your Europe. 2017-07-07. Retrieved 2017-08-27.
^ "Road Traffic Act 1988". Gov.UK. HM Government. Retrieved 25 August 2014. Section 7b refers to providing licence within 7 days.
^ "Road traffic". Home Office. Retrieved 2012-02-04.
^
"For organ donor entry column of driver's license (Japanese)". Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. 2013-07-22. Retrieved 2013-07-22.
^ "愛知県警察/運転免許に関すること" [Aichi Prefectural Police / Driver's License Concerns] (in Japanese). 愛知県警察 (Aichi Prefectural Police). Retrieved 2014-10-09.
^ "免許更新時講習について" [Regarding the Driver's License Renewal Period Training] (in Japanese). Fukui Prefecture. Retrieved 2014-10-09.
^ "福岡県警察 渡辺通優良運転者免許更新センター(渡辺通ゴールド免許センター" [Fukuoka Prefectural Police Watanabe Avenue Excellent Driver License Renewal Center (Watanabe Avenue Gold License Center)] (in Japanese). 福岡県警察 (Fukuoka Prefectural Police). Retrieved 2014-10-08.
^ "Applying driving license for the first time". tra.go.tz. Tanzania Revenue Authority. Retrieved 2017-07-04.
^ "Driving License Test in India - Driving Test". Learning Licence Test India. Retrieved 2016-09-15.
^ Haron, Sharif (2012-02-04). "Concern over teenage driving safety". New Straits Times. Retrieved 2014-01-22.
^ "Drivers can renew license on birthday from Nov 21". The Malaysian Insider. 2011-11-15. Archived from the original on 2014-02-01. Retrieved 2014-01-22.
^ "กรมการขนส่งทางบก" [Department of Land Transport] (in Thai). Thailand: กรมการขนส่งทางบก [Department of Land Transport]. Retrieved 2018-09-21.
^ "Motorcycles you can ride". Directgov. Retrieved 2011-06-08.
^ "Production of Documents". Sussex Police.
[dead link]
^ Mopeds, a variant name of European AM category
^ "Russia Driver License Translation". Retrieved 2015-10-13.
^ "ГАИ РУ - Информационный портал: автомобильные новости, оплата штрафов ГИБДД - Форум автомобилистов - Справочная информация для автовладельцев". Retrieved 2015-10-13.
^ "Driving in Moscow – Russian road rules". We heart Moscow. Retrieved 2015-10-13.
^ "Бесплатный онлайн экзамен ПДД 2015, тест на вождение онлайн скачать, сдать экзамены в ГИБДД - ГАИ РУ". Retrieved 2015-10-13.
^ "EU-Turkey relations". European Information on Enlargement & Neighbours. EurActiv.com. 23 September 2004. Retrieved 26 August 2008.
^ ab "Changes to Turkish driving licence laws affect expats". The Kalkan Turkey Web Site. 2016-01-07. Retrieved 2017-07-04.
^ Haber, Hürriyet (2016-02-22). "Ehliyet yenileme randevu işlemleri nasıl yapılır?". Gündem (in Turkish). Hürriyet Gazetecilik. Retrieved 2017-07-04.
^ "Driving license:Getting a driving license in Turkey". justlanded.com. Just Landed. Retrieved 2017-07-04.
^ "Costos de Licencia de Conducir". Csv.go.cr. Archived from the original on 2012-02-15. Retrieved 2012-02-04.
^ Carlos Josue Quinteros Berrios. "Primera Vez". Retrieved 2015-10-13.
^ Carlos Josue Quinteros Berrios. "404". Archived from the original on 2014-05-08. Retrieved 2015-10-13.
^ Administrator. "Clases de Licencia". Retrieved 2015-10-13.
^ "US Drivers License Application". US Immigration Support: Your Guide to US Visas, Green Cards, and Citizenship.
^ "California Commercial Driver Handbook". Retrieved 2006-10-25.
^ "Appendix C to Part 658". Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration. Archived from the original on 2008-02-13. Retrieved 2008-02-04.
^ "SOS - CDL Group Designations and Endorsements". www.michigan.gov. Retrieved 2017-09-01.
^ "New York State Commercial Driver's Manual". Retrieved 2006-10-25.
^ "Driving age to rise to 16". The New Zealand Herald. 2011-05-05. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
^ "About driver licences: Stage 1 – learner licence". NZ Transport Agency. Retrieved 2016-12-08.
^ "About drivers licences: Stage 2 – restricted licence". NZ Transport Agency.
^ "Advanced driving courses". NZ Transport Agency. 2017-07-05.
^ "Upgrading driver licences from paper to photo (Factsheet 54)". NZ Transport Agency. May 2017. Retrieved 2018-08-24.
^ "About driver licences: New Zealand's driver licensing system". NZ Transport Agency. Retrieved 2016-12-08.
^ "How to get a class 2 licence".
^ "Guía Licencia" (in Spanish). Venezuela: Instituto Nacional de Transporte Terrestre. 2012. Retrieved 2018-08-15.
^ "Transport - Driving license". Ec.europa.eu. 2003-10-22. Retrieved 2012-02-04.
^ "Living in France". Retrieved 2015-10-13.
^ "Agreement Promotes Safety And Convenience For New Residents". Archived from the original on 2010-08-22. Retrieved 2016-02-04.
^ "Texas Administrative Code". Info.sos.state.tx.us. Retrieved 2012-02-04.
^ "Driving on a foreign licence in New South Wales".
^ "Driving on a foreign licence in Victoria".
^ "ICBC - Driver licensing". Archived from the original on 2011-09-28.
^ "DriveTest - Exchanging a Reciprocal License". Drivetest.ca. Archived from the original on 2012-01-30. Retrieved 2012-02-04.
^ "New Residents of Québec and Holders of a Driver's Licence Issued Outside Québec". Saaq.gouv.qc.ca. 2011-01-19. Retrieved 2012-02-04.
^ "Permis de conduire étranger - Echange en France". Maison des Français de l'étranger (MFE). Retrieved 2013-05-29.
^ "American Driver's License - Germany - United States Diplomatic Mission". Retrieved 2015-10-13.
^ "Application For Direct Issue Of Full Hong Kong Driving Licence" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-02-04.
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2016-01-16. Retrieved 2016-02-04.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ "Foreign Driver's Licences" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-02-04.
^ "Directgov *'exchange driving licence' interactive tool". Direct.gov.uk. Retrieved 2012-02-04.
^ "State of Delaware Division of Motor Vehicles - Driver's License Over 18 FAQ's". Dmv.de.gov. Retrieved 2012-02-04.
^ "District of Columbia: Department of Motor Vehicles - Services - Drivers' Licenses - Getting Your Learners' Permit". Dmv.dc.gov. Archived from the original on 2012-02-26. Retrieved 2012-02-04.
^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-01-04. Retrieved 2012-01-20.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ "New York State Department of Motor Vehicles - NYS DMV - NYSDMV - Driver - Vehicle". Nydmv.state.ny.us. Retrieved 2012-02-04.
^ "Texas Department of Public Safety". xdps.state.tx.us. Retrieved 2015-09-27.
[permanent dead link]
^ "WA State Licensing: Moving? Get WA license". Dol.wa.gov. Retrieved 2012-02-04.
^ "Department of Motor Vehicles Virginia" (PDF). dmv.virginia.gov. Retrieved 2015-09-27.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Driver's licenses. |
- Information from the European Union in driving licences throughout the Community
- Drivers License General Information Office (Japanese)